从零搭建ssm整合环境(不使用springboot)代码版
下面的整合步骤了解即可,现代开发使用springBoot+mybatis-plus+maven 几乎是一键配置好环境
2.1 新建web工程
注意:
1.设置项目编码格式为UTF-8
2.创建项目时记得勾选web
2.2 导入jar包
1.spring的核心4+1jar包
- spring-context
- spring-beans
- spring-core
- spring-express
- spring-jcL
2.springMVC的jar包
- spring-aop
- spring-webmvc
- spring-web
- aspectjweaving (织入包 不一定能用上 但是建议导入)
- jackson包(四个)
3.mybatis的包
- mybatis核心包
- mybatis依赖包(一整个目录)
- mysql-connector.jar (mySql提供的驱动包)
- spring-jdbc (spring对jdbc的支持)
- spring-tx (spring对事物的支持)
- 数据源(可选 druid包 即连接池)
4.mybatis和spring的整合包
- mybatis-spring
- spring-test
- fileupload+io(可选的 用于文件上传)
从网上找jar包时不要找太远的版本也不要找最新版本,而是找用的人比较多的或者说热度比较高的近几年发布的包
druid找1.1.23
mybatis-spring找2.0.3
2.3 配置xml文件
接下来要设置spring MVC和spring的xml配置文件。
2.3.1 spring-mvc.xml
第一步配置包扫描
<context:component-scanbase-package="com.lwl.collection"></context:component-scan>第二步配置注解驱动:代替原来的处理器映射器 和 处理器适配器 注意代码来源MVC
<mvc:annotation-driven></mvc:annotation-driven>第三步放行静态资源
<mvc:default-servlet-handler></mvc:default-servlet-handler>
最后代码如下
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc https://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="com.lwl.collection"></context:component-scan>
<mvc:annotation-driven></mvc:annotation-driven>
<mvc:default-servlet-handler></mvc:default-servlet-handler>
</beans>
2.3.2 配置spring的业务层(service)配置文件 applicationContext-service.xml
第一步配置包扫描,专门扫描业务层的包
<context:component-scanbase-package="com.lwl.service"></context:component-scan>
第二步配置数据源事务管理器(和连接池有关,虽然说可选,但现在基本都用连接池)
注意 id 有讲究 是 transactionManager
ref指向的是mapper配置文件中的数据源连接池(2.3.3 第二步配置的东西)
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean>
第三步开启事务驱动,只要与业务层有关,肯定需要事务
<tx:annotation-driven/>
最后代码如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:tx="http://www.alibaba.com/schema/stat"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.alibaba.com/schema/stat http://www.alibaba.com/schema/stat.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="com.lwl.service"></context:component-scan>
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean>
<tx:annotation-driven/>
</beans>
2.3.3 配置spring的mapper配置文件 applicationContext-mapper.xml文件(干掉mybatis核心配置文件)
Spring-mybatis整合配置常用的两种方式_韩小文的博客-CSDN博客
第一步配置包扫描,其实就是将mybatis核心配置文件的包扫描拿过来了,这步操作用于读取所有的mybatis映射文件
<bean class="org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperScannerConfigurer">
<property name="basePackage" value="com.lwl.mapper"></property>
</bean>
第二步配置数据源(和连接池有关,虽然说可选,但现在基本都用连接池)
下面的案例将连接池的属性直接写在了配置文件中,有时候需要单独放在一个property文件,其实就是将mybatis核心配置文件的读取数据库代码拿过来了
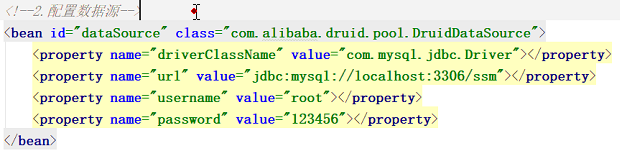
上面这一步可以拆成两小步
首先读取外部配置文件(2.3.4配置的)
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:db.properties"></context:property-placeholder>
然后替换上图的数据源配置方式
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="${jdbc.driverClassName}"></property>
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}"></property>
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}"></property>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"></property>
</bean>
第三步配置sqlSessionFactory
用一个bean标签配置sqlSessionFactory
首先配置一个数据源,引用的是上面第二步的dataSource(数据源)
<bean class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean>
然后依然可以写一个mybatis的核心配置文件,主要在其中设置mybatis的功能,比如开启log4j、启用驼峰命名,然后在当前bean标签中用property外接这个核心配置文件
举例:
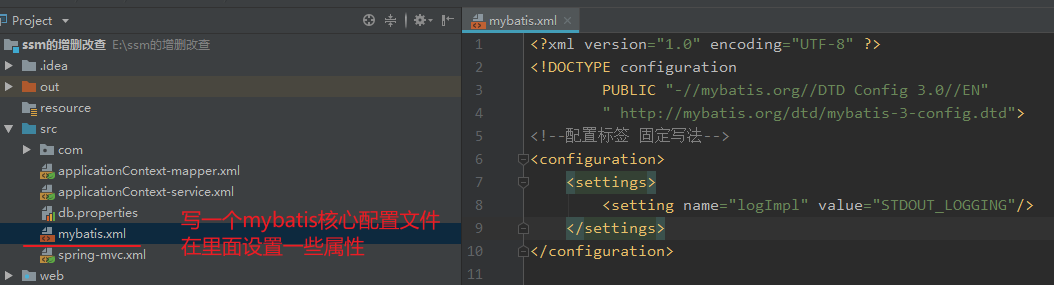
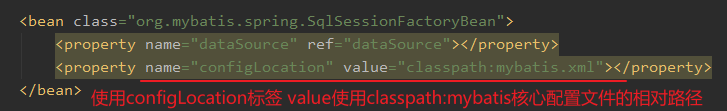
最后代码如下
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<bean class="org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperScannerConfigurer">
<property name="basePackage" value="com.lwl.mapper"></property>
</bean>
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:db.properties"></context:property-placeholder>
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="${jdbc.driverClassName}"></property>
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}"></property>
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}"></property>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"></property>
</bean>
<bean class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
<property name="configLocation" value="classpath:mybatis.xml"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
PS:如果用一些工具类快速生成mybatis的接口、映射文件时,将接口和映射文件放在一起,那么上方的配置没问题,但如果mapper层的映射文件和接口分离了,那么映射文件就需要额外在sqlSessionFactoryBean的bean标签下配置,具体见[spring]xml配置文件中bean属性的两种写法(p:configLocation <=> <property name="configLocation"/>) - vickylinj - 博客园 (cnblogs.com)。
另外实际开发时一般都是用maven统一管理映射文件,那又是另一种环境搭配。
2.3.4 准备外部配置文件db.properties
加前缀jdbc的原因是将key与项目中同名的key区分开,有时候这个操作能规避很多问题
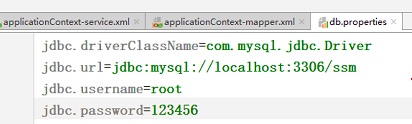
2.3.5 web.xml
上面的三个配置文件都写好了,下面要加载到web.xml中
加载三个配置文件:
springMVC.xml(基于DisPatchServlet)
applicationContext-Service.xml 和applicationContext-mapper.xml(一行代码解决两个配置文件的配置、需要配置监听器、后者替代了mybatis核心配置文件)
配置过滤器:
filter(解决乱码问题)
第一步 加载spring配置文件,配置contextLoader监听器
param-value 标签中的值用了* 此时就能实现一行代码把两个前缀相同的配置文件都给配置了
<!--1. 加载spring的配置文件-->
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath:applicationContext-*.xml</param-value>
<!-- <param-value>classpath:applicationContext-service.xml,classpath:applicationContext-mapper.xml</param-value>-->
</context-param>
<!--配置监听器-->
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class>
</listener>
第二步配置过滤器,解决post表单请求乱码问题
<!--2.配置filter 解决 post表单提交乱码问题-->
<filter>
<filter-name>encodingFilter</filter-name>
<filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>encoding</param-name>
<param-value>utf-8</param-value>
</init-param>
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>encodingFilter</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>
第三步配置前端控制器(dispatchServlet),加载springmvc配置文件
<!--3.配置DispatcherServlet -->
<servlet>
<servlet-name>dispatcherServlet</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath:spring-mvc.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>dispatcherServlet</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>

