CSS基础-定位
相对定位
什么是相对定位?
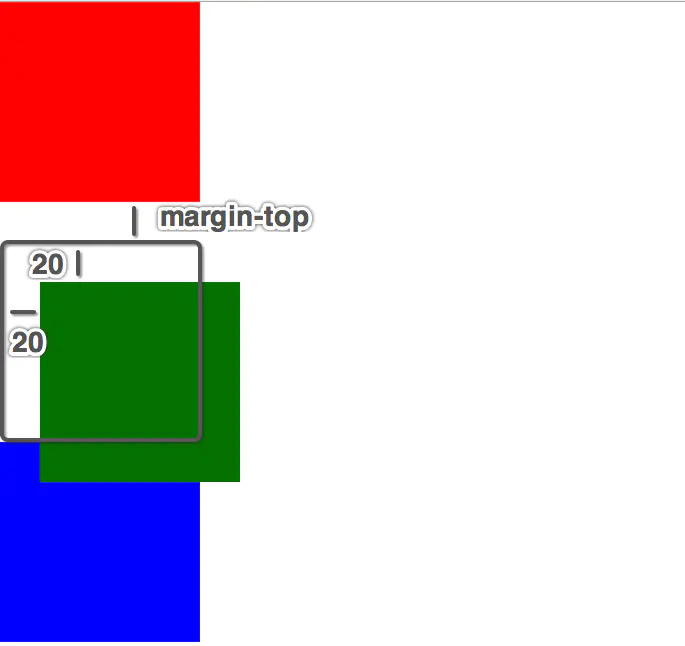
相对定位就是相对于自己以前在标准流中的位置来移动
格式如下
position: relative;
示例程序
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>相对定位</title>
<style>
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
div {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
}
.box1 {
background-color: red;
}
.box2 {
background-color: green;
position: relative;
top: 20px;
left: 20px;
}
.box3 {
background-color: blue;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box1"></div>
<div class="box2"></div>
<div class="box3"></div>
</body>
</html>
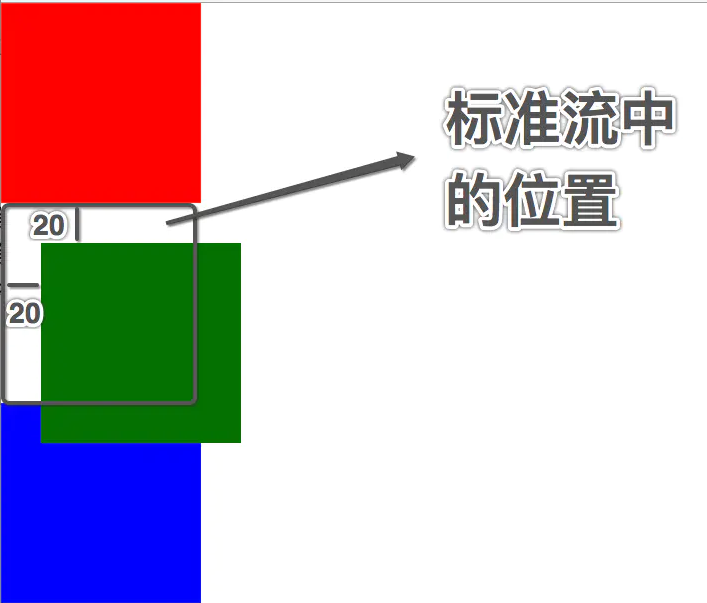
相对定位的注意点
- 在相对定位中同一个方向上的定位属性只能使用一个
- top / bottom 只能用一个
- left / right 只能用一个
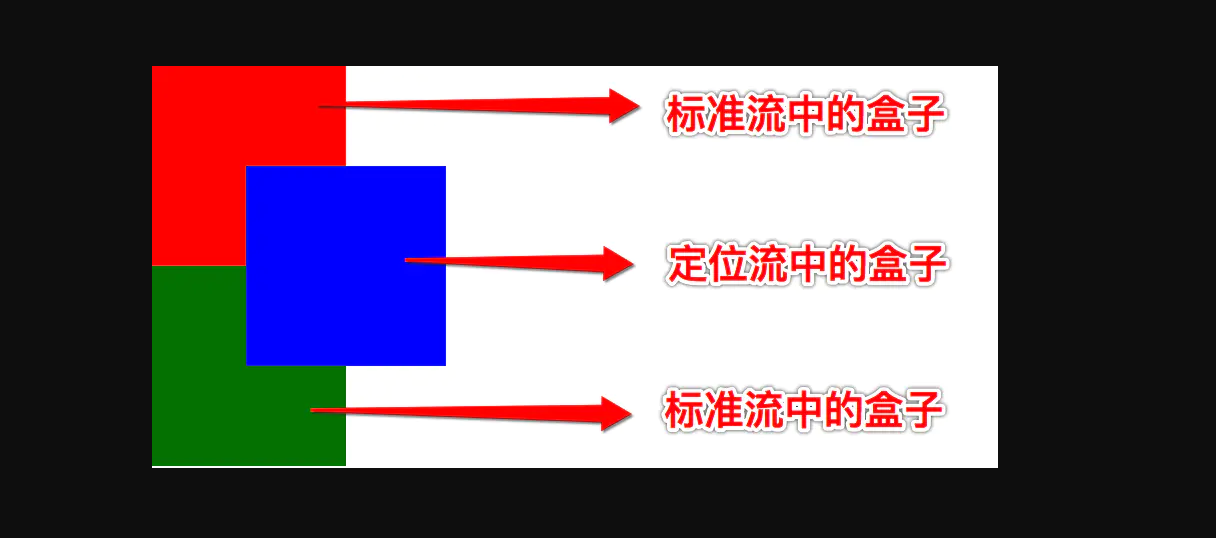
- 相对定位是不脱离标准流的, 会继续在标准流中占用一份空间
- 由于相对定位是不脱离标准流的, 所以在相对定位中区分块级元素 / 行内元素 / 行内块级元素
- 由于相对定位是不脱离标准流的, 并且相对定位的元素会占用标准流中的位置, 所以当给相对定位的元素设置 margin / padding 等属性时会影响到标准流的布局
相对定位的应用场景
- 用于对元素进行微调
- 配合后面学习的绝对定位来使用
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>定位流</title>
<style>
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
input {
width: 200px;
height: 50px;
}
img {
width: 100px;
height: 50px;
position: relative;
top: 20px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<input type="text" name="" id="">
<img src="images/vcode.jpg" alt="">
</body>
</html>
绝对定位
什么是绝对定位?
- 绝对定位就是相对于 body 或者某个定位流中的祖先元素来定位
格式如下
position: absolute;
示例代码
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>绝对定位</title>
<style>
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
div {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
}
.box1 {
background-color: red;
}
.box2 {
background-color: green;
position: absolute;
left: 0;
top: 0;
}
.box3 {
background-color: blue;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box1"></div>
<div class="box2"></div>
<div class="box3"></div>
</body>
</html>

绝对定位的注意点
- 绝对定位的元素是脱离标准流的, 不会占用标准流中的位置
- 由于绝对定位的元素是脱离标准流的, 所以绝对定位的元素不区分块级元素 / 行内元素 / 行内块级元素
- 如果一个绝对定位的元素是以 body 作为参考点, 那么其实是以网页首屏的宽度和高度作为参考点, 而不是以整个网页的宽度和高度作为参考点
- 相对于 body 定位会随着页面的滚动而滚动
- 一个绝对定位的元素会忽略祖先元素的 padding
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>绝对定位</title>
<style>
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
.box1 {
width: 300px;
height: 300px;
background-color: red;
border: 10px solid #000;
padding: 30px;
position: relative;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
.box2 {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: green;
position: absolute;
left: 0;
top: 0;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box1">
<div class="box2"></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>

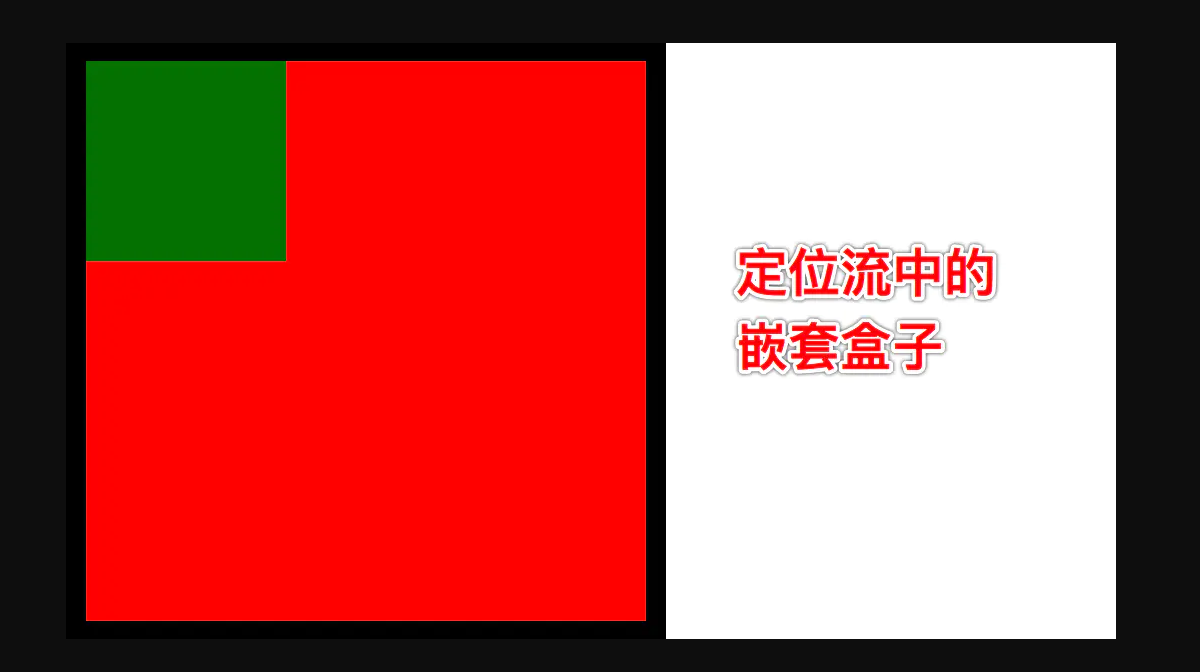
绝对定位的参考点
- 默认情况下所有的绝对定位的元素, 无论有没有祖先元素, 都会以 body 作为参考点
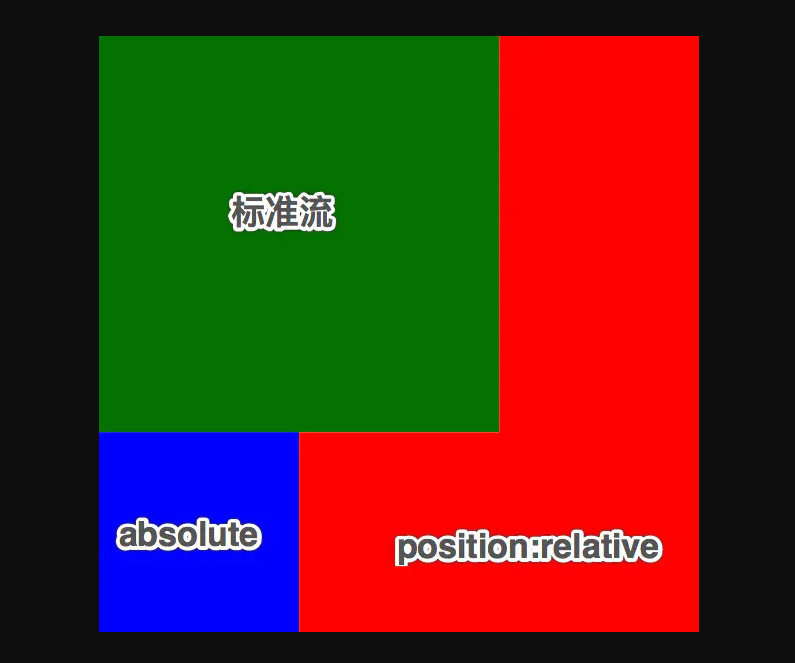
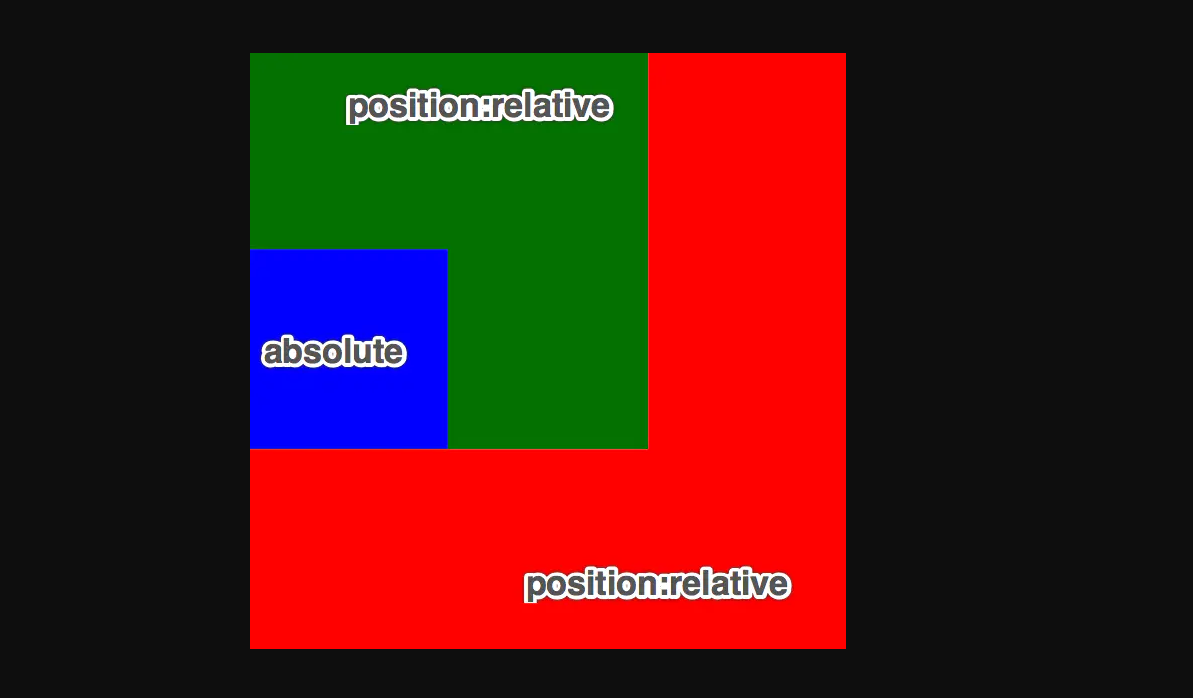
- 如果一个绝对定位的元素有祖先元素, 并且祖先元素中有一个是定位流中的元素, 那么这个绝对定位的元素就会以定位流的那个祖先元素作为参考点
- 如果一个绝对定位的元素有祖先元素, 并且祖先元素中有多个是定位流中的元素, 那么这个绝对定位的元素会以离它最近的那个定位流的祖先元素为参考点
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>绝对定位</title>
<style>
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
.box1 {
width: 300px;
height: 300px;
background-color: red;
position: relative;
}
.box2 {
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: green;
}
.box3 {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: blue;
position: absolute;
left: 0;
bottom: 0;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box1">
<div class="box2">
<div class="box3"></div>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>绝对定位</title>
<style>
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
.box1 {
width: 300px;
height: 300px;
background-color: red;
position: relative;
}
.box2 {
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: green;
position: relative;
}
.box3 {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: blue;
position: absolute;
left: 0;
bottom: 0;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box1">
<div class="box2">
<div class="box3"></div>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
绝对定位的水平居中
- 注意当一个盒子绝对定位之后不能使用
margin: 0 auto;让盒子自身居中 - 如果想让过一个绝对定位的盒子自身居中, 可以使用
left: 50%;、margin-left:-元素宽度一半px;
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>绝对定位水平居中</title>
<style>
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
div {
width: 400px;
height: 50px;
background-color: red;
position: absolute;
left: 50%;
margin-left: -200px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div></div>
</body>
</html>
绝对定位的应用场景
- 用于对元素进行微调
子绝父相
企业开发中一般相对定位和绝对定位都是一起出现, 很少单独使用
为什么要子绝父相?
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>子绝父相</title>
<style>
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
ul {
width: 800px;
height: 50px;
background-color: red;
list-style: none;
margin: 0px auto;
margin-top: 100px;
}
li {
width: 100px;
line-height: 50px;
float: left;
background-color: gray;
text-align: center;
}
.li03 {
background-color: darkgray;
position: relative;
}
ul li img {
position: absolute;
left: 37px;
top: -5px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<ul>
<li>服装城</li>
<li>美妆馆</li>
<li>京东超市</li>
<li class="li03">全球购<img src="images/hot.png"/></li>
<li>闪购</li>
<li>团购</li>
<li>拍卖</li>
<li>江哥</li>
</ul>
</body>
</html>

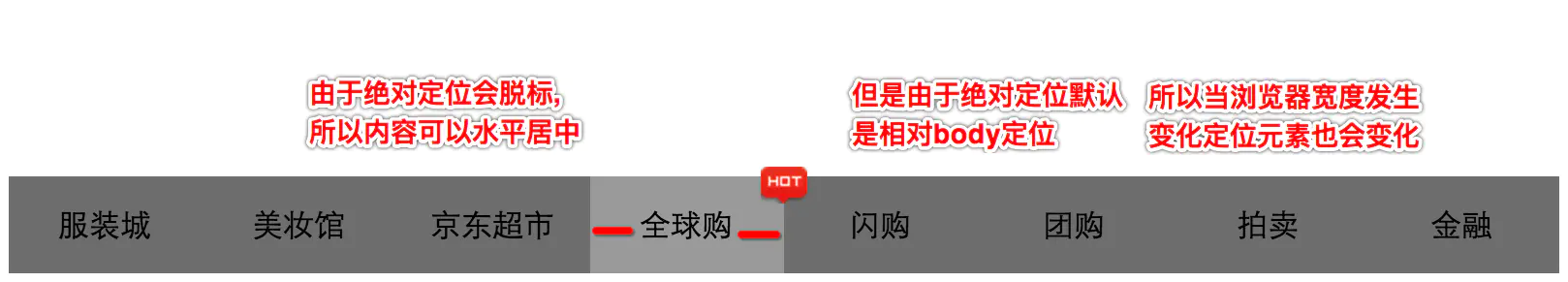
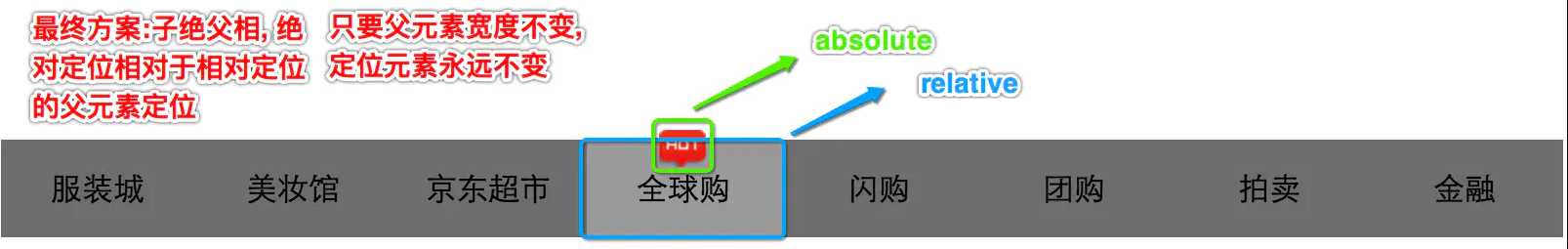
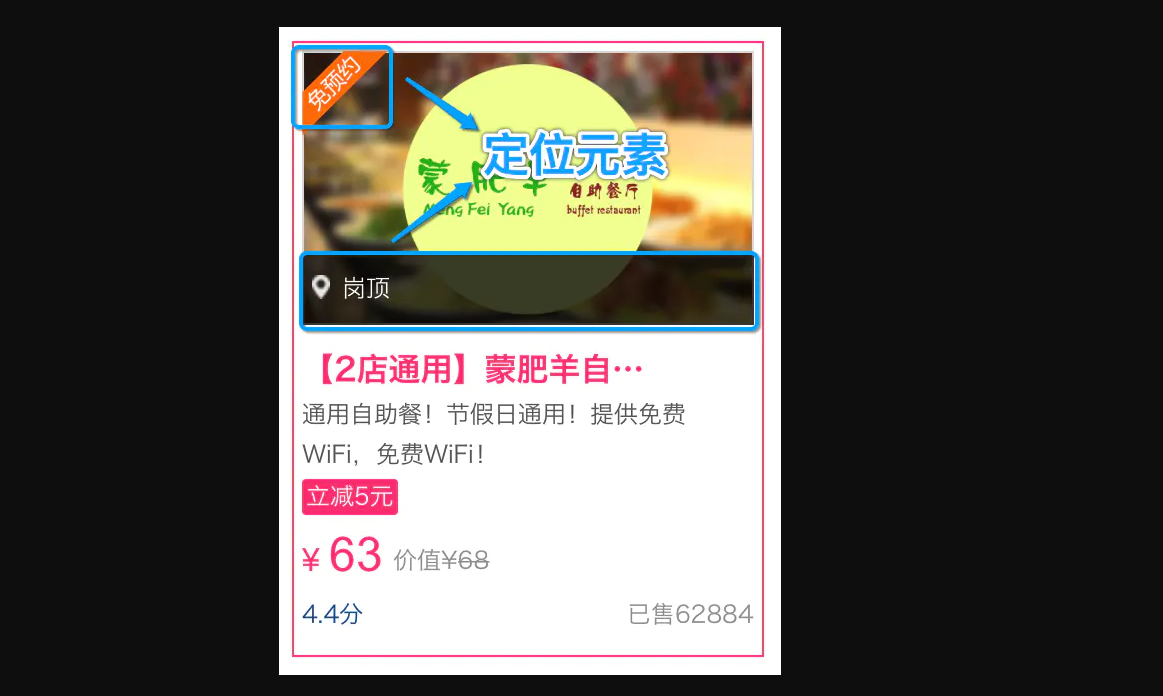
相对定位和绝对定位一般都是用来做覆盖效果的, 当看到某个元素覆盖在另外一个元素上时, 第一时间就要想到定位流

固定定位
什么是固定定位?
固定定位和前面学习的背景关联方式很像, 背景关联方式可以让某个图片不随着滚动条的滚动而滚动, 而固定定位可以让某个盒子不随着滚动条的滚动而滚动
格式如下
position: fixed;
示例代码
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>固定定位</title>
<style>
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
p {
width: 100px;
}
a {
width: 50px;
height: 50px;
background-color: rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.3);
border-radius: 25px;
text-decoration: none;
text-align: center;
color: #000;
position: fixed;
right: 10px;
bottom: 10px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字</p>
<a href="#">^<br>顶部</a>
</body>
</html>

固定定位的注意点
- 固定定位的元素是脱离标准流的, 不会占用标准流中的位置
- 由于固定定位的元素是脱离标准流的, 所以固定定位的元素不区分块级元素 / 行内元素 / 行内块级元素
- IE6 不支持固定定位
固定定位的应用场景
- 网页对联广告
- 网页头部通栏(穿透效果)
静态定位
什么是静态定位?
- 默认情况下标准流中的元素 position 属性就等于 static, 所以静态定位其实就是默认的标准流
静态定位的应用场景
- 一般用于配合 JS 清除定位属性
z-index 属性
什么是 z-index 属性?
用于指定定位的元素的覆盖关系
定位元素的覆盖关系
- 默认情况下定位的元素一定会盖住没有定位的元素
- 默认情况下写在后面的定位元素会盖住前面的定位元素
- 默认情况下所有元素的 z-index 值都是 0, 如果设置了元素的 z-index 值, 那么谁比较大谁就显示在前面
定位元素的从父现象
- 父元素没有 z-index 值, 那么子元素谁的 z-index 大谁盖住谁
- 父元素 z-index 值不一样, 那么父元素谁的 z-index 大谁盖住谁
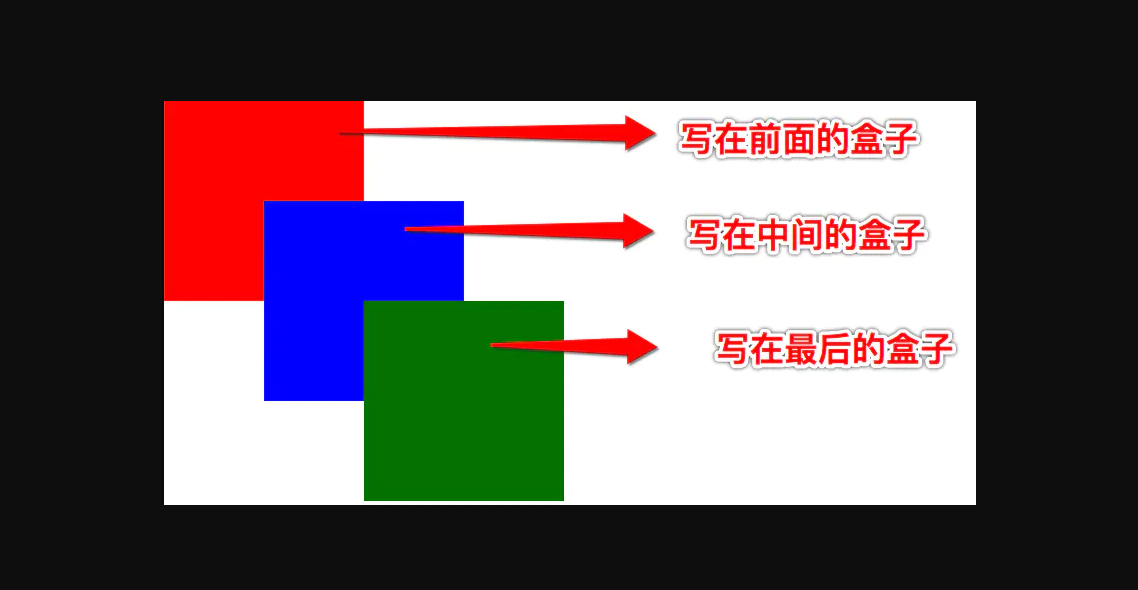
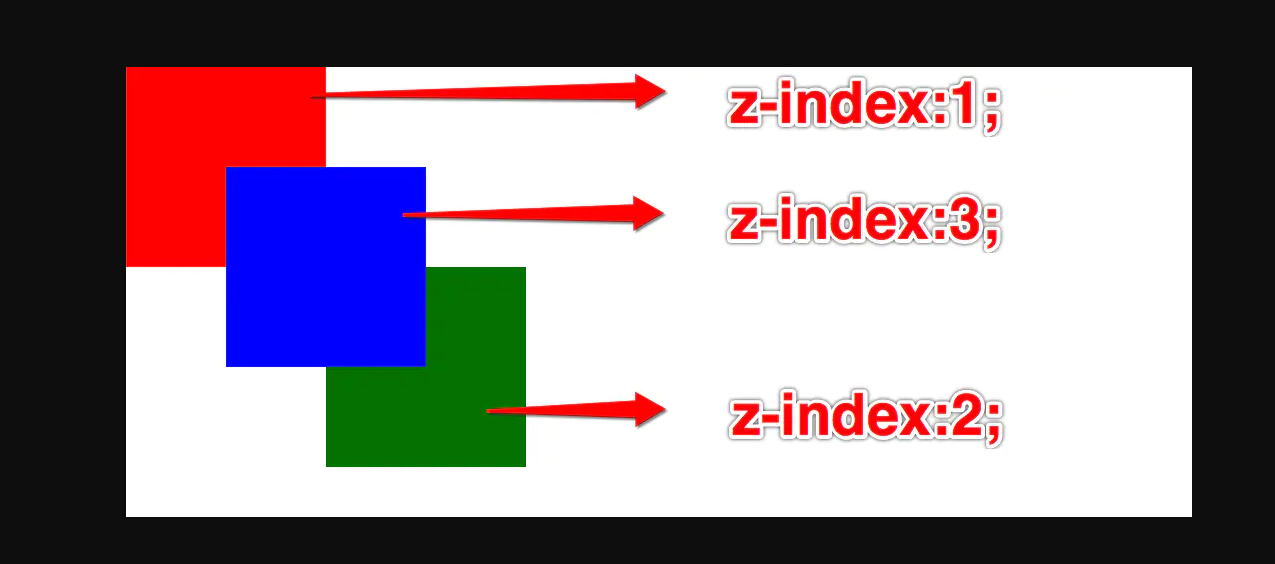
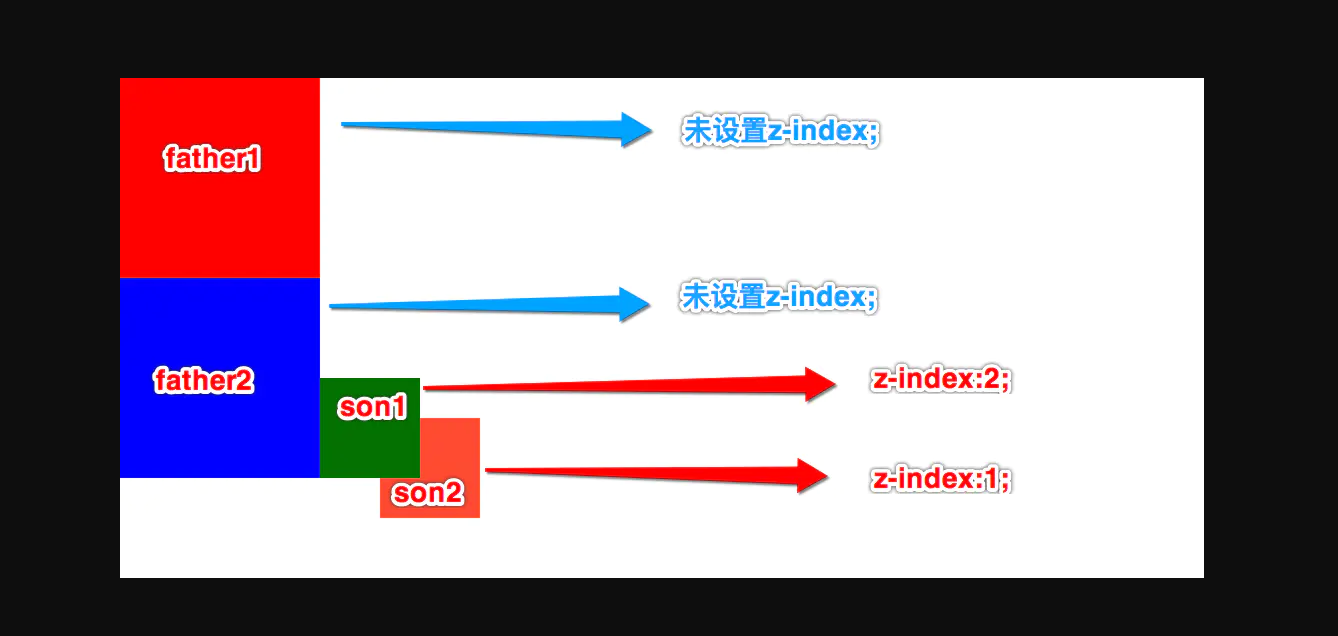
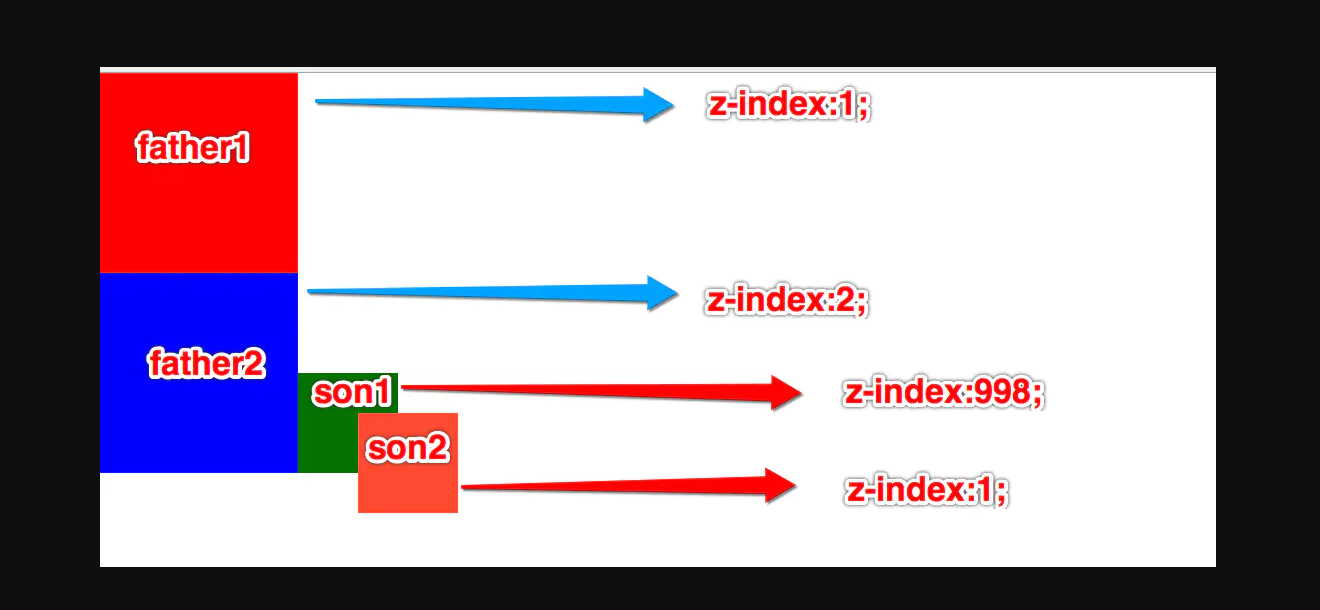
z-index 的应用场景
- 控制界面上的定位元素的覆盖关系, 例如网页中后面的定位元素不能覆盖前面的导航条通栏



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号