Java新特性-Stream流
Stream 流初体验
- Stream 是 Java8 中处理集合的关键抽象概念,它可以指定你希望对集合进行的操作,可以执行非常复杂的查找、过滤和映射数据等操作。
- 使用 Stream 中的 API 对集合中的数据进行操作,就类似于使用 SQL 执行的数据库查询。也可以使用 Stream 中的 API 来并行执行操作。
传统 Java 中操作集合的示例如下,首先给定一个集合内容如下
/**
* @author BNTang
*/
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> personList = new ArrayList<>();
personList.add("李四");
personList.add("张小宝");
personList.add("王五");
personList.add("赵六");
personList.add("张大");
personList.add("张三");
}
}
假如现在有一个需求,把集合中所有以 "张" 开头的元素存储到一个新的集合,所以具体实现这个需求的代码如下
/**
* @author BNTang
*/
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> personList = new ArrayList<>();
personList.add("李四");
personList.add("张小宝");
personList.add("王五");
personList.add("赵六");
personList.add("张大");
personList.add("张三");
List<String> zhangList = new ArrayList<>();
for (String s : personList) {
if (s.startsWith("张")) {
zhangList.add(s);
}
}
System.out.println(zhangList);
}
}
如上是一个需求,在来紧接着来看看第二个需求,内容为:把 "张" 开头的集合中的长度为 3 的元素存储到一个新的集合, 然后如上的代码改造如下
/**
* @author BNTang
*/
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> personList = new ArrayList<>();
personList.add("李四");
personList.add("张小宝");
personList.add("王五");
personList.add("赵六");
personList.add("张大");
personList.add("张三");
List<String> zhangList = new ArrayList<>();
for (String s : personList) {
if (s.startsWith("张")) {
zhangList.add(s);
}
}
System.out.println(zhangList);
List<String> threeList = new ArrayList<>();
for (String s : zhangList) {
if (s.length() == 3) {
threeList.add(s);
}
}
System.out.println(threeList);
}
}
假如现在又需要遍历上一步得到的集合,那么代码如下
/**
* @author BNTang
*/
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> personList = new ArrayList<>();
personList.add("李四");
personList.add("张小宝");
personList.add("王五");
personList.add("赵六");
personList.add("张大");
personList.add("张三");
List<String> zhangList = new ArrayList<>();
for (String s : personList) {
if (s.startsWith("张")) {
zhangList.add(s);
}
}
System.out.println(zhangList);
List<String> threeList = new ArrayList<>();
for (String s : zhangList) {
if (s.length() == 3) {
threeList.add(s);
}
}
System.out.println(threeList);
for (String s : threeList) {
System.out.println(s);
}
}
}
使用 Stream 流来完成如上的所有需求,Stream 完成的代码如下
/**
* @author BNTang
*/
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> personList = new ArrayList<>();
personList.add("李四");
personList.add("张小宝");
personList.add("王五");
personList.add("赵六");
personList.add("张大");
personList.add("张三");
personList.stream().filter(s -> s.startsWith("张")).filter(s -> s.length() == 3).forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
Stream 流把真正的函数式接口编程的风格引入到了 Java 中
Stream 流的使用方式
- 首先需要生成流
- 流的中间操作
- 流的终结操作

Stream 流的分类
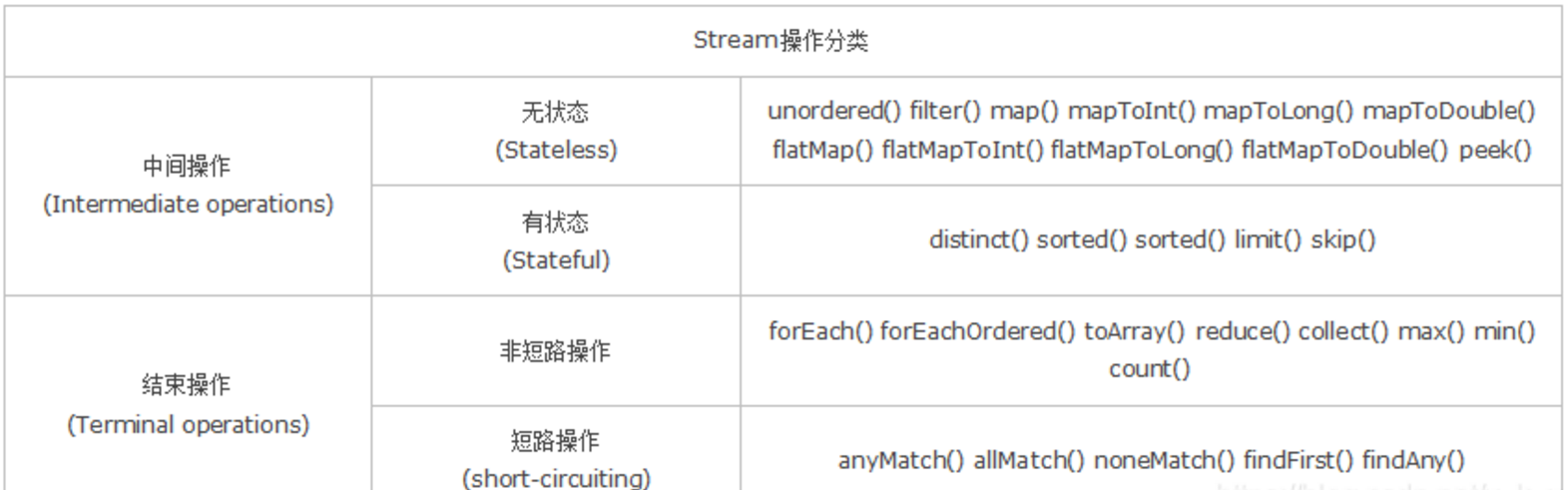
中间操作
- 无状态:指元素的处理不受之前元素的影响。
- 有状态:指该操作只有拿到所有元素之后才能继续下去。
结束操作
- 非短路操作:指必须处理所有元素才能得到最终结果。
- 短路操作:指遇到某些符合条件的元素就可以得到最终结果,如 A || B,只要 A 为 true,则无需判断 B 的结果。
生成 Stream 流的方式
使用 Collection 下的 stream() 和 parallelStream(), stream() 生成的是一个顺序流,parallelStream() 生成的是一个并行流
/**
* @author BNTang
*/
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> personList = new ArrayList<>();
Stream<String> stream = personList.stream();
Stream<String> parallelStream = personList.parallelStream();
}
}
使用 Arrays 中的 stream() 方法,将数组转成流
/**
* @author BNTang
*/
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer[] nums = new Integer[10];
Stream<Integer> stream = Arrays.stream(nums);
}
}
使用 Stream 中的静态方法:of()、iterate()、generate()
/**
* @author BNTang
*/
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stream<Integer> streamOne = Stream.of(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6);
Stream<Integer> streamTwo = Stream.iterate(0, f -> f + 2).limit(6);
Stream<Double> streamThree = Stream.generate(Math::random).limit(2);
}
}
使用 BufferedReader.lines() 方法
/**
* @author BNTang
*/
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException {
BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("D:\\stream.txt"));
Stream<String> stream = bufferedReader.lines();
stream.forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
使用 Pattern.splitAsStream() 方法,将字符串分隔成流
/**
* @author BNTang
*/
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile(",");
Stream<String> stream = pattern.splitAsStream("a,b,c,d");
stream.forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
Stream 流的中间操作方法
筛选与切片
Stream<T> filter(Predicate predicate):筛选满足条件的元素
找出集合当中所有的偶数
/**
* @author BNTang
*/
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Integer> arrayList = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
arrayList.add(i);
}
arrayList.stream().filter(s -> s % 2 == 0).forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
还是找出集合当中所有的偶数,但是多加了一个 filter
/**
* @author BNTang
*/
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Integer> arrayList = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
arrayList.add(i);
}
arrayList.stream().filter(s -> s % 2 == 0).filter(s -> s % 4 == 0).forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
上面是新的示例,下方给出的是之前的示例认真观察的就应该会发现,如下的内容是使用了 filter 改造了一下之前的示例
/**
* @author BNTang
*/
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> personList = new ArrayList<>();
personList.add("李四");
personList.add("张小宝");
personList.add("王五");
personList.add("赵六");
personList.add("张大");
personList.add("张三");
personList.stream().filter(s -> s.startsWith("张"))
.filter(s -> s.length() == 3)
.forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
Stream<T> limit(long maxSize):返回此流中的元素组成的流,截取前指定参数个数的数据
/**
* @author BNTang
*/
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Integer> arrayList = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
arrayList.add(i);
}
arrayList.stream().limit(5).forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
Stream<T> skip(long n):跳过指定参数个数的数据,返回由该流的剩余元素组成的流
如下代码含义为:截取前 8 个之后在跳过前两个
/**
* @author BNTang
*/
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Integer> arrayList = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
arrayList.add(i);
}
arrayList.stream().limit(8).skip(2).forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
Stream<T> distinct():去重操作
合并 a 和 b 两个流为一个流,合并之后在去重
/**
* @author BNTang
*/
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Integer> arrayList = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
arrayList.add(i);
}
Stream<Integer> streamOne = arrayList.stream().limit(5);
Stream<Integer> streamTwo = arrayList.stream().skip(4);
Stream<Integer> concat = Stream.concat(streamOne, streamTwo).distinct();
concat.forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
排序
Stream<T> sorted()
/**
* @author BNTang
*/
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Integer> arrayList = new ArrayList<>();
arrayList.add(1);
arrayList.add(5);
arrayList.add(2);
arrayList.add(7);
arrayList.add(3);
arrayList.stream().sorted((a, b) -> b - a).forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
Stream<T> sorted(Comparator comparator)
/**
* @author BNTang
*/
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("dbc");
list.add("cba");
list.add("a");
list.add("ab");
list.add("ef");
list.add("ga");
list.stream().sorted(Comparator.comparingInt(String::length).thenComparing(s -> s)).forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
上方的代码是简化过的,如下的代码是最初的样子
/**
* @author BNTang
*/
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("dbc");
list.add("cba");
list.add("a");
list.add("ab");
list.add("ef");
list.add("ga");
list.stream().sorted((s1, s2) -> {
int numOne = s1.length() - s2.length();
int numTwo = numOne == 0 ? s1.compareTo(s2) : numOne;
return numTwo;
}).forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
映射
map:接收一个函数作为参数,该函数会被应用到每个元素上,并将其映射成一个新的元素。flatMap:接收一个函数作为参数,将流中的每个值都换成另一个流,然后把所有流连接成一个流。
如下将给出一个示例来进行演示,代码如下
/**
* @author BNTang
*/
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] words = {"Hello", "World"};
List<String[]> a = Arrays.stream(words)
.map(word -> word.split(""))
.distinct()
.collect(Collectors.toList());
a.forEach(System.out::println);
String[] wordsTwo = {"Hello", "World"};
List<String> b = Arrays.stream(wordsTwo)
.map(word -> word.split(""))
.flatMap(Arrays::stream)
.distinct()
.collect(Collectors.toList());
b.forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
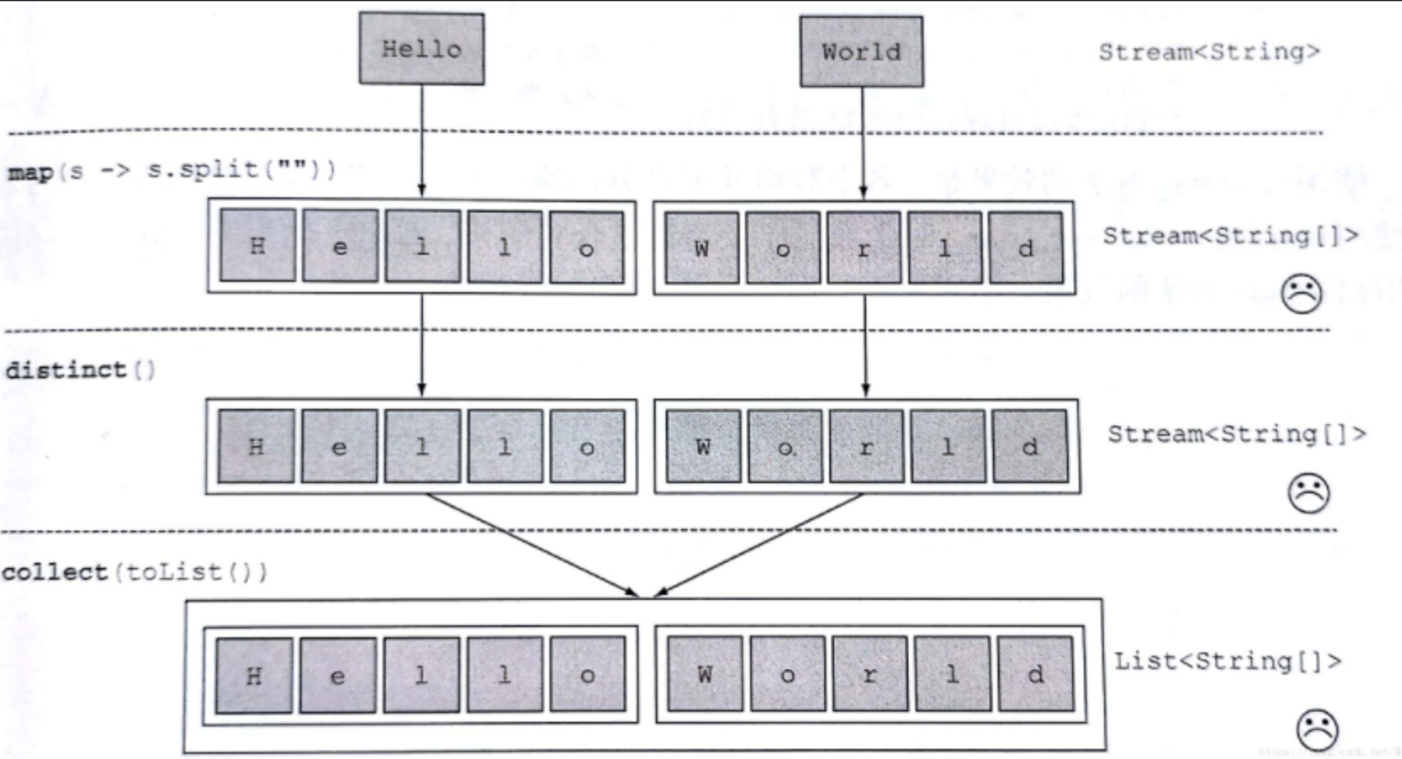
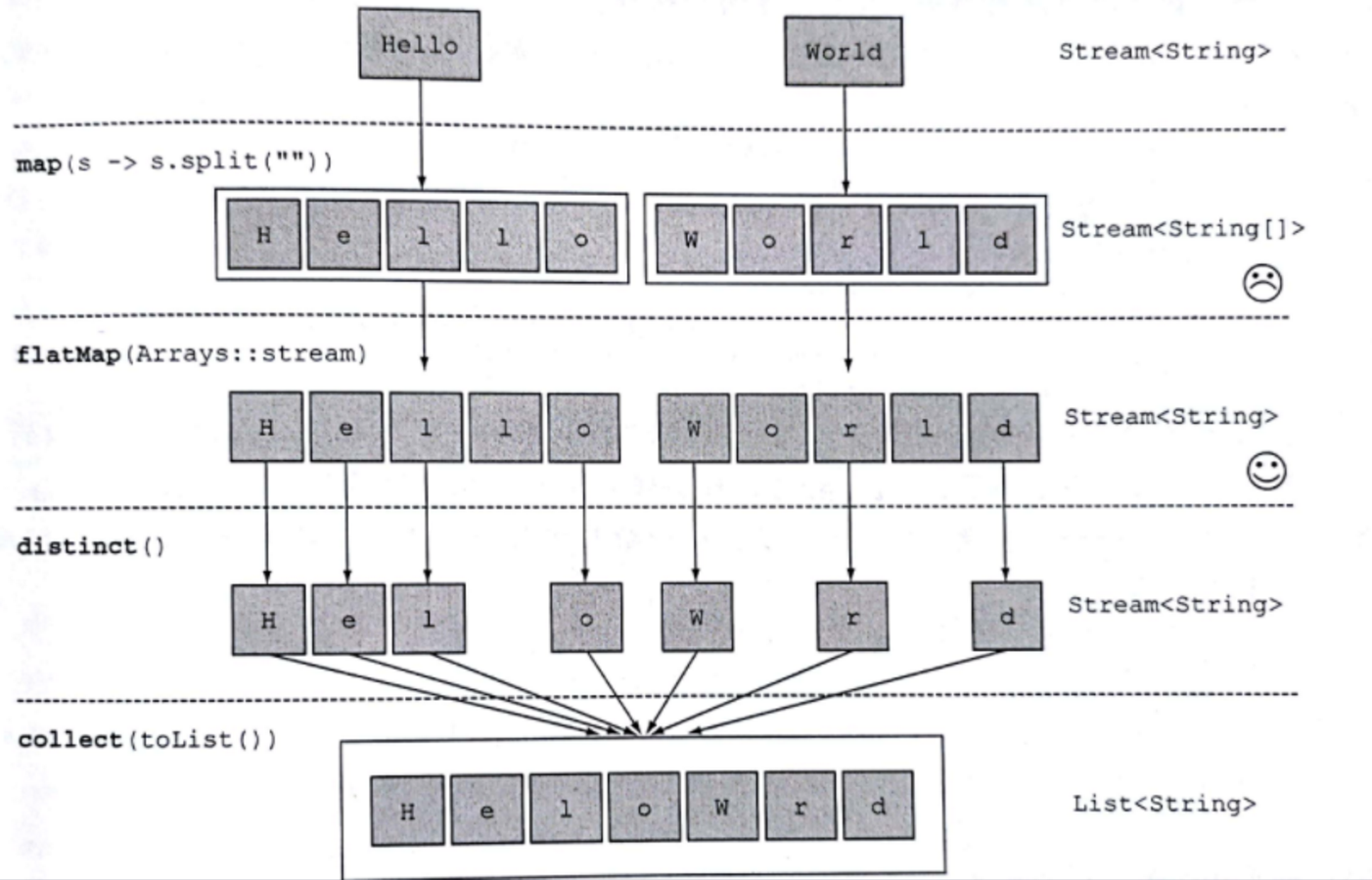
消费
peek:如同于 map,能得到流中的每一个元素。但 map 接收的是一个Function表达式,有返回值,而 peek 接收的是Consumer表达式,没有返回值。
/**
* @author BNTang
*/
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stream<String> stream = Stream.of("Hello", "https://www.cnblogs.com/BNTang");
List<String> strs = stream.peek(System.out::println).collect(Collectors.toList());
}
}
static <T> Stream<T> concat(Stream a, Stream b):将 a 与 b 两个流合并成为一个流。
/**
* @author BNTang
*/
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Integer> arrayList = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
arrayList.add(i);
}
Stream<Integer> streamOne = arrayList.stream().limit(5);
Stream<Integer> streamTwo = arrayList.stream().skip(4);
Stream<Integer> concat = Stream.concat(streamOne, streamTwo);
concat.forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
Stream 流的终结操作方法
匹配 聚合操作
allMatch:接收一个Predicate函数,当流中每个元素都符合该断言时才返回 true,否则返回 false。
noneMatch:接收一个Predicate函数,当流中每个元素都不符合该断言时才返回 true,否则返回 false。anyMatch:接收一个Predicate函数,只要流中有一个元素满足该断言则返回 true,否则返回 false。findFirst:返回流中的第一个元素。findAny:返回流中的任意元素。count:返回流中元素的总个数。max:返回流中的元素最大值。min:返回流中的元素最小值。
/**
* @author BNTang
*/
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Integer> list = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5);
System.out.println(list.stream().allMatch(e -> e > 10));
System.out.println(list.stream().noneMatch(e -> e > 10));
System.out.println(list.stream().anyMatch(e -> e > 4));
System.out.println(list.stream().findFirst().get());
System.out.println(list.stream().findAny().get());
long count = list.stream().count();
System.out.println(count);
System.out.println(list.stream().max(Integer::compareTo).get());
System.out.println(list.stream().min(Integer::compareTo).get());
}
}
收集操作
新建一个 Student 类,代码如下
/**
* @author BNTang
**/
public class Student {
private String name;
private Integer age;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
public Student(String name, Integer age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
}
收集为 List
/**
* @author BNTang
*/
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student studentOne = new Student("aa", 10);
Student studentTwo = new Student("bb", 20);
Student studentThree = new Student("cc", 10);
List<Student> studentList = Arrays.asList(studentOne, studentTwo, studentThree);
List<Integer> ageList = studentList.stream().map(Student::getAge).collect(Collectors.toList());
}
}
收集为 Set
/**
* @author BNTang
*/
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student studentOne = new Student("aa", 10);
Student studentTwo = new Student("bb", 20);
Student studentThree = new Student("cc", 10);
List<Student> studentList = Arrays.asList(studentOne, studentTwo, studentThree);
Set<Integer> ageList = studentList.stream().map(Student::getAge).collect(Collectors.toSet());
}
}
收集为 Map
/**
* @author BNTang
*/
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student studentOne = new Student("aa", 10);
Student studentTwo = new Student("bb", 20);
Student studentThree = new Student("cc", 10);
List<Student> studentList = Arrays.asList(studentOne, studentTwo, studentThree);
Map<String, Integer> studentMap = studentList.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(Student::getName, Student::getAge));
}
}
注意事项:收集为 Map,其中的 Key 值不能相同也就是存在重复 Key,否则会报错。
字符串分隔符连接
/**
* @author BNTang
*/
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student studentOne = new Student("aa", 10);
Student studentTwo = new Student("bb", 20);
Student studentThree = new Student("cc", 10);
List<Student> studentList = Arrays.asList(studentOne, studentTwo, studentThree);
String joinName = studentList.stream().map(Student::getName).collect(Collectors.joining(",", "(", ")"));
System.out.println(joinName);
}
}
聚合操作
获取总数
/**
* @author BNTang
*/
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student studentOne = new Student("aa", 10);
Student studentTwo = new Student("bb", 20);
Student studentThree = new Student("cc", 10);
List<Student> studentList = Arrays.asList(studentOne, studentTwo, studentThree);
Long count = studentList.stream().collect(Collectors.counting());
System.out.println(count);
}
}
获取最大值
/**
* @author BNTang
*/
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student studentOne = new Student("aa", 10);
Student studentTwo = new Student("bb", 20);
Student studentThree = new Student("cc", 10);
List<Student> studentList = Arrays.asList(studentOne, studentTwo, studentThree);
Integer maxAge = studentList.stream().map(Student::getAge).collect(Collectors.maxBy(Integer::compare)).get();
System.out.println(maxAge);
}
}
获取最小值
/**
* @author BNTang
*/
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student studentOne = new Student("aa", 10);
Student studentTwo = new Student("bb", 20);
Student studentThree = new Student("cc", 10);
List<Student> studentList = Arrays.asList(studentOne, studentTwo, studentThree);
Integer minAge = studentList.stream().map(Student::getAge).collect(Collectors.minBy(Integer::compare)).get();
System.out.println(minAge);
}
}
获取总数
/**
* @author BNTang
*/
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student studentOne = new Student("aa", 10);
Student studentTwo = new Student("bb", 20);
Student studentThree = new Student("cc", 10);
List<Student> studentList = Arrays.asList(studentOne, studentTwo, studentThree);
Integer sumAge = studentList.stream().collect(Collectors.summingInt(Student::getAge));
System.out.println(sumAge);
}
}
获取平均值
/**
* @author BNTang
*/
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student studentOne = new Student("aa", 10);
Student studentTwo = new Student("bb", 20);
Student studentThree = new Student("cc", 10);
List<Student> studentList = Arrays.asList(studentOne, studentTwo, studentThree);
Double averageAge = studentList.stream().collect(Collectors.averagingDouble(Student::getAge));
System.out.println(averageAge);
}
}
其实如上的方法有一个汇总的方法,也就是说调用这个方法如上的结果都会有,运行结果如下
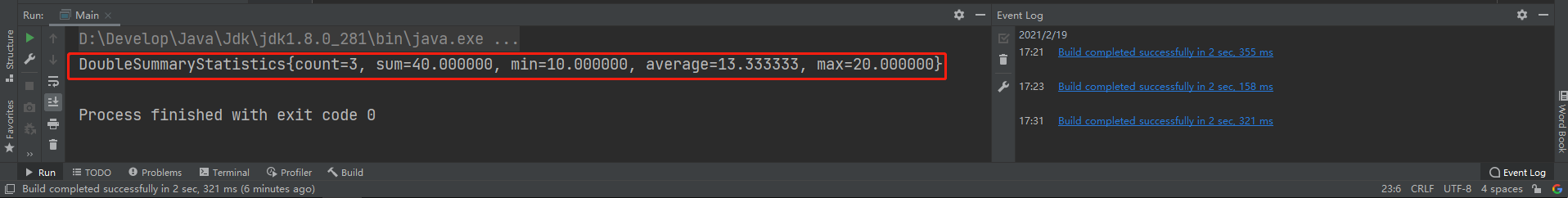
代码如下所示
/**
* @author BNTang
*/
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student studentOne = new Student("aa", 10);
Student studentTwo = new Student("bb", 20);
Student studentThree = new Student("cc", 10);
List<Student> studentList = Arrays.asList(studentOne, studentTwo, studentThree);
DoubleSummaryStatistics statistics = studentList.stream()
.collect(Collectors.summarizingDouble(Student::getAge));
System.out.println(statistics);
}
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号