数据结构考试题
数据结构考试题
目录
- 数据结构考试题
- 1.请默写堆排序
- 2. 请默写快速排序
- 3.请默写归并排序
- 4. 在一个给定的从1到100的整型数组中,如何快速找到缺失的数字?
- 5.给你一个有序数组 nums ,请你 原地 删除重复出现的元素,使每个元素 最多出现两次 , 返回删除后数组的新长度
- 6.分别用头插法和尾插法实现链表,并变量输出结果
- 7.给定一个单链表,但不知该表的大小,现要求只遍历一次,找出位于单链表中间的值
- 8.如何判断单链表中是否有环?
- 9.怎样发现这个环的起始节点?
- 10.怎样翻转链表?
- 11.截取单链表中的后k个节点
- 12.合并两个有序链表
- 13.实现一个栈,要求实现出栈,入栈,Min(返回最小值的操作)的时间复杂度为o(1)
- 14.用两个栈实现一个队列
- 15.用两个队列实现一个栈
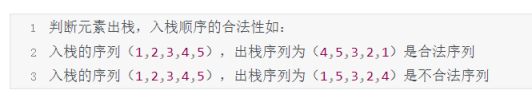
- 16.判断元素出栈,入栈顺序的合法性如:
1.请默写堆排序
package y2022.m3.d19Exam;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class HeapSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {4,1,2,3,5,14,23,12,7,14};
heapSort(arr);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
}
public static void heapSort(int[] arr){
for(int i = arr.length - 1;i>=0;i--){
heapAdjest(arr,i,arr.length);
}
for(int i = 1;i<arr.length;i++){
int temp = arr[arr.length - i];
arr[arr.length - i] = arr[0];
arr[0] = temp;
heapAdjest(arr,0,arr.length-i);
}
}
public static void heapAdjest(int[] arr,int parent,int length){
int temp = arr[parent];
int child = parent * 2 + 1;
while(child<length){
if(child+1<length&&arr[child]<arr[child+1]){
child++;
}
if(temp>arr[child]){
break;
}
arr[parent] = arr[child];
parent = child;
child = child * 2 + 1;
}
arr[parent] = temp;
}
}
运行结果:
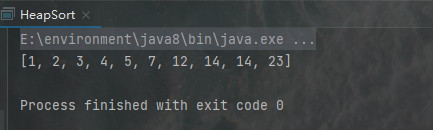
2. 请默写快速排序
package y2022.m3.d19Exam;
import java.lang.reflect.Array;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class FastSort{
public static void main(String[] args){
int[] arr = {4,1,2,3,5,14,23,12,7,14};
quickSort(arr,0,arr.length-1);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
}
public static void quickSort(int[] arr, int left, int right) {
if(left >= right) {
return ;
}
int i = left,j = right,base = arr[i];
while(i!=j) {
while(i<j && arr[j] >= base) {
j--;
}
while(i<j && arr[i] <= base) {
i++;
}
int temp = arr[j];
arr[j] = arr[i];
arr[i] = temp;
}
arr[left] = arr[i];
arr[i] = base;
quickSort(arr, left, i-1);
quickSort(arr, i+1,right);
}
}
运行结果:
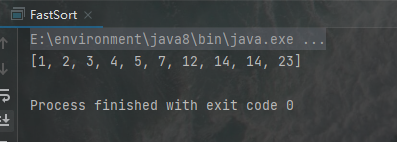
3.请默写归并排序
package y2022.m3.d19Exam;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class MergeSort {
public static void main(String []args){
int []arr = {4,1,2,3,5,14,23,12,7,14};
sort(arr);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
}
public static void sort(int []arr){
int []temp = new int[arr.length];
sort(arr,0,arr.length-1,temp);
}
private static void sort(int[] arr,int left,int right,int []temp){
if(left<right){
int mid = (left+right)/2;
sort(arr,left,mid,temp);
sort(arr,mid+1,right,temp);
merge(arr,left,mid,right,temp);
}
}
private static void merge(int[] arr,int left,int mid,int right,int[] temp){
int i = left;
int j = mid+1;
int t = 0;
while (i<=mid && j<=right){
if(arr[i]<=arr[j]){
temp[t++] = arr[i++];
}else {
temp[t++] = arr[j++];
}
}
while(i<=mid){
temp[t++] = arr[i++];
}
while(j<=right){
temp[t++] = arr[j++];
}
t = 0;
while(left <= right){
arr[left++] = temp[t++];
}
}
}
运行结果:
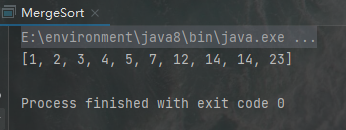
4. 在一个给定的从1到100的整型数组中,如何快速找到缺失的数字?
package y2022.m3.d19Exam;
public class FullNumber {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {1,2,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,16,17,18,19,20};
fullNumber(arr);
}
public static void fullNumber(int[] arr){
int i = 1,j = 0;
while(i<101){
if(j<arr.length&&i == arr[j]){
i++;
j++;
}else{
System.out.print(i+" ");
i++;
}
}
}
}
运行结果:


5.给你一个有序数组 nums ,请你 原地 删除重复出现的元素,使每个元素 最多出现两次 , 返回删除后数组的新长度
package y2022.m3.d19Exam;
public class DeleteNums {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {1,2,2,2,2,3,3,4,5,6,6,7};
int length = deleteNum(arr);
for(int i = 0;i<length;i++){
System.out.print(arr[i]+" ");
}
}
public static int deleteNum(int[] arr){
int flag = 0;
for(int i = arr.length - 1;i>=2;i--){
if(arr[i]==arr[i-1]&&arr[i-1]==arr[i-2]){
flag++;
for(int j = i-2;j<arr.length-1;j++){
arr[j] = arr[j+1];
}
}
}
//System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
return arr.length - flag;
}
}
输出结果:
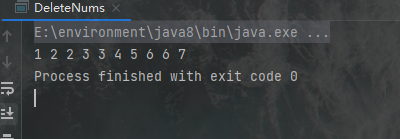
6.分别用头插法和尾插法实现链表,并变量输出结果
package y2022.m3.d19Exam;
public class LinkList {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LK lk = new LK();
lk.headInsert(1);
lk.headInsert(2);
lk.headInsert(3);
lk.headInsert(4);
lk.tailInsert(6);
lk.tailInsert(7);
lk.tailInsert(8);
lk.showLink();
}
}
class LK{
LinkNode head;
LinkNode tail;
public void headInsert(int val){
LinkNode ln = new LinkNode(val);
if(this.head==null){
this.head = ln;
this.tail = this.head;
}else{
ln.next = this.head;
this.head = ln;
}
}
public void tailInsert(int val){
LinkNode ln = new LinkNode(val);
if(this.head==null){
this.head = ln;
this.tail = this.head;
}else{
this.tail.next = ln;
this.tail = ln;
}
}
public void showLink(){
LinkNode p = this.head;
while(p!=null){
System.out.println(p.val+" ");
p = p.next;
}
}
}
class LinkNode{
int val;
LinkNode next;
public LinkNode(int val){
this.val = val;
next = null;
}
}
输出结果:
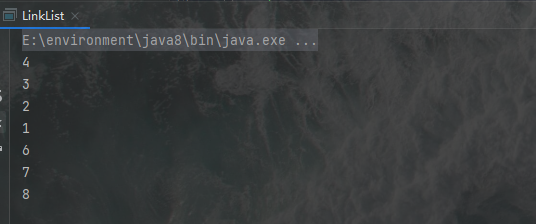
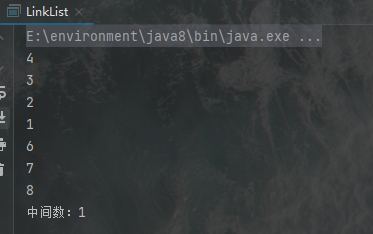
7.给定一个单链表,但不知该表的大小,现要求只遍历一次,找出位于单链表中间的值
public int finMid(){
LinkNode fast = this.head;
LinkNode slow = this.head;
while(fast.next!=null&&fast.next.next!=null){
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return slow.val;
}
运行结果:
8.如何判断单链表中是否有环?
public boolean isCycle(){
LinkNode fast = this.head;
LinkNode slow = this.head;
while(fast.next!=null&&fast.next.next!=null){
if(fast == slow)
return true;
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return false;
}
9.怎样发现这个环的起始节点?
public int cycleStart(){
LinkNode fast = this.head;
LinkNode slow = this.head;
while(fast.next!=null&&fast.next.next!=null){
if(fast == slow){
slow = this.head;
while(slow!=fast){
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next;
}
return slow.val;
}
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return -1;
}
10.怎样翻转链表?
public void fanzhuan() {
Node pre = null;
Node next = null;
while (head != null) {
next = head.next;
head.next = pre;
pre = head;
head = next;
}
head = pre;
}
11.截取单链表中的后k个节点
public Node NthFromEnd(int k) {
Node pionner = head;
Node support = head;
int dangerValue = 0;
while (pionner.next != null) {
pionner = pionner.next;
if (dangerValue >= k - 1) {
support = support.next;
}
dangerValue++;
}
System.out.print("后" + k + "位为:");
Node p = support;
while (p != null) {
System.out.print(p.value + " ");
p = p.next;
}
System.out.println();
return support;
}
12.合并两个有序链表
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {
ListNode p = list1;
ListNode q = list2;
if (p == null && q != null) {
return q;
} else if (p != null && q == null) {
return p;
} else if (p == null && q == null) {
return null;
} else {
ListNode head;
ListNode tail;
if (p.val < q.val) {
head = p;
p = p.next;
} else {
head = q;
q = q.next;
}
head.next = null;
tail = head;
while (p != null && q != null) {
if (p.val < q.val) {
tail.next = p;
p = p.next;
tail = tail.next;
tail.next = null;
} else {
tail.next = q;
q = q.next;
tail = tail.next;
tail.next = null;
}
}
if (p != null) {
tail.next = p;
} else {
tail.next = q;
}
return head;
}
}
13.实现一个栈,要求实现出栈,入栈,Min(返回最小值的操作)的时间复杂度为o(1)
package y2022.m3.d19Exam;
import java.util.Stack;
public class AlwaysMin {
public static void main(String[] args) {
myStack ms = new myStack();
ms.push(1);
ms.push(6);
ms.push(4);
ms.push(0);
ms.push(7);
System.out.println(ms.getMin());
ms.pop();
ms.pop();
System.out.println(ms.getMin());
}
}
class myStack{
Stack<Integer> num = new Stack<Integer>();
Stack<Integer> min = new Stack<Integer>();
public void push(int val){
num.push(val);
if(!min.empty()){
if(val<min.peek()){
min.push(val);
}
}else{
min.push(val);
}
}
public int pop(){
if(!num.empty()){
if(min.peek()==num.peek()){
min.pop();
return num.pop();
}else{
return num.pop();
}
}else {
return -1;
}
}
public int getMin(){
return min.peek();
}
}
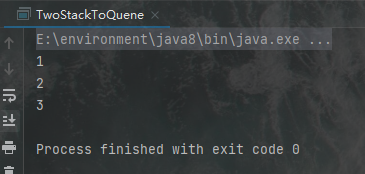
14.用两个栈实现一个队列
package y2022.m3.d19Exam;
import java.util.Stack;
public class TwoStackToQuene {
static Stack<Integer> stack1 = new Stack<>();
static Stack<Integer> stack2 = new Stack<>();
public static void main(String[] args) {
push(1);
push(2);
push(3);
push(4);
push(5);
System.out.println(pop());
System.out.println(pop());
System.out.println(pop());
}
public static void push(Integer data){
stack1.push(data);
}
public static int pop(){
Integer re = null;
if(!stack2.empty()){
re = stack2.pop();
}else{
while(!stack1.empty()){
re = stack1.pop();
stack2.push(re);
}
if(!stack2.empty()){
re = stack2.pop();
}
}
return re;
}
}
输出结果:
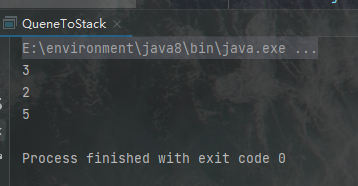
15.用两个队列实现一个栈
package y2022.m3.d19Exam;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
public class QueneToStack {
static Queue<Integer> quene1 = new LinkedList<>();
static Queue<Integer> quene2 = new LinkedList<>();
public static void main(String[] args) {
push(1);
push(2);
push(3);
System.out.println(pop());
System.out.println(pop());
push(5);
System.out.println(pop());
}
public static void push(Integer data){
quene1.offer(data);
}
public static int pop(){
Integer data = null;
while(!quene1.isEmpty()){
data = quene1.poll();
if(quene1.isEmpty()){
break;
}
quene2.offer(data);
}
while(!quene2.isEmpty()){
quene1.offer(quene2.poll());
}
return data;
}
}
输出结果:
16.判断元素出栈,入栈顺序的合法性如:
package y2022.m3.d19Exam;
import java.util.Stack;
public class CheckArrays {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] in = {1,2,3,4,5};
int[] out = {1,5,3,2,4};
System.out.println(cheackArrays(in, out));
}
public static boolean cheackArrays(int[] in,int[] out){
Stack<Integer> ins = new Stack<Integer>();
for(int i=0,j=0;i<in.length;i++){
ins.push(in[i]);
//System.out.println(ins.peek()+" "+out[j]);
while(ins.peek()==out[j]){
j++;
ins.pop();
if(ins.empty()){
break;
}
}
}
//System.out.println(ins.peek());
return ins.empty();
}
}





· 阿里巴巴 QwQ-32B真的超越了 DeepSeek R-1吗?
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语 ── 封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· 【设计模式】告别冗长if-else语句:使用策略模式优化代码结构
· 字符编码:从基础到乱码解决
· 提示词工程——AI应用必不可少的技术