python:np.argsort使用中的坑
np.argsort语法
argsort(a, axis=-1, kind=None, order=None)
Returns the indices that would sort an array.
Perform an indirect sort along the given axis using the algorithm specified
by the `kind` keyword. It returns an array of indices of the same shape as
`a` that index data along the given axis in sorted order.
Parameters
----------
a : array_like
Array to sort.
axis : int or None, optional
Axis along which to sort. The default is -1 (the last axis). If None,
the flattened array is used.
kind : {'quicksort', 'mergesort', 'heapsort', 'stable'}, optional
Sorting algorithm. The default is 'quicksort'. Note that both 'stable'
and 'mergesort' use timsort under the covers and, in general, the
actual implementation will vary with data type. The 'mergesort' option
is retained for backwards compatibility.
.. versionchanged:: 1.15.0.
The 'stable' option was added.
order : str or list of str, optional
When `a` is an array with fields defined, this argument specifies
which fields to compare first, second, etc. A single field can
be specified as a string, and not all fields need be specified,
but unspecified fields will still be used, in the order in which
they come up in the dtype, to break ties.
Returns
-------
index_array : ndarray, int
Array of indices that sort `a` along the specified `axis`.
If `a` is one-dimensional, ``a[index_array]`` yields a sorted `a`.
More generally, ``np.take_along_axis(a, index_array, axis=axis)``
always yields the sorted `a`, irrespective of dimensionality.
案例:
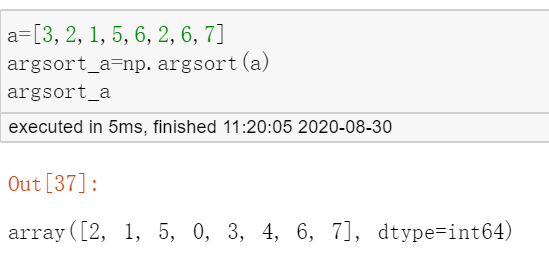
其中argsort_a返回的是a的值从小到大排序的索引。
argsort_a[0]=2表示a中最小的值是a[2]=a[argsort_a[0]].
对于重复值,
np.argsort是按照其出现的顺序进行排列。
含空值的应用
(1)案例:
a = [3, 2, np.nan, 1, 5, np.nan, 6, 2, 6, 7]
argsort_a = np.argsort(a)
print(f"a={a}")
for num, i in enumerate(argsort_a):
print(f"argsort_a[{num}]={i},对应的在a中的值{a[i]},排序:{i}")
#print结果
a=[3, 2, nan, 1, 5, nan, 6, 2, 6, 7]
argsort_a[0]=3,对应的在a中的值1,排序:3
argsort_a[1]=1,对应的在a中的值2,排序:1
argsort_a[2]=7,对应的在a中的值2,排序:7
argsort_a[3]=0,对应的在a中的值3,排序:0
argsort_a[4]=4,对应的在a中的值5,排序:4
argsort_a[5]=6,对应的在a中的值6,排序:6
argsort_a[6]=8,对应的在a中的值6,排序:8
argsort_a[7]=9,对应的在a中的值7,排序:9
argsort_a[8]=2,对应的在a中的值nan,排序:2
argsort_a[9]=5,对应的在a中的值nan,排序:5
特点:重复值按照出现顺序排序,np.nan排在最后。
(2)基于np.argsort的应用改进
基于上述案例背景,想实现的结果:相同的值编号应该相同(空值的排序为-1,表示不参与排序)。
def containsNanArgsort(List):
"""
获取含有nan值的列表的argsort
:param List:
:return:
"""
# 先获取排好序的索引
a = np.argsort(List)
# 用字典的形式存储
res = [(List[i], num) for num, i in enumerate(a)]
res=dict([i for i in res if not np.isnan(i[0])])
#返回排序情况,若不在字典中则返回-1
# print(res)
res2=[]
for i in List:
if i in res.keys():
res2.append(res[i])
else:
res2.append(-1)
return res2
上述列表的排序结果:
print(f"a={a}")
print(f'atgsort_a:{containsNanArgsort(a)}')
for num, i in enumerate(containsNanArgsort(a)):
print(f"argsort_a[{num}]={i},对应的在a中的值{a[i]},排序:{i}")
#print结果
a=[3, 2, nan, 1, 5, nan, 6, 2, 6, 7]
atgsort_a:[3, 2, -1, 0, 4, -1, 6, 2, 6, 7]
argsort_a[0]=3,对应的在a中的值1,排序:3
argsort_a[1]=2,对应的在a中的值nan,排序:2
argsort_a[2]=-1,对应的在a中的值7,排序:-1
argsort_a[3]=0,对应的在a中的值3,排序:0
argsort_a[4]=4,对应的在a中的值5,排序:4
argsort_a[5]=-1,对应的在a中的值7,排序:-1
argsort_a[6]=6,对应的在a中的值6,排序:6
argsort_a[7]=2,对应的在a中的值nan,排序:2
argsort_a[8]=6,对应的在a中的值6,排序:6
argsort_a[9]=7,对应的在a中的值2,排序:7
重复值的排序编号相同。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号