文件的相关操作(Java版)
一、文件的概念
文件是具有符号名的、在逻辑上具备完整意义的一组具备相关性的信息项的有序序列,可用于存储数据。其中信息项是构成文件内容的基本单位。除此之外。文件一般存储在外存介质上。
二、文件流
在Java中,文件的输入与输出一般均通过流(Stream)的形式来实现。针对于流而言,其并不关系数据如何进行传输,仅通过向源端输入数据,从目的端获取数据即可。除此之外,流可以根据处理数据的单位划分为字节流(仅读取字节数组)和字符流(仅读取字符数组)两种,而根据其实现功能则可以划分为输入流(读取文件)和输出流(写入文件)。
流:数据在数据源(文件)和程序(内存)之间经历的路径。
字节流:处理单元为1字节(byte)。
字符流:处理单元为2字节的Unicode字符。
输入流:数据从数据源(文件)到程序(内存)的路径。
输出流:数据从程序(内存)到数据源(文件)的路径。
| 抽象基类 | 字节流 | 字符流 |
| 输入流 | InputStream | Reader |
| 输出流 | OutputStream | Writer |
备注:在同一传输过程中,输入流与输出流的处理数据的单位具备一致性,即字节输入流,字节输出流;字符输入流,字符输出流。除此之外,1Unicode = 2Byte = 16bit。
三、文件的相关操作
1、创建文件对象的相关构造器及其相应方法
根据路径构建一个File对象:new File(String pathname)
根据父目录文件进行子路径构建:new File(File parent,String child)
根据父目录进行子路径构建:new File(String parent,Stringchild)
import org.testng.annotations.Test; import java.io.File; import java.io.IOException; public class testCreate { public static void main(String[] args){ } //方式一 @Test public void create1(){ String filePath = "D:\\file_1.docx"; File file = new File(filePath); try{ file.createNewFile(); System.out.println("创建成功"); }catch(IOException e){ e.printStackTrace(); } } //方式二 @Test public void create2(){ File parentFile = new File("D:\\"); String fileName = "file_2.docx"; File file = new File(parentFile,fileName); try{ file.createNewFile(); System.out.println("创建成功"); }catch(IOException e){ e.printStackTrace(); } } //方式三 @Test public void create3(){ String parentPath = "D:\\"; String filePath = "file_3.docx"; File file = new File(parentPath,filePath); try{ file.createNewFile(); System.out.println("创建成功"); }catch(IOException e){ e.printStackTrace(); } } }
备注:三种创建文件的方法最好选择单独运行以便于能够成功创建相关文件。
2、文件相关信息获取
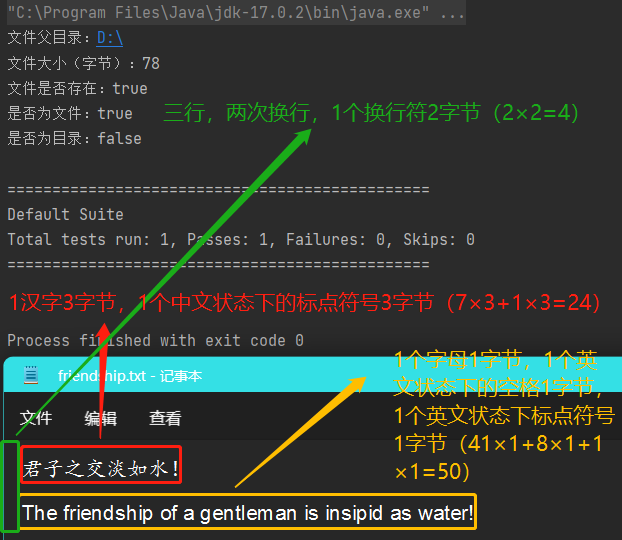
UTF-8编码方式:1个英文字母占1个字节(1Byte = 8bit),1个汉字占3个字节(3Byte = 3×8bit),1个英文状态下的标点符号占1个字节,1个中文状态下的标点符号占3个字节,一个换行符占2个字节。
import org.testng.annotations.Test; import java.io.File; public class Information { public static void main(String[] args){ } //获取文件信息 @Test public void Info(){ //创建文件对象 File file = new File("D:\\friendship.txt"); //调用方法得出相应信息 System.out.println("文件父目录:" + file.getParent()); System.out.println("文件大小(字节):" + file.length()); System.out.println("文件是否存在:" + file.exists()); System.out.println("是否为文件:" + file.isFile()); System.out.println("是否为目录:" + file.isDirectory()); } }
运行实例结果如下所示:
3、文件的目录操作
mkdir:创建一级目录。
mkdirs:创建多级目录。
delete:删除空白目录或文件。
import org.testng.annotations.Test; import java.io.File; public class directory { public static void main(String[] args){ } //删除文件 @Test public void fileDelete(){ String filePath = "D:\\file_1.docx"; File file = new File(filePath); if(file.exists()){ if(file.delete()){ System.out.println(filePath + "删除成功"); } else{ System.out.println(filePath + "删除失败"); } } else{ System.out.println("文件不存在"); } } //删除目录 @Test public void fileDeleted(){ String filePath = "D:\\file_1.docx"; File file = new File(filePath); if(file.exists()){ if(file.delete()){ System.out.println(filePath + "删除成功"); } else{ System.out.println(filePath + "删除失败"); } } else{ System.out.println("文件不存在"); } } //判断目录是否存在,不存在时创建目录 @Test public void fileDeleteds(){ String dirPath = "D:\\test\\dir.txt"; File file = new File(dirPath); if(file.exists()){ System.out.println(dirPath + "该目录已存在"); } else{ if(file.mkdirs()){ System.out.println("创建成功"); } else{ System.out.println("创建失败"); } } } }
4、Scanner与Println
①基本键盘输入
import java.util.Scanner; public class scannertest { public static void main(String[] args){ //创建Scanner对象,接受从控制台输入 Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); //接收String类型 String str = input.next(); //输出结果 System.out.println(str); System.out.println("Hello " + str); } }
输出结果如下所示:

②常见键盘输入类型
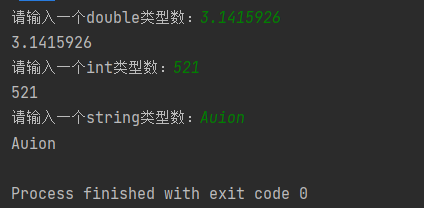
import java.util.Scanner; public class printlntest { public static void main(String[] args){ Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); //double类型数据 System.out.print("请输入一个double类型数:"); double d = input.nextDouble(); System.out.println(d); //int类型数据 System.out.print("请输入一个int类型数:"); int i = input.nextInt(); System.out.println(i); //字符串类型数据 System.out.print("请输入一个string类型数:"); String s = input.next(); System.out.println(s); } }
输出结果如下所示:
5、InputStream
文件输入流:FileInputStream
缓冲字节输入流:BufferedStream
对象字节输入流:ObjectedStream
import org.testng.annotations.Test; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.IOException; public class InputStream { public static void main(String[] args){ } @Test public void fileIn1(){ String filePath = "D:\\friendship.txt"; int readData; FileInputStream fileInputStream = null; try{ //创建FileInputStream对象,用于读取文件 fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(filePath); while ((readData = fileInputStream.read()) != -1){ System.out.println((char)readData); } }catch (IOException e){ e.printStackTrace(); }finally { //关闭文件流 try { fileInputStream.close(); } catch (IOException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } } @Test public void fileIn2(){ String filePath = "D:\\friendship.txt"; int readData; int readlength = 0; //字节数组,数字“8”表示输出时以8个字符为一行进行输出,该数字可根据自身输出需求进行修改 byte[] buf = new byte[8]; FileInputStream fileInputStream = null; try{ //创建FileInputStream对象,用于读取文件 fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(filePath); while ((readlength = fileInputStream.read(buf)) != -1){ System.out.println(new String(buf,0,readlength)); } }catch (IOException e){ e.printStackTrace(); }finally { //关闭文件流 try { fileInputStream.close(); } catch (IOException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } }
输出结果如下所示:
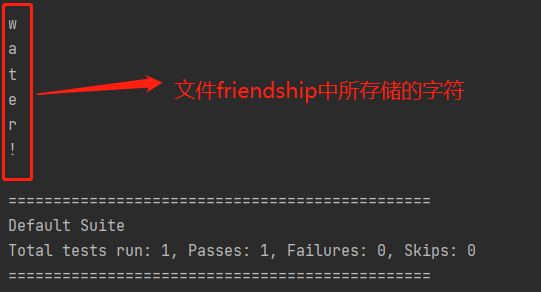
通过fileIn1()函数处理后进行输出时,会以单个字符的形式进行输出,即如下所示(文件friendship中所存储字符为water!):
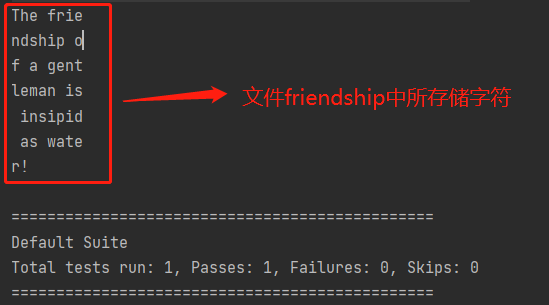
通过fileIn2()函数处理后进行输出时,会以8个字符的形式进行输出,即如下所示(文件friendship中所存储字符为The friendship of a gentleman is insipid as water!):
6、OutputStream
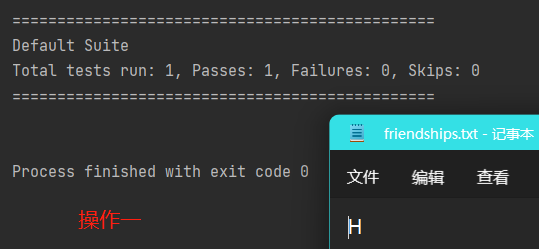
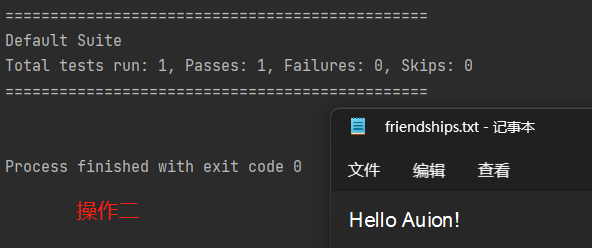
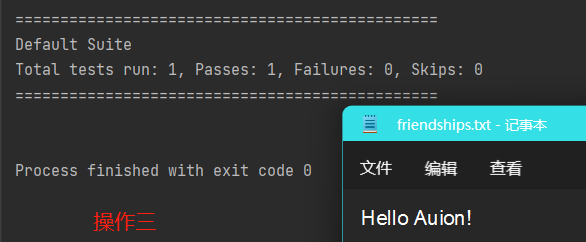
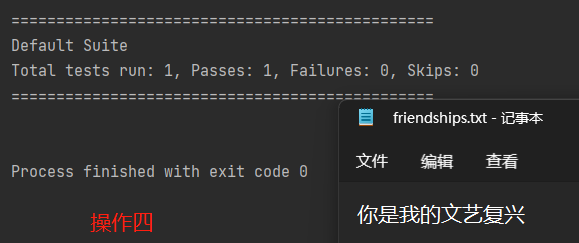
使用“FIleOutputStream”在文件夹中写入“××”,若文件不存在,则会直接创建相关文件。
import org.testng.annotations.Test; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; public class outputStream { public static void main(String[] args) { } //使用FileOutputStream将数据写到文件中 //如果文件不存在,则创建文件 @Test public void writeFile(){ String filePath = "D:\\friendships.txt"; //创建对象 FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = null; try { fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(filePath); // 加上true后则可以实现多次运行的文字叠加,而非覆盖。 // 下列四种操作多次实现对文件所进行的操作属于覆盖操作,而非叠加操作,在FilePath后加上“,true”则可以实现叠加。 // //1、写入一个字节 // fileOutputStream.write('H'); // //2、写入一个字符串 // String str = "Hello Auion!"; // str.getBytes(); //将字符串转换成字节数组 // fileOutputStream.write(str.getBytes()); // //3、写入字符串 // String str = "Hello Auion!"; // fileOutputStream.write(str.getBytes(),0,str.length()); //0表示从0位开始写入;str.length()可替换成数字,表示输入文件的字符数量,若此时写入字符为中文则只能写入三个汉字。 //4、写入中文状态下的字符串 String str = "你是我的"; String ptr = "文艺复兴"; fileOutputStream.write(str.getBytes(),0,12); //若写入字符为中文状态,则写入字符长度最大只可以设置为12(4个汉字),超出则会导致写入字符产生乱码现象。 fileOutputStream.write(ptr.getBytes(),0,12); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { //关闭流 try { fileOutputStream.close(); } catch (IOException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } } }
四种不同操作下的输出结果依次如下所示:
7、 文件复制
判断文件是否存在,存在则进行复制操作,反之则直接创建文件。
import java.io.File; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileOutputStream; public class copyPic { //file读和写实现复制文件 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { //创建file对象 File f=new File("D:\\sheep.jpg"); //判断文件是否存在 if(f.exists()){ System.out.println("sheep.jpg存在,可以复制"); } else{ f.createNewFile(); System.out.println("sheep.jpg不存在,新建成功,可以复制"); } //创建FileInputStream对象 FileInputStream inp=new FileInputStream(f); //创建FileOutputStream对象 //判断demo目录是否存在 File f1=new File("D:\\.metadata"); if(f1.isDirectory()){ FileOutputStream out=new FileOutputStream("D:\\.metadata\\"+f.getName()); byte bytes[]=new byte[1024]; int temp=0; //边读边写 while((temp=inp.read(bytes))!=-1){ //读 out.write(bytes,0,temp); //写 } //结束 inp.close(); out.close(); System.out.println("文件拷贝成功!"); } else{ //新建demo目录 f1.mkdir(); System.out.println("demo目录不存在,已经新建成功,继续复制"); FileOutputStream out=new FileOutputStream("D:\\.metadata\\"+f.getName()); byte bytes[]=new byte[1024]; int temp=0; //边读边写 while((temp=inp.read(bytes))!=-1){ //读 out.write(bytes,0,temp); //写 } //结束 inp.close(); out.close(); System.out.println("文件拷贝成功!"); } } }
运行结果如下所示:



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号