P4587 [FJOI2016] 神秘数 题解
题目链接:P4587 [FJOI2016] 神秘数 题解
先不考虑下标限制,考虑以下性质:
按 \(a_i\) 大小排序,考虑如果当前能得到的集合为 \([1,x]\),并且考虑可以组成它的集合为:
\(S_i=\{a_1,a_2,a_3,...a_i\}\),记 \(sum_i=\sum\limits_{i=1}^{n} a_i\),那么考虑对于在 \(S_i\) 中加入新的几个数 \(\{a_{i+1},a_{i+2},a_{i+3},a_{i+4}...\}\),这些数的和记作 \(NewSum\),来考虑几个性质。按序排序是为了先考虑小数是否可以被凑出来,再考虑大数。
对于新加入的集合的数应该有以下性质:
-
不能包含 \(S_i\),即 \(i<j\) 或者说 \(a_i<a_j\),\(a_j\) 为新加入的数,不能选取原来凑成 \([1,x]\) 的集合 \(S_i\)。
-
保证新加入的数 \(a_j \le x\)。
来说说性质二是怎么得到的,也是难点,对于 \([1,x]\),我们加入 \(a_j\),我们考虑是否能得到 \(x+1\),光由原来的集合 \(S_i\) 肯定无法得到 \(x+1\),那么考虑 \(a_j\) 加入以后,我们所需要 \(S_i\) 集合去凑出 \(x+1-a_j\),那么由于原来的可以凑的值域为 \([1,x]\),所以显然这个数 \(1 \le x+1-a_j \le x\) 才行,那么很显然可以得到 \(a_j\le x\),后者不等式在本题条件下则是恒成立。
而可以凑出 \(x+1\) 以后,那么考虑 \(x+2,x+3,....x+a_j\),我们则只需要 \(S_i\) 分别去凑出,\(x+2-a_j\),\(x+3-a_j,\) 一直到 \(...x+a_j-a_j=x\),容易看出来对于 \([x+1,x+a_j]\) 的数的构造我们只需要原来的 \(S_i\) 构造出 \(x+t-a_j\ (1 \le t\le a_j)\) 即可,这玩意显然是关于 \(t\) 的单增序列,而同上述证明,只要保证首项 \(\ge 1\),其他项自然满足了,而右不等式对于每一项都是成立的。综上所示,这个 \(x+t-a_j \in [1,x]\),可以由 \(S_i\) 构造出来。这样一来,我们的 \([1,x]\) 就能拓展到 \([1,x+a_j]\)。
现在考虑加入的不是一个数,而是满足上述两条性质的所有 \(a_j\),显然值域将能扩展为 \([1,x+newSum]\)。具体的 \([1,x]->[1,x+a_j]->[1,x+a_{j}+a_{j+1}]...\),证明:对于 \(a_{j+1}\le x < x+a_j\),其他的累加值域同理可证。
考虑两条性质拿出来显然是值域限制,再加题目一个下标限制:
-
\(l\le i \le r\)。
-
\(a_{k}=pre \le a_j \le x=currAns\)。
在上 \(ds\) 之前考虑一下,如果暴力的从值域 \(0\) 到最终的答案的 \(x\) 会做多少次操作。注意到每次操作,你的下界会变回上次的 \(x\),上界则为当前的 \(x\),每次都是 \(x\) 的一个置换,值域下界为 \(1\),上界为 \(sum_{n}\)。考虑这样的操作要几次会让 \(1\rightarrow sum_n\),每次操作变化为 \(val\),那么显然是 \(1+1+2+3+5+8...\),像斐波那契数列一样跳:
描述表达
当 \(x=1\) 时,增加最少为当前 \(a_j=1\),这样 \(x=1+1\),\(x=2\) 时,至少增加上次的上界为 \(1\),则 \(x=2+1\),然后再 \(x=3+2\),\(x=5+3\),\(x=8+5...\)。
数学表达
记 \(x\) 在第 \(i\) 时刻的值为 \(a_i\)。根据上述说的其实本质就为上次 \(x\) 作为下界,当前 \(x\) 为上界。那么最少增加下界。即有 \(i\) 时刻的下界为上一次的值,即为 \(a_{i-1}\)。考虑第 \(i+2\) 时刻,\(a_{i+2}=a_{i+1}+a_i\),\(a_i\) 为上次的下界,上次的下界为上上次的值。\(a_{i+1}\) 为上次的值,由上次的值加上上次的下界即为当前最坏的下界。
斐波那契数列
考虑第几项 \(x_i=INF\)?
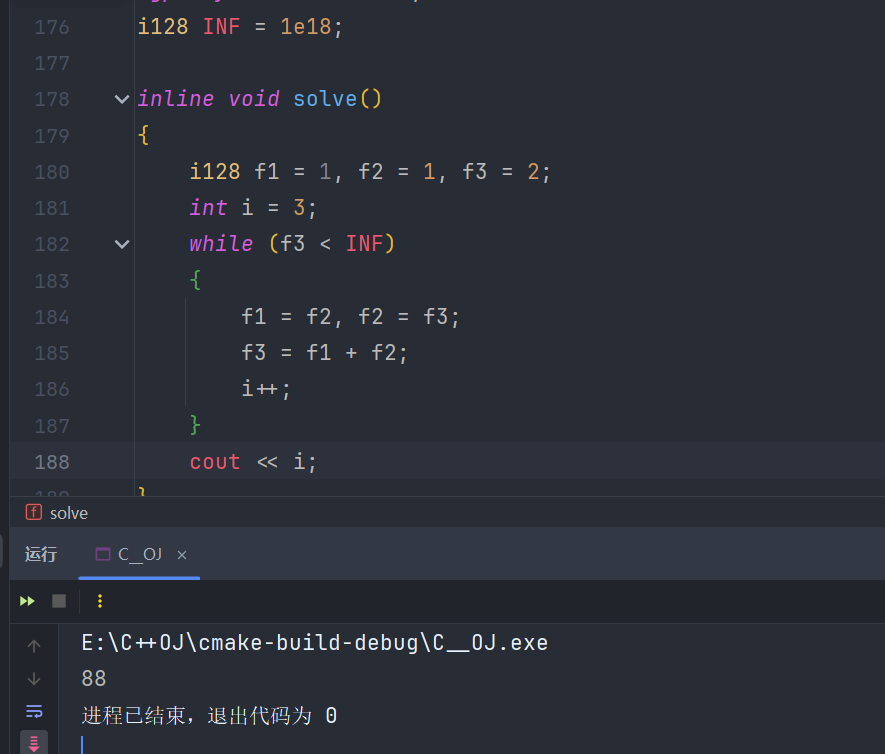
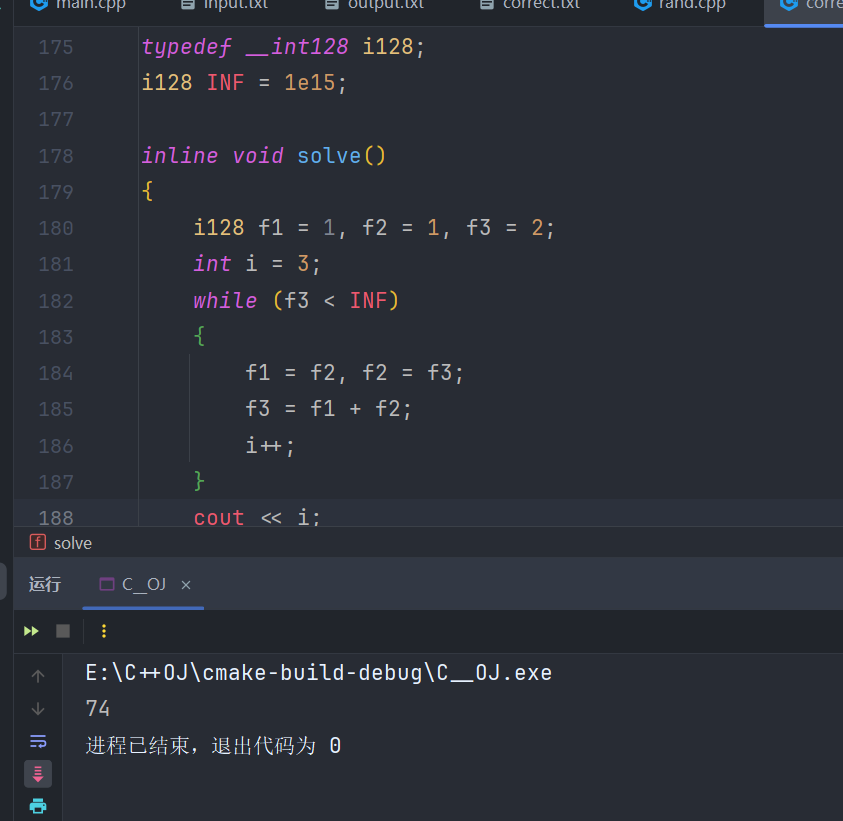
\(\log{1e15}=49\),所以这玩意其实和 \(\log\) 也差不多。因为它的解析解并不太好求出这个 \(i\) 的不等式范围。
本题显然最坏上界为 \(n\sum a_i\le 1e15\)。
所以这玩意暴力做也就 \(\log{\sum a_i}\) 次,考虑查询复杂度。\([l,r]\) 上 \([值域下界,值域上界]\) 上的数之和 \(newSum\)。这玩意显然树套树带双 \(\log\) 不可行,可以考虑主席树优化这类权值类信息查找,这样一来就是双 \(log\) 了。
细节
有个细节,当 \(a_j=x+1\) 时,虽然不满足 \(\le a_j\),但可以靠自身凑出 \(x+1\),而凑出 \(x+1\) 以后,剩余的 \(a_j \le x+1\) 了,也能凑了,所以真正的上界可以拓展到神秘数,即 \(x+1\)。
注意上一次的下界是属于不可取的:\(a_j>a_i\),所以查找应该为 \(\ge pre+1\)。当前神秘数则是可取的上界,所以 \([pre+1,x]\) 才是正确的,查找如果 \(sum=0\) 显然也可以提前结束了,因为 \(x\) 并不会再发生任何变化了。
参照代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
// #pragma GCC optimize(2)
// #pragma GCC optimize("Ofast,no-stack-protector,unroll-loops,fast-math")
// #pragma GCC target("sse,sse2,sse3,ssse3,sse4.1,sse4.2,avx,avx2,popcnt,tune=native")
#define isPbdsFile
#ifdef isPbdsFile
#include <bits/extc++.h>
#else
#include <ext/pb_ds/priority_queue.hpp>
#include <ext/pb_ds/hash_policy.hpp>
#include <ext/pb_ds/tree_policy.hpp>
#include <ext/pb_ds/trie_policy.hpp>
#include <ext/pb_ds/tag_and_trait.hpp>
#include <ext/pb_ds/hash_policy.hpp>
#include <ext/pb_ds/list_update_policy.hpp>
#include <ext/pb_ds/assoc_container.hpp>
#include <ext/pb_ds/exception.hpp>
#include <ext/rope>
#endif
using namespace std;
using namespace __gnu_cxx;
using namespace __gnu_pbds;
typedef long long ll;
typedef long double ld;
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
typedef pair<ll, ll> pll;
typedef tuple<int, int, int> tii;
typedef tuple<ll, ll, ll> tll;
typedef unsigned int ui;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
#define hash1 unordered_map
#define hash2 gp_hash_table
#define hash3 cc_hash_table
#define stdHeap std::priority_queue
#define pbdsHeap __gnu_pbds::priority_queue
#define sortArr(a, n) sort(a+1,a+n+1)
#define all(v) v.begin(),v.end()
#define yes cout<<"YES"
#define no cout<<"NO"
#define Spider ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(nullptr);cout.tie(nullptr);
#define MyFile freopen("..\\input.txt", "r", stdin),freopen("..\\output.txt", "w", stdout);
#define forn(i, a, b) for(int i = a; i <= b; i++)
#define forv(i, a, b) for(int i=a;i>=b;i--)
#define ls(x) (x<<1)
#define rs(x) (x<<1|1)
#define endl '\n'
//用于Miller-Rabin
[[maybe_unused]] static int Prime_Number[13] = {0, 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19, 23, 29, 31, 37};
template <typename T>
int disc(T* a, int n)
{
return unique(a + 1, a + n + 1) - (a + 1);
}
template <typename T>
T lowBit(T x)
{
return x & -x;
}
template <typename T>
T Rand(T l, T r)
{
static mt19937 Rand(time(nullptr));
uniform_int_distribution<T> dis(l, r);
return dis(Rand);
}
template <typename T1, typename T2>
T1 modt(T1 a, T2 b)
{
return (a % b + b) % b;
}
template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3>
T1 qPow(T1 a, T2 b, T3 c)
{
a %= c;
T1 ans = 1;
for (; b; b >>= 1, (a *= a) %= c) if (b & 1) (ans *= a) %= c;
return modt(ans, c);
}
template <typename T>
void read(T& x)
{
x = 0;
T sign = 1;
char ch = getchar();
while (!isdigit(ch))
{
if (ch == '-') sign = -1;
ch = getchar();
}
while (isdigit(ch))
{
x = (x << 3) + (x << 1) + (ch ^ 48);
ch = getchar();
}
x *= sign;
}
template <typename T, typename... U>
void read(T& x, U&... y)
{
read(x);
read(y...);
}
template <typename T>
void write(T x)
{
if (typeid(x) == typeid(char)) return;
if (x < 0) x = -x, putchar('-');
if (x > 9) write(x / 10);
putchar(x % 10 ^ 48);
}
template <typename C, typename T, typename... U>
void write(C c, T x, U... y)
{
write(x), putchar(c);
write(c, y...);
}
template <typename T11, typename T22, typename T33>
struct T3
{
T11 one;
T22 tow;
T33 three;
bool operator<(const T3 other) const
{
if (one == other.one)
{
if (tow == other.tow) return three < other.three;
return tow < other.tow;
}
return one < other.one;
}
T3()
{
one = tow = three = 0;
}
T3(T11 one, T22 tow, T33 three) : one(one), tow(tow), three(three)
{
}
};
template <typename T1, typename T2>
void uMax(T1& x, T2 y)
{
if (x < y) x = y;
}
template <typename T1, typename T2>
void uMin(T1& x, T2 y)
{
if (x > y) x = y;
}
constexpr ll INF = 1e15;
constexpr int N = 1e5 + 10;
int cnt;
struct Node
{
ll sum;
int left, right;
} node[N << 7];
#define left(x) node[x].left
#define right(x) node[x].right
#define sum(x) node[x].sum
inline void add(const int pre, int& curr, const ll pos, const ll l = 1, const ll r = INF)
{
node[curr = ++cnt] = node[pre];
sum(curr) += pos;
const ll mid = l + r >> 1;
if (l == r) return;
if (pos <= mid) add(left(pre),left(curr), pos, l, mid);
else add(right(pre),right(curr), pos, mid + 1, r);
}
inline ll query(const int L, const int R, const ll l, const ll r, const ll s = 1, const ll e = INF)
{
const ll sum = sum(R) - sum(L);
if (!sum) return 0;
if (l <= s and e <= r) return sum;
const ll mid = s + e >> 1;
ll ans = 0;
if (l <= mid) ans += query(left(L),left(R), l, r, s, mid);
if (r > mid) ans += query(right(L),right(R), l, r, mid + 1, e);
return ans;
}
int root[N];
int n, q, x;
inline void solve()
{
cin >> n;
forn(i, 1, n) cin >> x, add(root[i - 1], root[i], x);
cin >> q;
while (q--)
{
int l, r;
cin >> l >> r;
ll ans = 1, sum; //当前神秘数,当前和
ll pre = 0; //上一次的下界,也即上一次的神秘数
do
{
sum = query(root[l - 1], root[r], pre + 1, ans); //符合条件的和
pre = ans;
ans += sum;
}
while (sum != 0);
cout << ans << endl;
}
}
signed int main()
{
// MyFile
Spider
//------------------------------------------------------
// clock_t start = clock();
int test = 1;
// read(test);
// cin >> test;
forn(i, 1, test) solve();
// while (cin >> n, n)solve();
// while (cin >> test)solve();
// clock_t end = clock();
// cerr << "time = " << double(end - start) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC << "s" << endl;
}
常数空间优化,由于 \(\sum a_i \le 1e9\),而查找 \(INF=1e15\),所以我们可以对上界取 \(min\),因为查找的 \(a_i\le \max{a}\)。下界则可以当 \(> 值域上界\) 时停止。
参照代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
// #pragma GCC optimize(2)
// #pragma GCC optimize("Ofast,no-stack-protector,unroll-loops,fast-math")
// #pragma GCC target("sse,sse2,sse3,ssse3,sse4.1,sse4.2,avx,avx2,popcnt,tune=native")
#define isPbdsFile
#ifdef isPbdsFile
#include <bits/extc++.h>
#else
#include <ext/pb_ds/priority_queue.hpp>
#include <ext/pb_ds/hash_policy.hpp>
#include <ext/pb_ds/tree_policy.hpp>
#include <ext/pb_ds/trie_policy.hpp>
#include <ext/pb_ds/tag_and_trait.hpp>
#include <ext/pb_ds/hash_policy.hpp>
#include <ext/pb_ds/list_update_policy.hpp>
#include <ext/pb_ds/assoc_container.hpp>
#include <ext/pb_ds/exception.hpp>
#include <ext/rope>
#endif
using namespace std;
using namespace __gnu_cxx;
using namespace __gnu_pbds;
typedef long long ll;
typedef long double ld;
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
typedef pair<ll, ll> pll;
typedef tuple<int, int, int> tii;
typedef tuple<ll, ll, ll> tll;
typedef unsigned int ui;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
#define hash1 unordered_map
#define hash2 gp_hash_table
#define hash3 cc_hash_table
#define stdHeap std::priority_queue
#define pbdsHeap __gnu_pbds::priority_queue
#define sortArr(a, n) sort(a+1,a+n+1)
#define all(v) v.begin(),v.end()
#define yes cout<<"YES"
#define no cout<<"NO"
#define Spider ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(nullptr);cout.tie(nullptr);
#define MyFile freopen("..\\input.txt", "r", stdin),freopen("..\\output.txt", "w", stdout);
#define forn(i, a, b) for(int i = a; i <= b; i++)
#define forv(i, a, b) for(int i=a;i>=b;i--)
#define ls(x) (x<<1)
#define rs(x) (x<<1|1)
#define endl '\n'
//用于Miller-Rabin
[[maybe_unused]] static int Prime_Number[13] = {0, 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19, 23, 29, 31, 37};
template <typename T>
int disc(T* a, int n)
{
return unique(a + 1, a + n + 1) - (a + 1);
}
template <typename T>
T lowBit(T x)
{
return x & -x;
}
template <typename T>
T Rand(T l, T r)
{
static mt19937 Rand(time(nullptr));
uniform_int_distribution<T> dis(l, r);
return dis(Rand);
}
template <typename T1, typename T2>
T1 modt(T1 a, T2 b)
{
return (a % b + b) % b;
}
template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3>
T1 qPow(T1 a, T2 b, T3 c)
{
a %= c;
T1 ans = 1;
for (; b; b >>= 1, (a *= a) %= c) if (b & 1) (ans *= a) %= c;
return modt(ans, c);
}
template <typename T>
void read(T& x)
{
x = 0;
T sign = 1;
char ch = getchar();
while (!isdigit(ch))
{
if (ch == '-') sign = -1;
ch = getchar();
}
while (isdigit(ch))
{
x = (x << 3) + (x << 1) + (ch ^ 48);
ch = getchar();
}
x *= sign;
}
template <typename T, typename... U>
void read(T& x, U&... y)
{
read(x);
read(y...);
}
template <typename T>
void write(T x)
{
if (typeid(x) == typeid(char)) return;
if (x < 0) x = -x, putchar('-');
if (x > 9) write(x / 10);
putchar(x % 10 ^ 48);
}
template <typename C, typename T, typename... U>
void write(C c, T x, U... y)
{
write(x), putchar(c);
write(c, y...);
}
template <typename T11, typename T22, typename T33>
struct T3
{
T11 one;
T22 tow;
T33 three;
bool operator<(const T3 other) const
{
if (one == other.one)
{
if (tow == other.tow) return three < other.three;
return tow < other.tow;
}
return one < other.one;
}
T3()
{
one = tow = three = 0;
}
T3(T11 one, T22 tow, T33 three) : one(one), tow(tow), three(three)
{
}
};
template <typename T1, typename T2>
void uMax(T1& x, T2 y)
{
if (x < y) x = y;
}
template <typename T1, typename T2>
void uMin(T1& x, T2 y)
{
if (x > y) x = y;
}
constexpr int N = 1e5 + 10;
ll mx;
int cnt;
struct Node
{
ll sum;
int left, right;
} node[N << 6];
#define left(x) node[x].left
#define right(x) node[x].right
#define sum(x) node[x].sum
inline void add(const int pre, int& curr, const int pos, const int l = 1, const int r = mx)
{
node[curr = ++cnt] = node[pre];
sum(curr) += pos;
const int mid = l + r >> 1;
if (l == r) return;
if (pos <= mid) add(left(pre),left(curr), pos, l, mid);
else add(right(pre),right(curr), pos, mid + 1, r);
}
inline ll query(const int L, const int R, const int l, const int r, const int s = 1, const int e = mx)
{
const ll sum = sum(R) - sum(L);
if (!sum) return 0;
if (l <= s and e <= r) return sum;
const ll mid = s + e >> 1;
ll ans = 0;
if (l <= mid) ans += query(left(L),left(R), l, r, s, mid);
if (r > mid) ans += query(right(L),right(R), l, r, mid + 1, e);
return ans;
}
int root[N], a[N];
int n, q, x;
inline void solve()
{
cin >> n;
forn(i, 1, n) cin >> a[i], uMax(mx, a[i]);
forn(i, 1, n) add(root[i - 1], root[i], a[i]);
cin >> q;
while (q--)
{
int l, r;
cin >> l >> r;
ll ans = 1, sum; //当前神秘数,当前和
ll pre = 0; //上一次的下界,也即上一次的神秘数
do
{
if (pre + 1 > mx) break;
sum = query(root[l - 1], root[r], pre + 1, min(ans, mx)); //符合条件的和
pre = ans;
ans += sum;
}
while (sum != 0);
cout << ans << endl;
}
}
signed int main()
{
// MyFile
Spider
//------------------------------------------------------
// clock_t start = clock();
int test = 1;
// read(test);
// cin >> test;
forn(i, 1, test) solve();
// while (cin >> n, n)solve();
// while (cin >> test)solve();
// clock_t end = clock();
// cerr << "time = " << double(end - start) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC << "s" << endl;
}



