CF526F Pudding Monsters 题解
1.CF1916E Happy Life in University 题解2.CF763E Timofey and our friends animals题解3.CF1270G Subset with Zero Sum4.CF1045G AI robots题解5.CF940F Machine Learning题解6.CF678F Lena and Queries题解7.CF1921F Sum of Progression 题解
8.CF526F Pudding Monsters 题解
9.CF455D Serega and Fun 题解10.CF351D Jeff and Removing Periods 题解11.CF452F Permutation 与 P2757 [国家集训队] 等差子序列 题解12.CF911G Mass Change Queries 题解13.CF145E Lucky Queries 题解14.CF1515F Phoenix and Earthquake 题解15.CF765F Souvenirs 题解16.CF1764H Doremy's Paint 2 题解17.CF1000F One Occurrence题解18.CF813E Army Creation 题解19.CF1706E Qpwoeirut and Vertices 题解20.CF620E New Year Tree 题解21.CF1454F Array Partition 题解22.CF1771F Hossam and Range Minimum Query 题解23.CF1931F Chat Screenshots 另一种题解24.CF896C Willem, Chtholly and Seniorious 题解25.CF55D Beautiful numbers 题解26.CF916E Jamie and Tree 题解27.CF696B Puzzles 题解28.CF383C Propagating tree 题解29.CF1436E Complicated Computations 题解30.CF817F MEX Queries 题解31.CF1638E Colorful Operations 题解32.CF1618G Trader Problem 题解33.CF794F Leha and security system 题解34.CF371E Subway Innovation 题解35.CF1200E Compress Words 题解36.CF1884D Counting Rhyme 题解37.CF1982F Sorting Problem Again 题解题目链接:CF 或者 洛谷
析合树真是连续段问题的降智神器
先看下题目的一些特殊性,每行每列恰好有一个棋子。考虑特殊性,
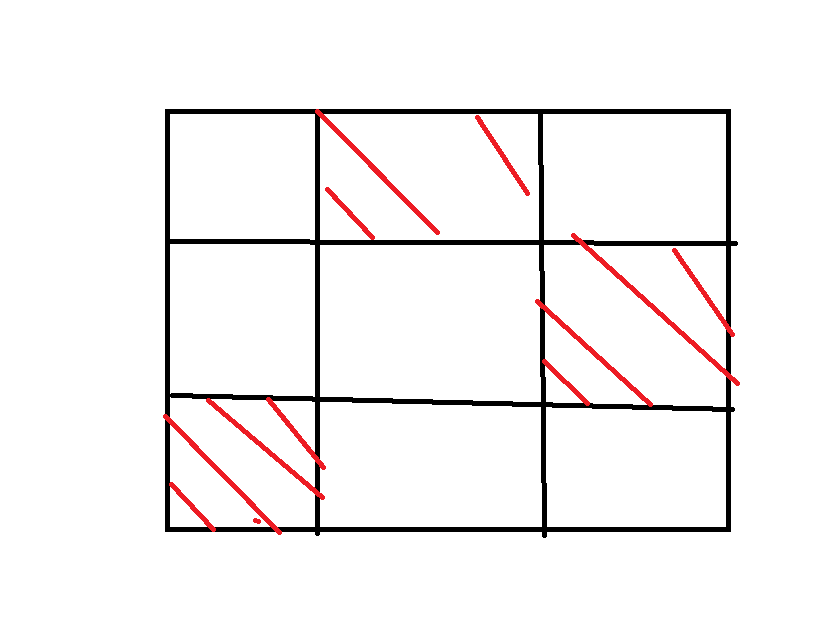
容易知道一个事实,如果你的行是连续的,并且列是连续的,那么一定能够组成答案,但如果只满足其中一个,就不一定了:
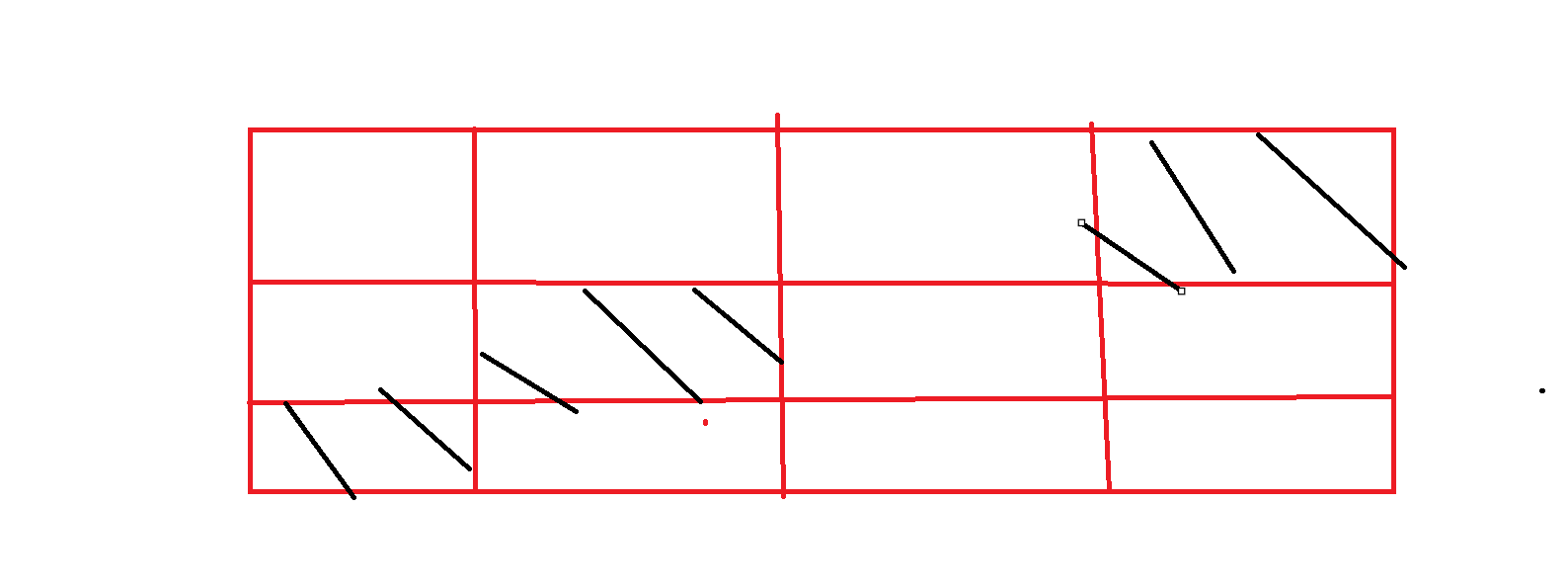
比如如图所示,这三个黑色格子是属于行连续的,但列并不连续,而它们并不能组成答案。同理,列连续但行不连续也无法组成答案。
我们得到了本题的一个贡献的充要条件,行需要连续,列也需要连续,但这个二维问题比较难以解决,我们考虑让某一维先连续,即比如以行为关键字进行排序,这样一来任意一段都是行连续了,这个时候在来考虑列连续性即可。当然了也可以这样去写:
接下来就转变为了一个数组上,有多少个连续段区间的问题,线段树确实处理起来比较需要思维难度,但析合树解决起来就不需要太多思考。
-
如果某个点是析点,显然贡献为
-
如果某个点是合点,显然贡献为
那么只需要建析合树,然后遍历一遍树节点就行了。
参照代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h> // #pragma GCC optimize("Ofast,unroll-loops") // #pragma GCC optimize(2) // #define isPbdsFile #ifdef isPbdsFile #include <bits/extc++.h> #else #include <ext/pb_ds/priority_queue.hpp> #include <ext/pb_ds/hash_policy.hpp> #include <ext/pb_ds/tree_policy.hpp> #include <ext/pb_ds/trie_policy.hpp> #include <ext/pb_ds/tag_and_trait.hpp> #include <ext/pb_ds/hash_policy.hpp> #include <ext/pb_ds/list_update_policy.hpp> #include <ext/pb_ds/assoc_container.hpp> #include <ext/pb_ds/exception.hpp> #include <ext/rope> #endif using namespace std; using namespace __gnu_cxx; using namespace __gnu_pbds; typedef long long ll; typedef long double ld; typedef pair<int, int> pii; typedef pair<ll, ll> pll; typedef tuple<int, int, int> tii; typedef tuple<ll, ll, ll> tll; typedef unsigned int ui; typedef unsigned long long ull; typedef __int128 i128; #define hash1 unordered_map #define hash2 gp_hash_table #define hash3 cc_hash_table #define stdHeap std::priority_queue #define pbdsHeap __gnu_pbds::priority_queue #define sortArr(a, n) sort(a+1,a+n+1) #define all(v) v.begin(),v.end() #define yes cout<<"YES" #define no cout<<"NO" #define Spider ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(nullptr);cout.tie(nullptr); #define MyFile freopen("..\\input.txt", "r", stdin),freopen("..\\output.txt", "w", stdout); #define forn(i, a, b) for(int i = a; i <= b; i++) #define forv(i, a, b) for(int i=a;i>=b;i--) #define ls(x) (x<<1) #define rs(x) (x<<1|1) #define endl '\n' //用于Miller-Rabin [[maybe_unused]] static int Prime_Number[13] = {0, 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19, 23, 29, 31, 37}; template <typename T> int disc(T* a, int n) { return unique(a + 1, a + n + 1) - (a + 1); } template <typename T> T lowBit(T x) { return x & -x; } template <typename T> T Rand(T l, T r) { static mt19937 Rand(time(nullptr)); uniform_int_distribution<T> dis(l, r); return dis(Rand); } template <typename T1, typename T2> T1 modt(T1 a, T2 b) { return (a % b + b) % b; } template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3> T1 qPow(T1 a, T2 b, T3 c) { a %= c; T1 ans = 1; for (; b; b >>= 1, (a *= a) %= c)if (b & 1)(ans *= a) %= c; return modt(ans, c); } template <typename T> void read(T& x) { x = 0; T sign = 1; char ch = getchar(); while (!isdigit(ch)) { if (ch == '-')sign = -1; ch = getchar(); } while (isdigit(ch)) { x = (x << 3) + (x << 1) + (ch ^ 48); ch = getchar(); } x *= sign; } template <typename T, typename... U> void read(T& x, U&... y) { read(x); read(y...); } template <typename T> void write(T x) { if (typeid(x) == typeid(char))return; if (x < 0)x = -x, putchar('-'); if (x > 9)write(x / 10); putchar(x % 10 ^ 48); } template <typename C, typename T, typename... U> void write(C c, T x, U... y) { write(x), putchar(c); write(c, y...); } template <typename T11, typename T22, typename T33> struct T3 { T11 one; T22 tow; T33 three; bool operator<(const T3 other) const { if (one == other.one) { if (tow == other.tow)return three < other.three; return tow < other.tow; } return one < other.one; } T3() { one = tow = three = 0; } T3(T11 one, T22 tow, T33 three) : one(one), tow(tow), three(three) { } }; template <typename T1, typename T2> void uMax(T1& x, T2 y) { if (x < y)x = y; } template <typename T1, typename T2> void uMin(T1& x, T2 y) { if (x > y)x = y; } constexpr int N = 6e5 + 10; constexpr int T = 25; int idx[N]; int n; struct { int MAX[N][T], MIN[N][T]; int LOG2[N]; void build() { forn(i, 2, n)LOG2[i] = LOG2[i >> 1] + 1; const int k = LOG2[n] + 1; forn(i, 1, n)MAX[i][0] = MIN[i][0] = idx[i]; forn(j, 1, k) { forn(i, 1, n-(1<<j)+1) { MAX[i][j] = max(MAX[i][j - 1], MAX[i + (1 << j - 1)][j - 1]); MIN[i][j] = min(MIN[i][j - 1], MIN[i + (1 << j - 1)][j - 1]); } } } int query(const int l, const int r) const { const int k = LOG2[r - l + 1]; return max(MAX[l][k], MAX[r - (1 << k) + 1][k]) - min(MIN[l][k], MIN[r - (1 << k) + 1][k]); } } ST; struct { struct Node { int Min, Add; } node[N << 2]; #define Min(x) node[x].Min #define Add(x) node[x].Add void push_up(const int curr) { Min(curr) = min(Min(ls(curr)),Min(rs(curr))); } void push_down(const int curr) { if (Add(curr)) { Min(ls(curr)) += Add(curr), Min(rs(curr)) += Add(curr); Add(ls(curr)) += Add(curr), Add(rs(curr)) += Add(curr); Add(curr) = 0; } } void add(const int curr, const int l, const int r, const int val, const int s = 1, const int e = n) { if (l <= s and e <= r) { Min(curr) += val, Add(curr) += val; return; } const int mid = s + e >> 1; push_down(curr); if (l <= mid)add(ls(curr), l, r, val, s, mid); if (r > mid)add(rs(curr), l, r, val, mid + 1, e); push_up(curr); } int query(const int curr = 1, const int l = 1, const int r = n) { if (l == r)return l; const int mid = l + r >> 1; push_down(curr); if (!Min(ls(curr)))return query(ls(curr), l, mid); return query(rs(curr), mid + 1, r); } } Seg; struct DCT { int left, right, type, rightL; DCT(const int left, const int right, const int type = 0, const int right_l = 0) : left(left), right(right), type(type), rightL(right_l) { } DCT() = default; } dct[N]; inline bool isContinue(const int l, const int r) { return ST.query(l, r) == r - l; } #define left(x) dct[x].left #define right(x) dct[x].right #define type(x) dct[x].type #define rightL(x) dct[x].rightL int cnt; int stMax[N], stMin[N], maxCnt, minCnt; #define maxTop idx[stMax[maxCnt]] #define minTop idx[stMin[minCnt]] int node[N]; vector<int> child[N]; stack<int> st; #define root st.top() int dctRoot; inline void build() { forn(i, 1, n) { while (maxCnt and idx[i] >= maxTop)Seg.add(1, stMax[maxCnt - 1] + 1, stMax[maxCnt], -maxTop), --maxCnt; while (minCnt and idx[i] <= minTop)Seg.add(1, stMin[minCnt - 1] + 1, stMin[minCnt],minTop), --minCnt; Seg.add(1, stMax[maxCnt] + 1, i, idx[i]), Seg.add(1, stMin[minCnt] + 1, i, -idx[i]); stMax[++maxCnt] = stMin[++minCnt] = i; int curr; dct[curr = node[i] = ++cnt] = DCT(i, i); const int L = Seg.query(); while (!st.empty() and left(root) >= L) { if (type(root) and isContinue(rightL(root), i)) { right(root) = i, rightL(root) = left(curr); child[root].push_back(curr); curr = root; st.pop(); } else if (isContinue(left(root), i)) { dct[++cnt] = DCT(left(root), i, 1,left(curr)); child[cnt].push_back(root), child[cnt].push_back(curr); curr = cnt; st.pop(); } else { child[++cnt].push_back(curr); do child[cnt].push_back(root), st.pop(); while (!isContinue(left(root), i)); dct[cnt] = DCT(left(root), i); child[cnt].push_back(root); curr = cnt; st.pop(); } } st.push(curr); Seg.add(1, 1, i, -1); } dctRoot = root; } ll ans; inline void dfs(const int curr) { ll siz = child[curr].size(); if (type(curr))ans += siz * (siz - 1) / 2; else ans++; for (const auto nxt : child[curr])dfs(nxt); } inline void solve() { cin >> n; forn(i, 1, n) { int x, y; cin >> x >> y; idx[x] = y; } ST.build(); build(); dfs(dctRoot); cout << ans; } signed int main() { // MyFile Spider //------------------------------------------------------ // clock_t start = clock(); int test = 1; // read(test); // cin >> test; forn(i, 1, test)solve(); // while (cin >> n, n)solve(); // while (cin >> test)solve(); // clock_t end = clock(); // cerr << "time = " << double(end - start) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC << "s" << endl; }
合集:
codeforces题解集1




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· Manus的开源复刻OpenManus初探
· 三行代码完成国际化适配,妙~啊~
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 如何调用 DeepSeek 的自然语言处理 API 接口并集成到在线客服系统