P3509 [POI2010] ZAB-Frog 题解
题目链接:ZAB-Frog
基于一个根据距离第 \(k\) 大的事实:
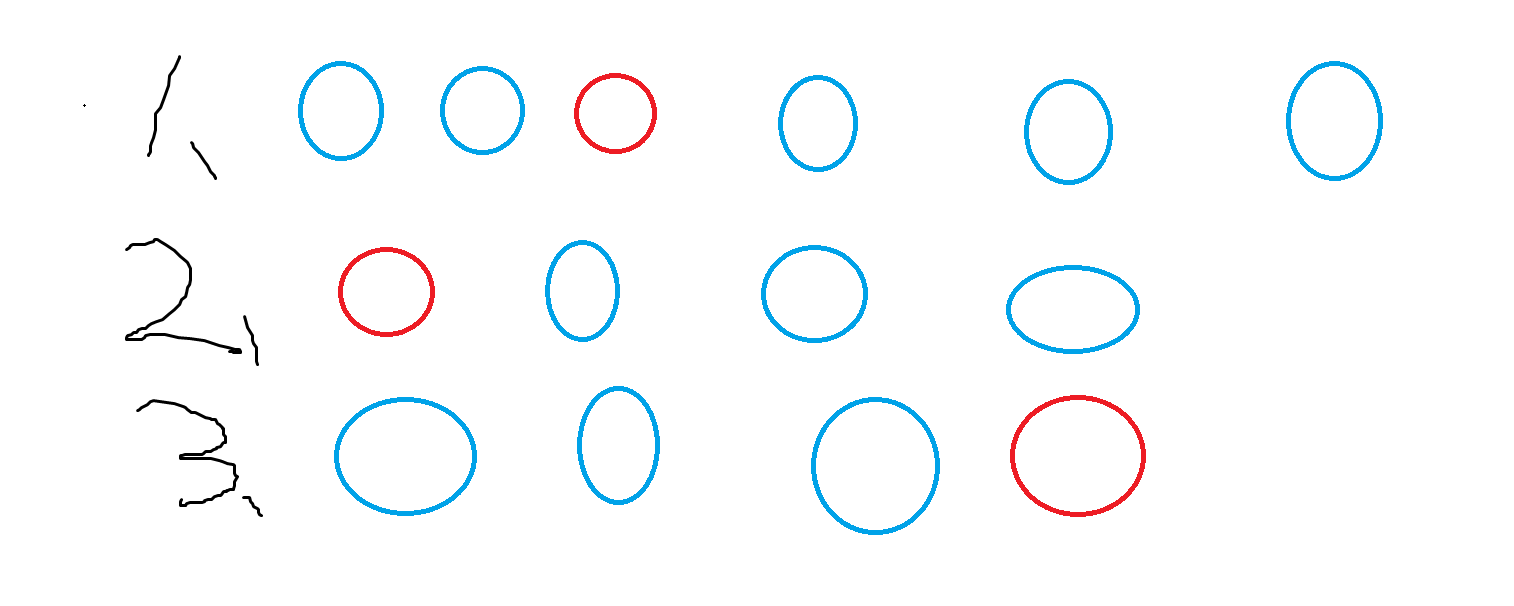
容易知道,对于红色的点而言,与它相近最近的 \(k\) 个点是连续的。而第 \(k\) 远的要么是最左侧要么是最右侧。而我们注意到原数组是升序,那么考虑红色点往右走到新的位置,这些蓝色单点整天有什么影响:
-
左边的点离它更远了。
-
右边原本不属于第 \(k\) 远范围内的点离它更近了。
那么当移动以后会有这么个情况,最左边开始的部分蓝色点太远了,不如最右边的新出现的蓝色的点。那么显然可以看做整体蓝色连续段往右移动了。更一般来说,将当前点与离它最近的 \(k\) 个点,放在一个窗口里,显然是连续的,而随着这个点往右移动,窗口也会往右移动,窗口大小为 \(k+1\)。那么这个窗口移动规则也很简单,新的最右边的点比最左边的点更近,就需要移除这个最左边的点,加入新的最右边的点。也就是每个点的第一次移动是很好处理出来的,滑窗处理完以后,判断左右端点谁更远就是谁是第 \(k\) 远。
考虑走 \(m\) 步,\(m\) 特别大,知道每个点走一步的情况,直接倍增预处理就能知道走 \(m\) 步的情况了。
参照代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
// #pragma GCC optimize("Ofast,unroll-loops")
// #pragma GCC optimize(2)
#define isPbdsFile
#ifdef isPbdsFile
#include <bits/extc++.h>
#else
#include <ext/pb_ds/priority_queue.hpp>
#include <ext/pb_ds/hash_policy.hpp>
#include <ext/pb_ds/tree_policy.hpp>
#include <ext/pb_ds/trie_policy.hpp>
#include <ext/pb_ds/tag_and_trait.hpp>
#include <ext/pb_ds/hash_policy.hpp>
#include <ext/pb_ds/list_update_policy.hpp>
#include <ext/pb_ds/assoc_container.hpp>
#include <ext/pb_ds/exception.hpp>
#include <ext/rope>
#endif
using namespace std;
using namespace __gnu_cxx;
using namespace __gnu_pbds;
typedef long long ll;
typedef long double ld;
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
typedef pair<ll, ll> pll;
typedef tuple<int, int, int> tii;
typedef tuple<ll, ll, ll> tll;
typedef unsigned int ui;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
typedef __int128 i128;
#define hash1 unordered_map
#define hash2 gp_hash_table
#define hash3 cc_hash_table
#define stdHeap std::priority_queue
#define pbdsHeap __gnu_pbds::priority_queue
#define sortArr(a, n) sort(a+1,a+n+1)
#define all(v) v.begin(),v.end()
#define yes cout<<"YES"
#define no cout<<"NO"
#define Spider ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(nullptr);cout.tie(nullptr);
#define MyFile freopen("..\\input.txt", "r", stdin),freopen("..\\output.txt", "w", stdout);
#define forn(i, a, b) for(int i = a; i <= b; i++)
#define forv(i, a, b) for(int i=a;i>=b;i--)
#define ls(x) (x<<1)
#define rs(x) (x<<1|1)
#define endl '\n'
//用于Miller-Rabin
[[maybe_unused]] static int Prime_Number[13] = {0, 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19, 23, 29, 31, 37};
template <typename T>
int disc(T* a, int n)
{
return unique(a + 1, a + n + 1) - (a + 1);
}
template <typename T>
T lowBit(T x)
{
return x & -x;
}
template <typename T>
T Rand(T l, T r)
{
static mt19937 Rand(time(nullptr));
uniform_int_distribution<T> dis(l, r);
return dis(Rand);
}
template <typename T1, typename T2>
T1 modt(T1 a, T2 b)
{
return (a % b + b) % b;
}
template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3>
T1 qPow(T1 a, T2 b, T3 c)
{
a %= c;
T1 ans = 1;
for (; b; b >>= 1, (a *= a) %= c)if (b & 1)(ans *= a) %= c;
return modt(ans, c);
}
template <typename T>
void read(T& x)
{
x = 0;
T sign = 1;
char ch = getchar();
while (!isdigit(ch))
{
if (ch == '-')sign = -1;
ch = getchar();
}
while (isdigit(ch))
{
x = (x << 3) + (x << 1) + (ch ^ 48);
ch = getchar();
}
x *= sign;
}
template <typename T, typename... U>
void read(T& x, U&... y)
{
read(x);
read(y...);
}
template <typename T>
void write(T x)
{
if (typeid(x) == typeid(char))return;
if (x < 0)x = -x, putchar('-');
if (x > 9)write(x / 10);
putchar(x % 10 ^ 48);
}
template <typename C, typename T, typename... U>
void write(C c, T x, U... y)
{
write(x), putchar(c);
write(c, y...);
}
template <typename T11, typename T22, typename T33>
struct T3
{
T11 one;
T22 tow;
T33 three;
bool operator<(const T3 other) const
{
if (one == other.one)
{
if (tow == other.tow)return three < other.three;
return tow < other.tow;
}
return one < other.one;
}
T3() { one = tow = three = 0; }
T3(T11 one, T22 tow, T33 three) : one(one), tow(tow), three(three)
{
}
};
template <typename T1, typename T2>
void uMax(T1& x, T2 y)
{
if (x < y)x = y;
}
template <typename T1, typename T2>
void uMin(T1& x, T2 y)
{
if (x > y)x = y;
}
constexpr int N = 1e6 + 10;
constexpr int T = 100;
int go[N][T];
ll a[N];
ll n, k, m;
inline void solve()
{
cin >> n >> k >> m;
forn(i, 1, n)cin >> a[i];
const int MX = log2(m);
int l = 1, r = k + 1;//包括当前点的k+1大小的滑窗
forn(i, 1, n)
{
while (r + 1 <= n and a[r + 1] - a[i] < a[i] - a[l])l++, r++;//新的点更优
go[i][0] = a[r] - a[i] > a[i] - a[l] ? r : l;//谁更远谁就是第k大,也即是第一次移动位置
}
forn(j, 1, MX)forn(i, 1, n)go[i][j] = go[go[i][j - 1]][j - 1];//倍增预处理
forn(i, 1, n)
{
int pos = i;
ll siz = m;
forv(i, MX, 0)if (siz >= 1ll << i)siz -= 1ll << i, pos = go[pos][i];//倍增查找
cout << pos << " ";
}
}
signed int main()
{
// MyFile
Spider
//------------------------------------------------------
// clock_t start = clock();
int test = 1;
// read(test);
// cin >> test;
forn(i, 1, test)solve();
// while (cin >> n, n)solve();
// while (cin >> test)solve();
// clock_t end = clock();
// cerr << "time = " << double(end - start) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC << "s" << endl;
}
\[时间复杂度为 \ O(n\log{m})
\]



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号