CSS 小结笔记之定位
定位也是Css中一个非常强大的属性。定位主要是用来移动盒子,将其移动到我们想要的位置。
定位分为两部分
1、边偏移 left | right |top |bottom:偏移大小;(边偏移一般制定上就不指定下,指定左就不指定右)
2、定位模式 position :static| relative |absolute | fixed
(1)position :static默认值,使用static时 边偏移不起效果。常用于取消定位。
(2)position :relative 相对定位,相对于其原文档流的位置进行定位 可以通过边偏移移动位置,但是原来位置继续占有 每次移动以自己的左上角为基点进行移动

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"> <title>Document</title> <style> /* */ .son1 { width: 100px; height: 100px; background-color: red; } .son2 { width: 100px; height: 100px; background-color: pink; position: relative; left: 90px; top: 50px; } .son3 { width: 100px; height: 100px; background-color: red; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="fa"> <div class="son1"> </div> <div class="son2"> </div> <div class="son3"> </div> </div> </body> </html>
显示结果为:
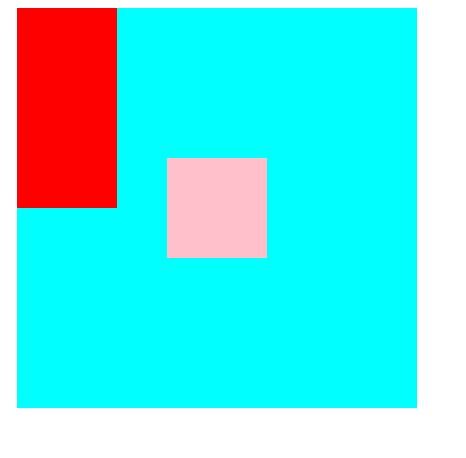
(3)position :absolute 绝对定位,相对于上一个已经定位的父元素进行定位 脱离标准流,与浮动类似完全不占位置
a、如果父亲没有定位,则以浏览器为准对齐,原位置不保留

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"> <title>Document</title> <style> /* */ .fa { width: 400px; height: 400px; background-color: aqua; margin: 0 auto; } .son1 { width: 100px; height: 100px; background-color: red; } .son2 { width: 100px; height: 100px; background-color: pink; position: absolute; left: 90px; top: 50px; } .son3 { width: 100px; height: 100px; background-color: red; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="fa"> <div class="son1"> </div> <div class="son2"> </div> <div class="son3"> </div> </div> </body> </html>

b、父亲有定位,则以最近的父亲元素为基准点对齐 (父亲可以是absolute也可以是relative) 一半来说子元素绝对定位,父元素相对定位即“子绝父相”
在上例中给.fa 样式增加 一个相对定位 即position: relative; 截个图变为:
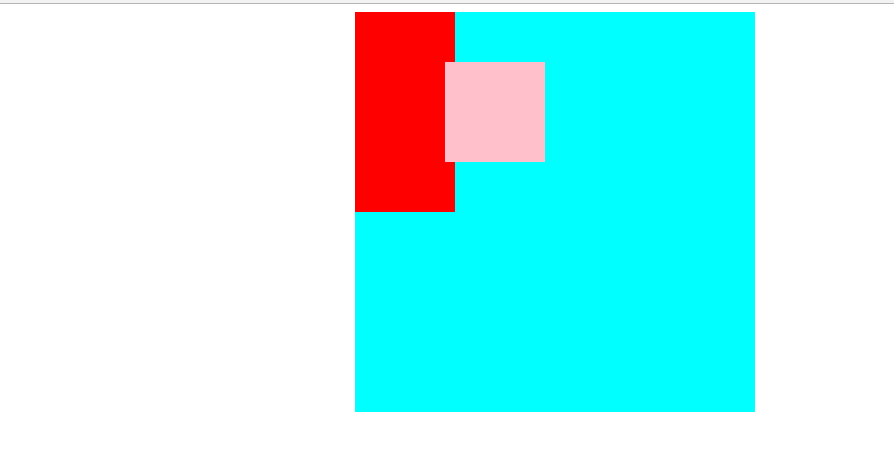
c、绝对定位 想要水平垂直居中,则先设置left50% 再设置自身宽度的一半 margin-left:-50px
.son2 { width: 100px; height: 100px; background-color: pink; position: absolute; left: 50%; top: 50%; margin: -50px 0 0 -50px; }
将a中.son的样式改为如上所示代码,可以将.son2 改为水平居中,垂直居中,结果图如下
(4)position :fixed 固定定位 相对于浏览器窗口进行定位,与父元素没有任何关系 。不占位置,不随滚动条滚动, 固定定位一定要写宽和高(除非有内容撑开盒子) 。
其他注意点:
1、在定位中,会产生层叠关系,设置层叠显示顺序使用z-index:1;数字越大优先级越高(只对定位元素(静态定位除外)产生效果)
如下例

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"> <title>Document</title> <style> * { margin: 0; padding: 0; } div { width: 200px; height: 200px; margin: 0; } div:first-child { background-color: aqua; z-index: 3; } div:nth-child(2) { background-color: red; position: absolute; left: 10px; top: 10px; z-index: 2; } div:last-child { background-color: pink; position: absolute; left: 20px; top: 20px; z-index: 1; } </style> </head> <body> <div></div> <div></div> <div></div> </body>
在有定位元素中设置z-index 数值高的 显示在最上面。

2、绝对定位和固定定位会将元素转换为行内块元素,因此设置绝对定位和固定定位后就不需要在转换模式了




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号