算法复习——数位dp




开头由于不知道讲啥依然搬讲义
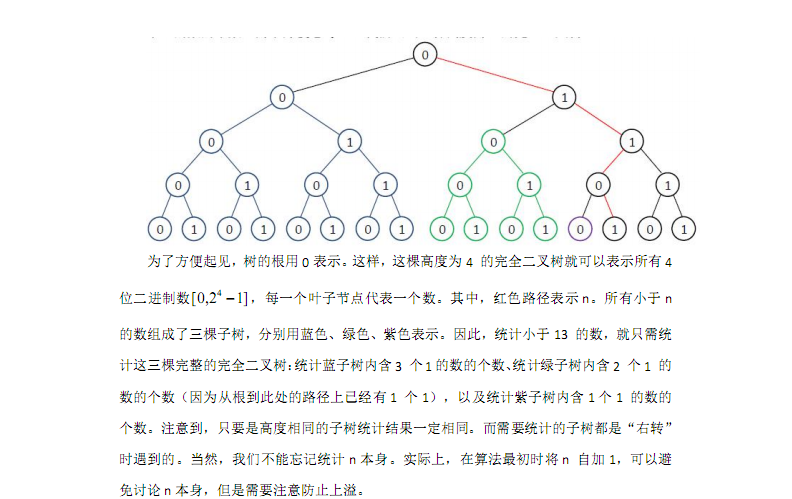
对于引入的这个问题,讲义里已经很清楚了,我更喜欢用那个建树的理解····
相当于先预处理f,然后从起点开始在树上走··记录目前已经找到了多少个满足题意的数k,如果枚举到第i位,下一位要走的是1,需要加上左子树的总数f[i-1][K-k],如果下一位走的是0直接走左子树即可····
#include<iostream> #include<cstdio> #include<cstdlib> #include<cmath> #include<ctime> #include<cctype> #include<cstring> #include<string> #include<algorithm> using namespace std; const int N=32; int f[N][N],x,y,k,b,num[N],n,ans1,ans2; inline void pre() { for(int i=0;i<=31;i++) { f[i][0]=f[i][i]=1; for(int j=1;j<i;j++) f[i][j]=f[i-1][j]+f[i-1][j-1]; } } inline void trans(int x) { int temp=x;n=0; while(temp) num[++n]=temp%b,temp/=b; } inline int solve() { int tot=0,sum=0,i; for(i=n;i>=1;i--) { if(num[i]>1) //大于1的话此时整个子树代表的数都是小于x的,因此直接统计答案 { sum+=f[i][k-tot]; break; } else if(num[i]==1) { sum+=f[i-1][k-tot]; //等于1统计左儿子的答案(即小于该数且又有k个1的数的个数) if(++tot>k) break; } } if(i!=1&&tot==k) sum++; //如果该数本身就符合答案的话答案加1 return sum; } int main() { //freopen("a.in","r",stdin); pre(); scanf("%d%d%d%d",&x,&y,&k,&b); trans(y),ans1=solve(); trans(x-1),ans2=solve(); cout<<ans1-ans2<<endl; return 0; }
例题:
1.windy数(bzoj1026)
Description
windy定义了一种windy数。不含前导零且相邻两个数字之差至少为2的正整数被称为windy数。 windy想知道,
在A和B之间,包括A和B,总共有多少个windy数?
Input
包含两个整数,A B。
Output
一个整数
Sample Input
【输入样例一】
1 10
【输入样例二】
25 50
1 10
【输入样例二】
25 50
Sample Output
【输出样例一】
9
【输出样例二】
20
9
【输出样例二】
20
HINT
【数据规模和约定】
100%的数据,满足 1 <= A <= B <= 2000000000 。
Source
首先运用数位dp的常规思想,用ans(B)-ans(A-1);
这道题我们用f[i][j][0/1]表示第j位为i且小于/大于原数前i为满足题意的数的个数,然后枚举上一位进行dp即可·····具体看代码··
#include<iostream> #include<cstdio> #include<cstdlib> #include<cmath> #include<ctime> #include<cctype> #include<cstring> #include<string> #include<algorithm> using namespace std; const int N=15; int f[N][N][2],num[N],n,a,b; inline int Abs(int a) { return a<0?-a:a; } inline int solve(int x) { if(!x) return 0; n=0;memset(f,0,sizeof(f));int ans=0; while(x) num[++n]=x%10,x/=10; for(int i=0;i<=9;i++) if(i<=num[1]) f[i][1][0]=1; else f[i][1][1]=1; for(int i=2;i<=n;i++) for(int j=0;j<=9;j++) for(int k=0;k<=9;k++) if(Abs(j-k)>=2) { if(j<num[i]) f[j][i][0]+=f[k][i-1][1]+f[k][i-1][0]; else if(j==num[i]) f[j][i][0]+=f[k][i-1][0],f[j][i][1]+=f[k][i-1][1]; else f[j][i][1]+=f[k][i-1][1]+f[k][i-1][0]; } for(int i=1;i<=9;i++) { ans+=f[i][n][0]; if(i==num[n]) break; } for(int i=n-1;i>=1;i--) for(int j=1;j<=9;j++) ans+=f[j][i][0]+f[j][i][1]; return ans; } int main() { //freopen("a.in","r",stdin); scanf("%d%d",&a,&b); printf("%d\n",solve(b)-solve(a-1)); return 0; }
2.不要62(hdu2089)
Problem Description
杭州人称那些傻乎乎粘嗒嗒的人为62(音:laoer)。
杭州交通管理局经常会扩充一些的士车牌照,新近出来一个好消息,以后上牌照,不再含有不吉利的数字了,这样一来,就可以消除个别的士司机和乘客的心理障碍,更安全地服务大众。
不吉利的数字为所有含有4或62的号码。例如:
62315 73418 88914
都属于不吉利号码。但是,61152虽然含有6和2,但不是62连号,所以不属于不吉利数字之列。
你的任务是,对于每次给出的一个牌照区间号,推断出交管局今次又要实际上给多少辆新的士车上牌照了。
杭州交通管理局经常会扩充一些的士车牌照,新近出来一个好消息,以后上牌照,不再含有不吉利的数字了,这样一来,就可以消除个别的士司机和乘客的心理障碍,更安全地服务大众。
不吉利的数字为所有含有4或62的号码。例如:
62315 73418 88914
都属于不吉利号码。但是,61152虽然含有6和2,但不是62连号,所以不属于不吉利数字之列。
你的任务是,对于每次给出的一个牌照区间号,推断出交管局今次又要实际上给多少辆新的士车上牌照了。
Input
输入的都是整数对n、m(0<n≤m<1000000),如果遇到都是0的整数对,则输入结束。
Output
对于每个整数对,输出一个不含有不吉利数字的统计个数,该数值占一行位置。
Sample Input
1 100
0 0
Sample Output
80
来一道非常经典的数位dp,这道题也包含了许多数位dp的常用方法:拆位+记忆化搜索+判断封顶
具体的就不多说了···直接看代码吧
#include<iostream> #include<cstdio> #include<cstdlib> #include<cmath> #include<ctime> #include<cctype> #include<cstring> #include<string> #include<algorithm> using namespace std; const int N=15; int f[N][N][2],a,b,num[N],n,ans1,ans2; inline int R() { char c;int f=0; for(c=getchar();c<'0'||c>'9';c=getchar()); for(;c<='9'&&c>='0';c=getchar()) f=(f<<3)+(f<<1)+c-'0'; return f; } inline void trans(int x) { memset(f,-1,sizeof(f)); int temp=x;n=0; while(temp) n++,temp/=10; temp=x; for(int i=n;i;i--) num[i]=temp%10,temp/=10; } inline int dfs(int pos,int pre,bool jud) { if(pos==n+1) return 1; if(f[pos][pre][jud]!=-1) return f[pos][pre][jud]; int maxx=jud?num[pos]:9,ans=0; for(int i=0;i<=maxx;i++) { if(i==4||(pre==6&&i==2)) continue; ans+=dfs(pos+1,i,jud&&i==maxx); } return f[pos][pre][jud]=ans; } int main() { while(true) { a=R(),b=R(); if(a==0&&b==0) break; trans(a-1);ans1=dfs(1,0,1); trans(b);ans2=dfs(1,0,1); cout<<ans2-ans1<<endl; } return 0; }
3.B-number(hdu3652)
Problem Description
A wqb-number, or B-number for short, is a non-negative integer whose decimal form contains the sub- string "13" and can be divided by 13. For example, 130 and 2613 are wqb-numbers, but 143 and 2639 are not. Your task is to calculate how many wqb-numbers from 1 to n for a given integer n.
Input
Process till EOF. In each line, there is one positive integer n(1 <= n <= 1000000000).
Output
Print each answer in a single line.
Sample Input
13 100 200 1000
Sample Output
1 1 2 2
和上道题很像啊···只是需要在dfs时多加入一个mod和一个jud来判断是否整除和是否找到13即可·······
代码:
#include<iostream> #include<cstdio> #include<cstdlib> #include<cmath> #include<ctime> #include<cctype> #include<cstring> #include<string> #include<algorithm> using namespace std; const int N=15; int f[N][N][2][2][N],num[N],n,a; inline void trans(int x) { memset(f,-1,sizeof(f)); int temp=x;n=0; while(temp) temp/=10,n++; temp=x; for(int i=n;i>=1;i--) num[i]=temp%10,temp/=10; } inline int dfs(int pos,int mod,int jud,int lim,int pre) { if(pos==n+1) return jud&&!mod; if(f[pos][mod][jud][lim][pre]!=-1) return f[pos][mod][jud][lim][pre]; int maxx=lim?num[pos]:9,ans=0,vmod,vjud; for(int i=0;i<=maxx;i++) { vmod=(mod*10+i)%13;vjud=jud; if(pre==1&&i==3) vjud=1; ans+=dfs(pos+1,vmod,vjud,lim&&i==maxx,i); } return f[pos][mod][jud][lim][pre]=ans; } int main() { //freopen("a.in","r",stdin); while(scanf("%d",&a)!=EOF) { trans(a); printf("%d\n",dfs(1,0,0,1,0)); } return 0; }
4.beautiful number(codeforces 55d)
题目描述
如果一个数能够被其每个除0的数位的数都整除,那么这个数就叫做美丽数。
给定一个区间 [x,y] ,计算该区间内有多少个美丽数。
输入格式
输入文件中有一行,为空格隔开的两个正整数 x 和 y(1≤x≤y≤9*1018)。
输出格式
输出一个整数,即区间 [x,y] 内的美丽数个数。
样例数据 1
输入
1 9
输出
9
样例数据 2
输入
12 15
输出
2
这道题首先先到的是用四维dp,第一维记录位数,第二维记录之前数的公倍数,第三维记录目前凑成的数的数字之和,最后一维记录是否封顶····
然而第二维和第三维是在太大···直接记录会超空间···
第三维其实是很好优化的···因为1到9的公倍数只有2520,因此每次之和模掉一个2520就可以了··
至于第二维···由于1到9各个数字组成的数的公倍数最多只有48个·····因此可以利用hash表来储存····(其实也不叫hash表··只是一个普通数组而已)
然后就可以了···另外注意要开long long啊···
#include<iostream> #include<cstdio> #include<cstdlib> #include<cmath> #include<ctime> #include<cctype> #include<cstring> #include<string> #include<algorithm> using namespace std; const int N=30; int num[N],n,tot,hash[55],id[3005]; long long dp[N][50][2525][2],x,y,ans1,ans2; inline void pre() { for(int i=1;i<=2520;i++) if(!(2520%i)) hash[++tot]=i,id[i]=tot; } inline void trans(long long x) { memset(dp,-1,sizeof(dp)); long long temp=x;n=0; while(temp) n++,temp/=10; temp=x; for(int i=n;i>=1;i--) num[i]=temp%10,temp/=10; } inline int gcd(int a,int b) { if(b==0) return a; else return gcd(b,a%b); } inline int getlcm(int a,int b) { return a*b/gcd(a,b); } inline long long dfs(int pos,int gbs,int mod,int lim) { if(pos==n+1) return mod%hash[gbs]==0; if(dp[pos][gbs][mod][lim]!=-1) return dp[pos][gbs][mod][lim]; int maxx=lim?num[pos]:9;int vgbs,vmod;long long ans=0; for(int i=0;i<=maxx;i++) { vmod=(mod*10+i)%2520;vgbs=gbs; if(i) { vgbs=getlcm(i,hash[gbs]);vgbs=id[vgbs]; } ans+=dfs(pos+1,vgbs,vmod,lim&&i==maxx); } return dp[pos][gbs][mod][lim]=ans; } int main() { // freopen("a.in","r",stdin); pre(); scanf("%I64d%I64d",&x,&y); trans(y);ans1=dfs(1,1,0,1); trans(x-1);ans2=dfs(1,1,0,1); printf("%I64d",ans1-ans2); return 0; }

