集合——Collection
为什么出现集合类?
面向对象语言对事物的体现都是以对象的形式,所以为了方便对多个对象的操作,Java就提供了集合类。
数组和集合类同是容器,有何不同?
数组虽然也可以存储对象,但长度是固定的;集合长度是可变的。数组中可以存储基本数据类型,集合只能存储对象。
集合类的特点:
集合只用于存储对象,集合长度是可变的,集合可以存储不同类型的对象。

Collection接口概述(它是一个接口,不是对象):
是Collection层次结构中的根接口。
Collection 表示一组对象,这些对象也称为 collection 的元素。一些 collection内的对象允许有重复的元素,而另一些则不允许。一些collection内的对象是有序的,而另一些则是无序的。(有序则可以指定存放位置)
Collection集合的继承体系结构图:
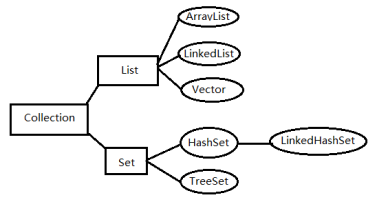
(方框里面的是接口类型,圆框里面的是具体的实现类,注意接口不能实例化)
Collection接口成员方法:
1:添加功能
boolean add(Object obj):添加一个元素
boolean addAll(Collection c):添加一个集合的元素
2:删除功能
void clear():移除所有元素
boolean remove(Object o):移除一个元素
boolean removeAll(Collection c):移除一个集合的元素
假如定义了两个集合c1和c2,
c1.removeAll(c1):表示移除c1中的所有元素,返回true
c1.removeAll(c2):表示移除c1中与c2中相同的元素,有移除元素则返回true
3:判断功能
boolean contains(Object o):判断集合中是否包含指定的元素
boolean containsAll(Collection c):判断集合中是否包含指定的集合元素
(只有包含所有的元素,才叫包含)
boolean isEmpty():判断集合是否为空
4:获取功能
(重点)Iterator<E> iterator()迭代器,集合的专用遍历方式
5:长度功能
int size():元素的个数
6:交集功能
boolean retainAll(Collection c):两个集合都有的元素?元素去哪了?返回的boolean又是什么意思呢?
假设有两个集合A,B:
A对B做交集,最终的结果保存在A中,B不变。
返回值表示的是A是否发生过改变。
集合的遍历:(一种方法是把集合转为数组,另一种方法是使用Iterator 迭代器,这是集合的专用方式)
1、把集合转换为数组
Object[] toArray():把集合转成数组,可以实现集合的遍历。
(集合的遍历;其实就是依次获取集合中的每一个元素)
/*集合转数组遍历*/ public class CollectionDemo3 { public static void main(String[] args) { // 创建集合对象 Collection c = new ArrayList(); // 添加元素 c.add("hello"); // Object obj = "hello"; 向上转型 c.add("world"); c.add("java"); // 遍历 // Object[] toArray():把集合转成数组,可以实现集合的遍历 Object[] objs = c.toArray(); for (int x = 0; x < objs.length; x++) { // System.out.println(objs[x]);//这个也是可以实现的 /*我知道元素是字符串,我在获取到元素的的同时,还想知道元素的长度。 //System.out.println(objs[x] + "---" + objs[x].length()); 上面的实现不了,原因是Object中没有length()方法 我们要想使用字符串的方法,就必须把元素还原成字符串 向下转型*/ String s = (String) objs[x];//把元素还原成字符串 System.out.println(s + "---" + s.length());//这个还输出了元素的长度 } } }
2、Iterator接口概述:
对 collection 进行迭代的迭代器,是集合的获取元素的方式,依赖于集合而存在
集合的操作步骤:
A:创建集合对象
B:创建元素对象
C:把元素添加到集合
D:遍历集合
A:存储字符串并遍历 import java.util.Collection; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Iterator; public class CollectionDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { //创建集合对象 Collection c = new ArrayList(); //创建并添加元素 c.add("hello"); c.add("world"); c.add("java"); //遍历集合 Iterator it = c.iterator(); while(it.hasNext()) { String s =(String) it.next(); System.out.println(s); } } }
B:存储自定义对象并遍历 学生类: public class Student { private String name; private int age; public Student(){ } public Student(String name,int age) { this.name = name; this.age = age; } //getXxx()/setXxx()(此处省略了get/set方法) } 主类: import java.util.Collection; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Iterator; public class StudentDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { //创建集合对象 Collection c = new ArrayList(); //创建学生对象 Student s1 = new Student("刘备",33); Student s2 = new Student("关羽",30); Student s3 = new Student("张飞",30); Student s4 = new Student("孙权",25); Student s5 = new Student("曹操",40); //添加元素 c.add(s1); c.add(s2); c.add(s3); c.add(s4); c.add(s5); //遍历集合 Iterator it = c.iterator(); while(it.hasNext()) { Student s = (Student)it.next(); System.out.println(s.getName()+"---"+s.getAge()); } }


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号