Mapreduce实例——单表join
现有某电商的用户好友数据文件,名为 buyer1,buyer1中包含(buyer_id,friends_id)两个字段,内容是以"\t"分隔,编写MapReduce进行单表连接,查询出用户的间接好友关系。例如:10001的好友是10002,而10002的好友是10005,那么10001和10005就是间接好友关系。

buyer1(buyer_id,friends_id)
10001 10002
10002 10005
10003 10002
10004 10006
10005 10007
10006 10022
10007 10032
10009 10006
10010 10005
10011 10013
mapreduce程序:
package mapreduce7; import java.io.IOException; import java.util.Iterator; import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration; import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path; import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat; //04.Mapreduce实例——单表join public class DanJoin { public static class Map extends Mapper<Object,Text,Text,Text>{ public void map(Object key,Text value,Context context) throws IOException,InterruptedException{ String line = value.toString(); String[] arr = line.split("\t"); String mapkey=arr[0]; String mapvalue=arr[1]; String relationtype=new String(); relationtype="1"; context.write(new Text(mapkey),new Text(relationtype+"+"+mapvalue)); //System.out.println(relationtype+"+"+mapvalue); relationtype="2"; context.write(new Text(mapvalue),new Text(relationtype+"+"+mapkey)); //System.out.println(relationtype+"+"+mapvalue); } } public static class Reduce extends Reducer<Text, Text, Text, Text>{ public void reduce(Text key,Iterable<Text> values,Context context) throws IOException,InterruptedException{ int buyernum=0; String[] buyer=new String[20]; int friendsnum=0; String[] friends=new String[20]; Iterator ite=values.iterator(); while(ite.hasNext()){ String record=ite.next().toString(); int len=record.length(); int i=2; if(0==len){ continue; } char relationtype=record.charAt(0); if('1'==relationtype){ buyer [buyernum]=record.substring(i); buyernum++; } if('2'==relationtype){ friends[friendsnum]=record.substring(i); friendsnum++; } } if(0!=buyernum&&0!=friendsnum){ for(int m=0;m<buyernum;m++){ for(int n=0;n<friendsnum;n++){ if(buyer[m]!=friends[n]){ context.write(new Text(buyer[m]),new Text(friends[n])); } } } } } } public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ Configuration conf=new Configuration(); String[] otherArgs=new String[2]; otherArgs[0]="hdfs://192.168.51.100:8020/mymapreduce7/in/buyer1"; otherArgs[1]="hdfs://192.168.51.100:8020/mymapreduce7/out"; Job job=new Job(conf," Table join"); job.setJarByClass(DanJoin.class); job.setMapperClass(Map.class); job.setReducerClass(Reduce.class); job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class); job.setOutputValueClass(Text.class); FileInputFormat.addInputPath(job, new Path(otherArgs[0])); FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(otherArgs[1])); System.exit(job.waitForCompletion(true)?0:1); } }
结果:
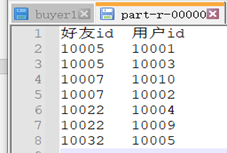
原理:
以本实验的buyer1(buyer_id,friends_id)表为例来阐述单表连接的实验原理。单表连接,连接的是左表的buyer_id列和右表的friends_id列,且左表和右表是同一个表。因此,在map阶段将读入数据分割成buyer_id和friends_id之后,会将buyer_id设置成key,friends_id设置成value,直接输出并将其作为左表;再将同一对buyer_id和friends_id中的friends_id设置成key,buyer_id设置成value进行输出,作为右表。为了区分输出中的左右表,需要在输出的value中再加上左右表的信息,比如在value的String最开始处加上字符1表示左表,加上字符2表示右表。这样在map的结果中就形成了左表和右表,然后在shuffle过程中完成连接。reduce接收到连接的结果,其中每个key的value-list就包含了"buyer_idfriends_id--friends_idbuyer_id"关系。取出每个key的value-list进行解析,将左表中的buyer_id放入一个数组,右表中的friends_id放入一个数组,然后对两个数组求笛卡尔积就是最后的结果


