MVVM更容易内存泄露吗?
由于MVVM是把View, ViewModel, Model紧紧绑定在一起的模式,特别视图和视图模型通过实现观察者模式双向绑定和NotifyPropertyChanged事件,似乎更加容易造成内存泄露/内存不释放。网上也有这种说法。真的是这样的吗?我们来实际测试一下。
实际测试MVVM是不是容易内存泄露
为了说明问题,我把MVVM搞复杂一点,在ViewModel里面引用一个Singleton单例模式的Service,这个Service定义如下:
1: namespace SilverlightApplication1.Service
2: {
3: public class GlobalService
4: {
5: private static readonly GlobalService Instance = new GlobalService();
6:
7: static GlobalService()
8: {
9: }
10:
11: public static GlobalService GetInstance()
12: {
13: return Instance;
14: }
15: }
16: }
写一个ViewModel,里面引用了Service,用到了ICommand,实现了INotifyPorpertyChanged接口:
1: using System.ComponentModel;
2: using System.Windows.Input;
3: using SilverlightApplication1.Service;
4:
5: namespace SilverlightApplication1.MVVM
6: {
7: public class ViewModel1 : INotifyPropertyChanged
8: {
9: private GlobalService _injectSingletonService;
10:
11: public ViewModel1(GlobalService injectSingletonService)
12: {
13: Property1 = "test1";
14: Command1 = new DelegateCommand(LoadMe, CanLoadMe);
15:
16: _injectSingletonService = injectSingletonService;
17: }
18:
19: private string _property1;
20: public string Property1
21: {
22: get { return _property1; }
23: set
24: {
25: _property1 = value;
26:
27: if (PropertyChanged != null)
28: {
29: PropertyChanged(this,
30: new PropertyChangedEventArgs("Property1"));
31: }
32: }
33: }
34:
35: public ICommand Command1 { get; set; }
36: public event PropertyChangedEventHandler PropertyChanged;
37:
38: private void LoadMe(object param)
39: {
40:
41: }
42:
43: private bool CanLoadMe(object param)
44: {
45: return true;
46: }
47: }
48: }
来一个视图View,绑定ViewModel,有个button绑定了ICommand,属性也绑定了。
1: <UserControl x:Class="SilverlightApplication1.MVVM.View1"
2: xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
3: xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
4: xmlns:d="http://schemas.microsoft.com/expression/blend/2008"
5: xmlns:mc="http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/markup-compatibility/2006"
6: mc:Ignorable="d"
7: d:DesignHeight="300" d:DesignWidth="400">
8:
9: <Grid x:Name="LayoutRoot" Background="White">
10: <TextBlock Height="65" HorizontalAlignment="Left" Margin="57,82,0,0" Name="textBlock1" Text="this is view1" VerticalAlignment="Top" Width="224" FontSize="18" />
11: <Button Content="Button" Command="{Binding Command1}" Height="28" HorizontalAlignment="Left" Margin="55,130,0,0" Name="button1" VerticalAlignment="Top" Width="111" />
12: <TextBlock Height="28" HorizontalAlignment="Left" Margin="56,173,0,0" Name="textBlock2" Text="{Binding Property1}" VerticalAlignment="Top" Width="114" />
13: </Grid>
14: </UserControl>
这个View1的界面是这样子的:
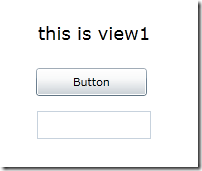
View1.xaml.cs代码:
1: using System.Windows.Controls;
2: using SilverlightApplication1.Service;
3:
4: namespace SilverlightApplication1.MVVM
5: {
6: public partial class View1 : UserControl
7: {
8: public View1()
9: {
10: InitializeComponent();
11:
12: this.DataContext = new ViewModel1(GlobalService.GetInstance());
13: }
14: }
15: }
辅助类DelegateCommand源码:
1: using System;
2: using System.Windows.Input;
3:
4: namespace SilverlightApplication1
5: {
6: public class DelegateCommand : ICommand
7: {
8: public event EventHandler CanExecuteChanged;
9:
10: Func<object, bool> canExecute;
11: Action<object> executeAction;
12: bool canExecuteCache;
13:
14: public DelegateCommand(Action<object> executeAction,
15: Func<object, bool> canExecute)
16: {
17: this.executeAction = executeAction;
18: this.canExecute = canExecute;
19: }
20:
21: #region ICommand Members
22:
23: /// <summary>
24:
25: /// Defines the method that determines whether the command
26:
27: /// can execute in its current state.
28:
29: /// </summary>
30:
31: /// <param name="parameter">
32:
33: /// Data used by the command.
34:
35: /// If the command does not require data to be passed,
36:
37: /// this object can be set to null.
38:
39: /// </param>
40:
41: /// <returns>
42:
43: /// true if this command can be executed; otherwise, false.
44:
45: /// </returns>
46:
47: public bool CanExecute(object parameter)
48: {
49:
50: bool tempCanExecute = canExecute(parameter);
51:
52:
53:
54: if (canExecuteCache != tempCanExecute)
55: {
56:
57: canExecuteCache = tempCanExecute;
58:
59: if (CanExecuteChanged != null)
60: {
61:
62: CanExecuteChanged(this, new EventArgs());
63:
64: }
65:
66: }
67:
68:
69:
70: return canExecuteCache;
71:
72: }
73:
74:
75:
76: /// <summary>
77:
78: /// Defines the method to be called when the command is invoked.
79:
80: /// </summary>
81:
82: /// <param name="parameter">
83:
84: /// Data used by the command.
85:
86: /// If the command does not require data to be passed,
87:
88: /// this object can be set to null.
89:
90: /// </param>
91:
92: public void Execute(object parameter)
93: {
94:
95: executeAction(parameter);
96:
97: }
98:
99: #endregion
100: }
101: }
MainPage的代码:
1: <UserControl x:Class="SilverlightApplication1.MainPage"
2: xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
3: xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
4: xmlns:d="http://schemas.microsoft.com/expression/blend/2008"
5: xmlns:mc="http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/markup-compatibility/2006"
6: mc:Ignorable="d"
7: d:DesignHeight="300" d:DesignWidth="400" xmlns:sdk="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation/sdk">
8:
9: <Grid x:Name="LayoutRoot" Background="White">
10: <Button Content="Add view" Height="36" HorizontalAlignment="Left" Margin="20,31,0,0" Name="button1" VerticalAlignment="Top" Width="115" Click="button1_Click" />
11: <sdk:TabControl Height="197" HorizontalAlignment="Left" Margin="28,82,0,0" Name="tabControl1" VerticalAlignment="Top" Width="346">
12: <sdk:TabItem Header="tabItem1" Name="tabItem1">
13: <Grid />
14: </sdk:TabItem>
15: </sdk:TabControl>
16: <Button Content="Close view" Height="35" HorizontalAlignment="Left" Margin="148,32,0,0" Name="button2" VerticalAlignment="Top" Width="108" Click="button2_Click" />
17: </Grid>
18: </UserControl>
MainPage界面,主要是在Tab里面打开View1,不断打开关闭,打开关闭,因为View1是用MVVM模式实现的,看看有内存泄露:
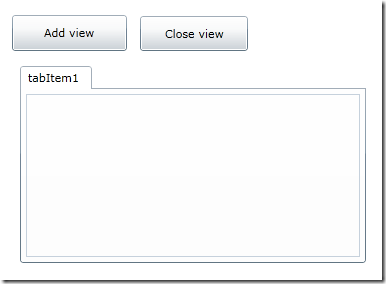
MainPage.xaml.cs,就是测试代码,正常情况下点击关闭tab,可能GC不会立即回收内存,这里为了便于测试,手动加了GC.Collect。(正常情况下,不推荐使用GC.Collect())
1: using System;
2: using System.Windows;
3: using System.Windows.Controls;
4: using SilverlightApplication1.MVVM;
5:
6: namespace SilverlightApplication1
7: {
8: public partial class MainPage : UserControl
9: {
10: public MainPage()
11: {
12: InitializeComponent();
13: }
14:
15: private void button1_Click(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e)
16: {
17: var v = new View1();
18: TabItem t = new TabItem {Content = v, Header = "header " + DateTime.Now.Second.ToString()};
19: this.tabControl1.Items.Add(t);
20: }
21:
22: private void button2_Click(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e)
23: {
24: this.tabControl1.Items.RemoveAt(0);//view1, viewModel1并没有立即释放,由GC决定何时决定。
25:
26: System.GC.Collect();
27: System.GC.WaitForPendingFinalizers();
28:
29: //{
30: // FooContext context = new FooContext();
31: // context.Load(context.MyQuery);
32: //}
33: }
34: }
35: }
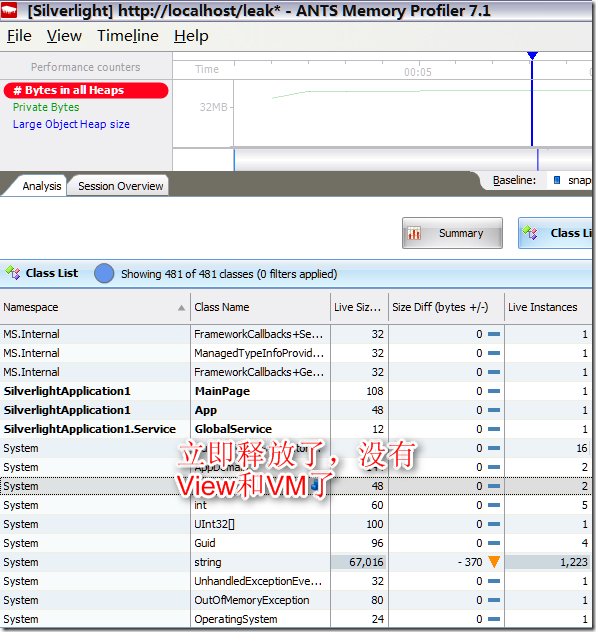
测试结果:内存泄露和MVVM无关
我的测试结果是内存能够释放,没有内存泄露问题,也就是说MVVM模式和内存泄露无关。那种所谓的MVVM更容易内存泄露的说法没有什么道理。但不排除你的ViewModel和Model里面有复杂的引用关系,比如你的VIewModel或者Model引用了其他的类,你可能没有察觉,而那些类可能是Public Static的(是GC Root,不释放),或者是永远不释放的(如MainForm)引用,那就复杂了。由于你的ViewModel被那些不释放的对象引用着,而你却不知道,那就是内存泄露了。这和MVVM没有关系。
深入思考和继续阅读
通常.NET程序的内存泄露原因:
- Static references
- Event with missing unsubscription
- Static event with missing unsubscription
- Dispose method not invoked
- Incomplete Dispose method
有关如何避免.NET程序的内存泄露,请仔细阅读MSDN这两篇文章,详细讲述了<如何检测.NET程序内存泄露>以及<如何写高性能的托管程序>
- How to detect and avoid memory and resources leaks in .NET applications
- Writing High-Performance Managed Applications : A Primer
有关.NET的自动内存管理机制、GC机制,垃圾回收原理等深层次内容,请仔细阅读下面的内容:
- 买书《CLR Via C#(3rd Edition)》,里面有《Memory Management》这一章专门讲述了.NET CLR的自动内存管理和垃圾回收机制
- CodeProject上的文章《Memory Management Misconceptions》有助你深入理解Root, Generation 0, 1…
@:Mainz → http://www.cnblogs.com/Mainz
®: 博文是本人当时的学习笔记及知识整理,由于自身局限错误在所难免,敬请斧正. 博文中源码只作为例子学习参考之用,不保证能运行,对后果不负任何责且无任何质保,如有不明请给我留言
©: 本文版权属于博客园和本人,版权基于署名 2.5 中国大陆许可协议发布,欢迎转载,但未经作者同意必须保留此段声明,且在文章页面明显位置给出原文连接和署名Mainz(包含链接),不得删节,否则保留追究法律责任的权利。




