[Algorithm] Permutations
Write a function that takes in an array of unique integers and returns an array of all permutations of those integers in no particular order.
If the input array is empty, the function should return an empty array.
Sample Input
array = [1, 2, 3]Sample Output
[[1, 2, 3], [1, 3, 2], [2, 1, 3], [2, 3, 1], [3, 1, 2], [3, 2, 1]]
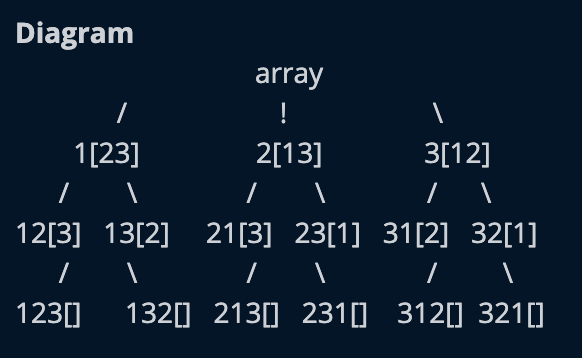
when array is empty at the end []
which is our edge case
// T: O(N! * N *N)
// S: O(N! * N)
// array filter or array concat is O(N)
function getPermutations(array) {
const perms = [];
helper(array, [], perms)
return perms
}
function helper (array, perm = [], perms = []) {
// T: O(N!)
if (!array.length && perm.length !== 0) {
perms.push(perm)
} else {
//O(N * N)
for (let i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
const newArray = array.filter((_, idx) => idx !== i); // don't mutate the array T: O(N)
const newPerm = [...perm, array[i]]; // don't mutate the perm array T: O(N)
helper(
newArray,
newPerm,
perms
)
}
}
}
// Do not edit the line below.
exports.getPermutations = getPermutations;
// Idea modify array in place
// 1. swap to get new
// 2. swap back for next iteration
// S: O (N!* N)
// T: O(N! * N)
// swap will be O(1)
function getPermutations(array) {
const perms = []
helper(0, array, perms)
return perms
}
function helper(i, array, perms) {
if (i === array.length - 1) {
perms.push([...array])
} else {
for (let j = i; j < array.length; j++) {
swap(array, i ,j);
helper(i + 1, array, perms)
swap(array, i, j);
}
}
}
function swap(array, i, j) {
const temp = array[i];
array[i] = array[j];
array[j] = temp;
}
// Do not edit the line below.
exports.getPermutations = getPermutations;


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号