[AWS SAP] Exam Tips 2 -- Continues Improvement for Existing Solutions

VPC peering is for VPC within AWS network, not for branch office.
VPN CloudHub is for low-cost connectivity between remote offices.
If you have multiple AWS Site-to-Site VPN connections, you can provide secure communication between sites using the AWS VPN CloudHub. This enables your remote sites to communicate with each other, and not just with the VPC. Sites that use AWS Direct Connect connections to the virtual private gateway can also be part of the AWS VPN CloudHub. The VPN CloudHub operates on a simple hub-and-spoke model that you can use with or without a VPC. This design is suitable if you have multiple branch offices and existing internet connections and would like to implement a convenient, potentially low-cost hub-and-spoke model for primary or backup connectivity between these remote offices.
Per the given use-case, the corporate headquarters has an AWS Direct Connect connection to the VPC and the branch offices have Site-to-Site VPN connections to the VPC. Therefore using the AWS VPN CloudHub, branch offices can send and receive data with each other as well as with their corporate headquarters.
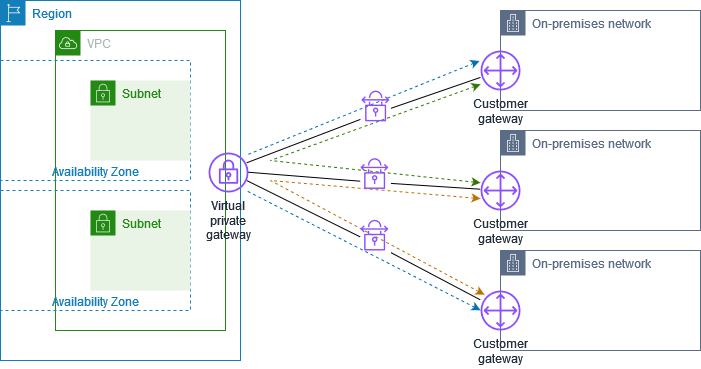
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/vpn/latest/s2svpn/VPN_CloudHub.html
A VPC peering connection is a networking connection between two VPCs that enables you to route traffic between them using private IPv4 addresses or IPv6 addresses. Instances in either VPC can communicate with each other as if they are within the same network.
VPC peering facilitates a connection between two VPCs within the AWS network, therefore this option cannot be used to send and receive data between the remote branch offices of the company.

RAID is only for EBS, not for database
Read Replicas - can help
In addition to using Read Replicas to reduce the load on your source DB instance, you can also use Read Replicas to implement a DR solution for your production DB environment. If the source DB instance fails, you can promote your Read Replica to a standalone source server. Read Replicas can also be created in a different Region than the source database. Using a cross-Region Read Replica can help ensure that you get back up and running if you experience a regional availability issue.

"The AWS Management Console is the preferred method for the in-house teams wanting to provision resources." - SDK is not best fit for Console
"Governance, complaince" - Config & CloudTrail;
Mainly in Management Console - those are mainly Management Event.
API related call "GetObject" - those are Data Event.
CloudTrail is an AWS service that helps you enable governance, compliance, and operational and risk auditing of your AWS account. Actions taken by a user, role, or an AWS service are recorded as events in CloudTrail. An event in CloudTrail is the record of activity in an AWS account. This activity can be an action taken by a user, role, or service that is monitorable by CloudTrail. CloudTrail events provide a history of both API and non-API account activity made through the AWS Management Console, AWS SDKs, command line tools, and other AWS services.
CloudTrail data events are disabled by default. You can enable logging at an additional cost. Data events are also known as data plane operations and are often high-volume activities. Data events aren't viewable in CloudTrail event history and are charged for all copies at a reduced rate compared to management events.
CloudTrail records management events for the last 90 days free of charge, and are viewable in the Event History with the CloudTrail console. For Amazon S3 delivery of CloudTrail events, the first copy delivered is free. Additional copies of management events are charged.

You can use AWS X-Ray to visualize the components of your application, identify performance bottlenecks such as the one described in the use-case for processing images and troubleshoot those requests that resulted in an error. Your Lambda functions send trace data to X-Ray, and X-Ray processes the data to generate a service map and searchable trace summaries.
 via - https://docs.aws.amazon.com/lambda/latest/dg/services-xray.html
via - https://docs.aws.amazon.com/lambda/latest/dg/services-xray.html
For an API Gateway, a "504 Gateway Timeout" error implies an "Endpoint Request Timed-out Exception".
 via - https://docs.aws.amazon.com/apigateway/api-reference/handling-errors/
via - https://docs.aws.amazon.com/apigateway/api-reference/handling-errors/
To troubleshoot an API Gateway REST API or WebSocket API that you're developing, enable execution logging and access logging to Amazon CloudWatch Logs. Execution logs contain helpful information that you can use to identify and fix most errors with your APIs. Access logs contain details about who accessed your API and how they accessed it, which you can also use for troubleshooting.
 via - https://aws.amazon.com/premiumsupport/knowledge-center/api-gateway-cloudwatch-logs/
via - https://aws.amazon.com/premiumsupport/knowledge-center/api-gateway-cloudwatch-logs/
However, neither execution logs nor access logs at the API Gateway level will provide information to identify the root cause for the "504 Gateway Timeout" error as it needs to be analyzed at the source system level which is Lambda function for the given use-case, as that's where the images are being processing and the application is lagging or timing out for some of those images. Another thing to note is that only access logs are available for HTTP APIs, so you do not have access to execution logs for the given use-case.
Therefore, both of these options are incorrect.

"message timers to set an initial invisibility period for a message"
"Delay queues let you postpone the delivery of all new messages"
You can use message timers to set an initial invisibility period for a message added to a queue. So, if you send a message with a 60-second timer, the message isn't visible to consumers for its first 60 seconds in the queue. The default (minimum) delay for a message is 0 seconds. The maximum is 15 minutes. Therefore, you should use message timers to postpone the delivery of certain messages to the queue by one minute.
Delay queues let you postpone the delivery of all new messages to a queue for several seconds, for example, when your consumer application needs additional time to process messages. If you create a delay queue, any messages that you send to the queue remain invisible to consumers for the duration of the delay period. The default (minimum) delay for a queue is 0 seconds. The maximum is 15 minutes. You cannot use delay queues to postpone the delivery of only certain messages to the queue by one minute.
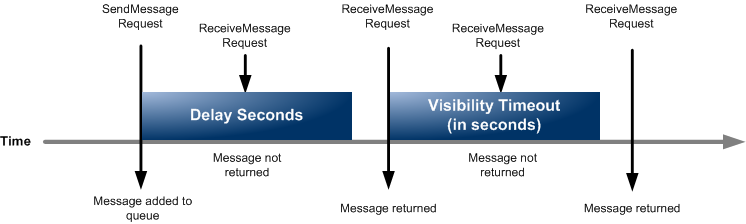
via - https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AWSSimpleQueueService/latest/SQSDeveloperGuide/sqs-delay-queues.html

To use a certificate with an Application Load Balancer for the same site in a different Region, you must request a new certificate for each Region in which you plan to use it.
AWS Certificate Manager is a service that lets you easily provision, manage, and deploy public and private Secure Sockets Layer/Transport Layer Security (SSL/TLS) certificates for use with AWS services and your internal connected resources. SSL/TLS certificates are used to secure network communications and establish the identity of websites over the Internet as well as resources on private networks. AWS Certificate Manager removes the time-consuming manual process of purchasing, uploading, and renewing SSL/TLS certificates.
A fully qualified domain name (FQDN) is the complete DNS name for a computer, website, or other resource connected to a network or to the internet. For example, aws.amazon.com is the FQDN for Amazon Web Services. An FQDN includes all domains up to the top–level domain. For example, [subdomain1].[subdomain2]...[subdomainn].[apex domain].[top–level domain] represents the general format of an FQDN.
To use a certificate with an Application Load Balancer for the same site (the same fully qualified domain name, or FQDN, or set of FQDNs) in a different Region, you must request a new certificate for each Region in which you plan to use it. To use an ACM certificate with Amazon CloudFront, you must request the certificate in the US East (N. Virginia) Region.
Therefore, to migrate the web applications to a multi-Region architecture, you must request a separate certificate for each FQDN in each AWS Region using AWS Certificate Manager and then associate the certificates with the corresponding ALBs in the relevant AWS Region.
 via - https://docs.aws.amazon.com/acm/latest/userguide/acm-regions.html
via - https://docs.aws.amazon.com/acm/latest/userguide/acm-regions.html


 via -
via - 
 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号