[SAA] 32. Data Engineering
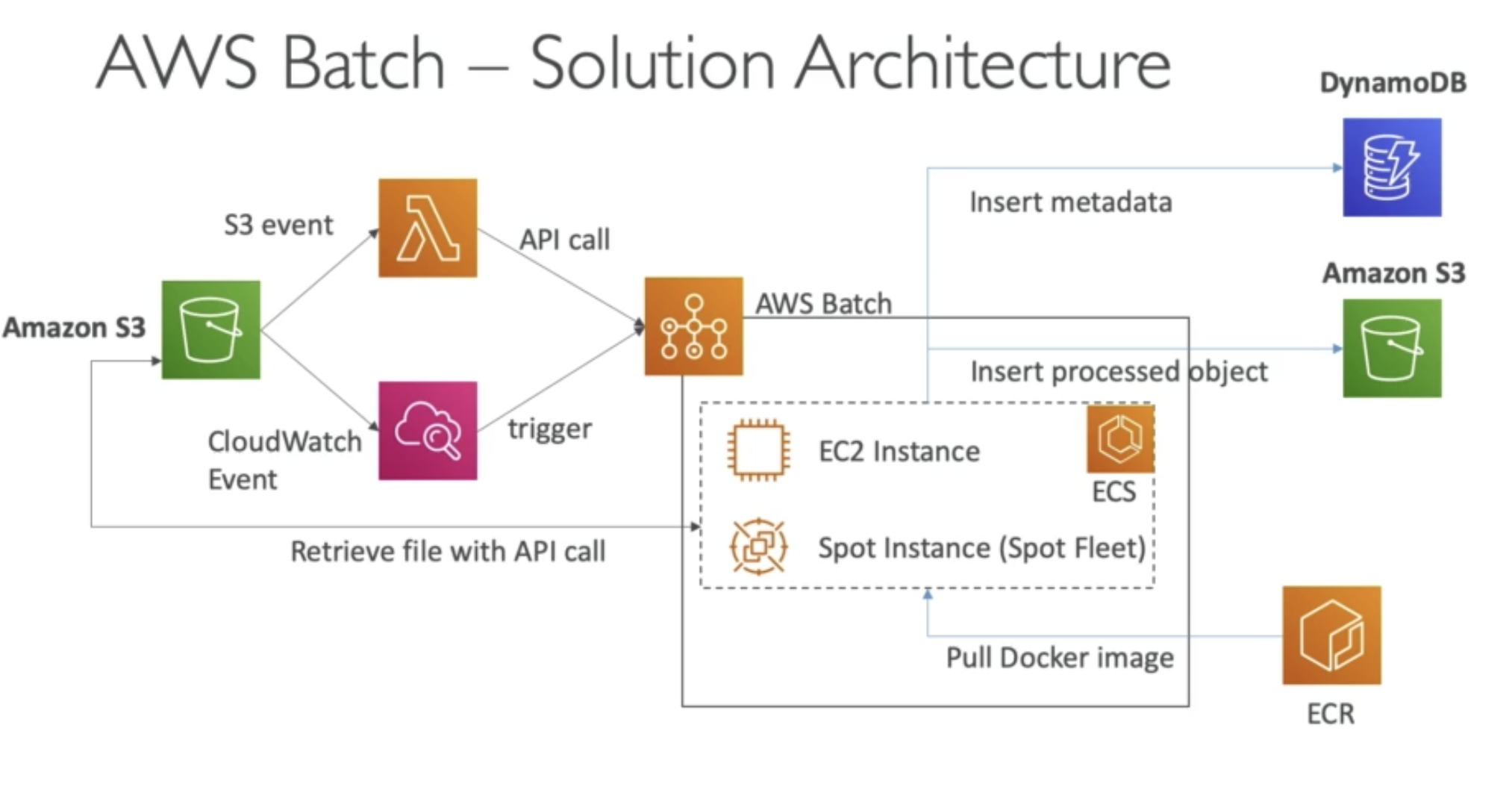
AWS Batch Overview
- Run batch jobs as Docker images
- Dynamic provisioning of the instances (EC2 & Spot Instances) - in VPC
- Optimal quantity and type based on volume and requirements
- No need to manage clusters, fully serverless
- You just pay for the underlying EC2 instance
- Example: batch process of images, running thousands of concurrent jobs
- Schedule Batch Jobs using CloudWatch Events
- Orchestrate Batch Jobs using AWS Step Functions
Lambda vs Batch
Lambda
- Time limit: 15 mins
- Limted runtime
- Limited temporary disk space
- Serverless
Batch
- No time limit
- Any runtinme as long as it's package as a Docker image
- Rely on EBS / instance store for disk space
- Relies on EC2 (can be managed by AWS)
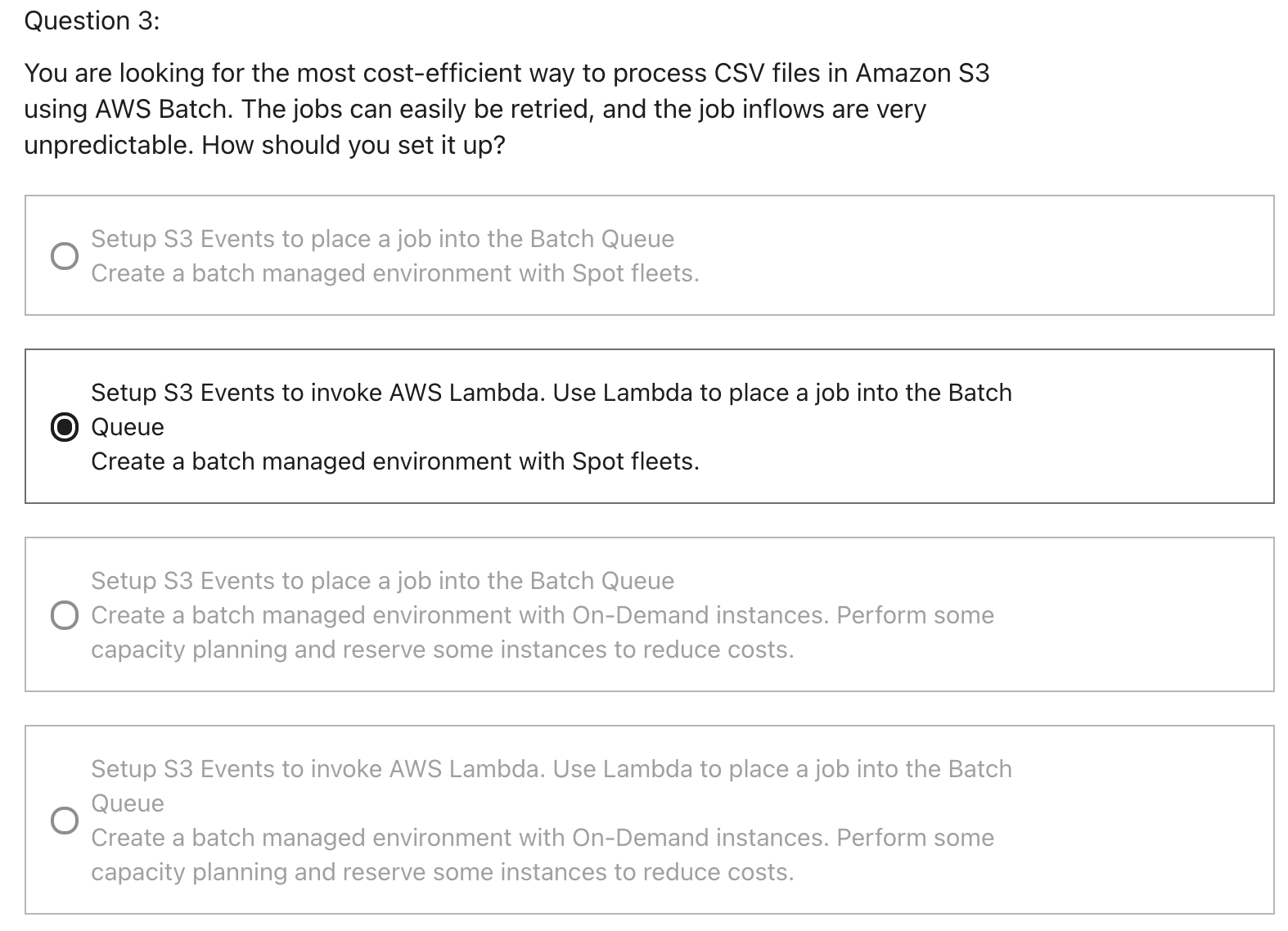
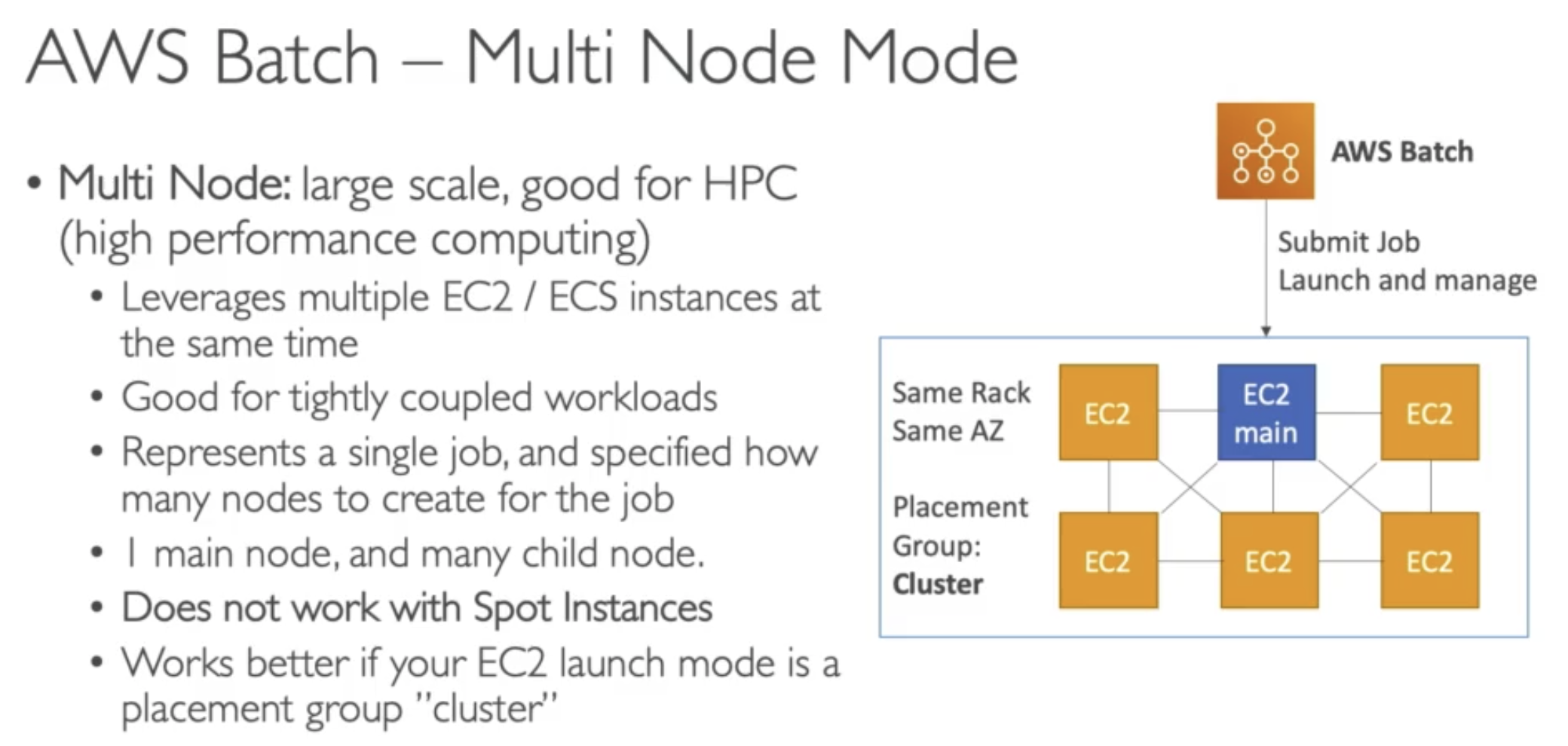
Compute Environments
Managed Compute Environment
- AWS Batch managed the capacity and instance types within the environment
- You can choose On-Demand or Spot Instance
- You can set a maximum price for Spot instance
- Launched within your own VPC
- If you launch within your own private subnet, make sure it has access to the ECS service
- Either using a NAT Gateway / instance or using VPC Endpoint for ECS
Unmanaged Compute Environment
- You control and manage instance configuration, provisioning and scaling

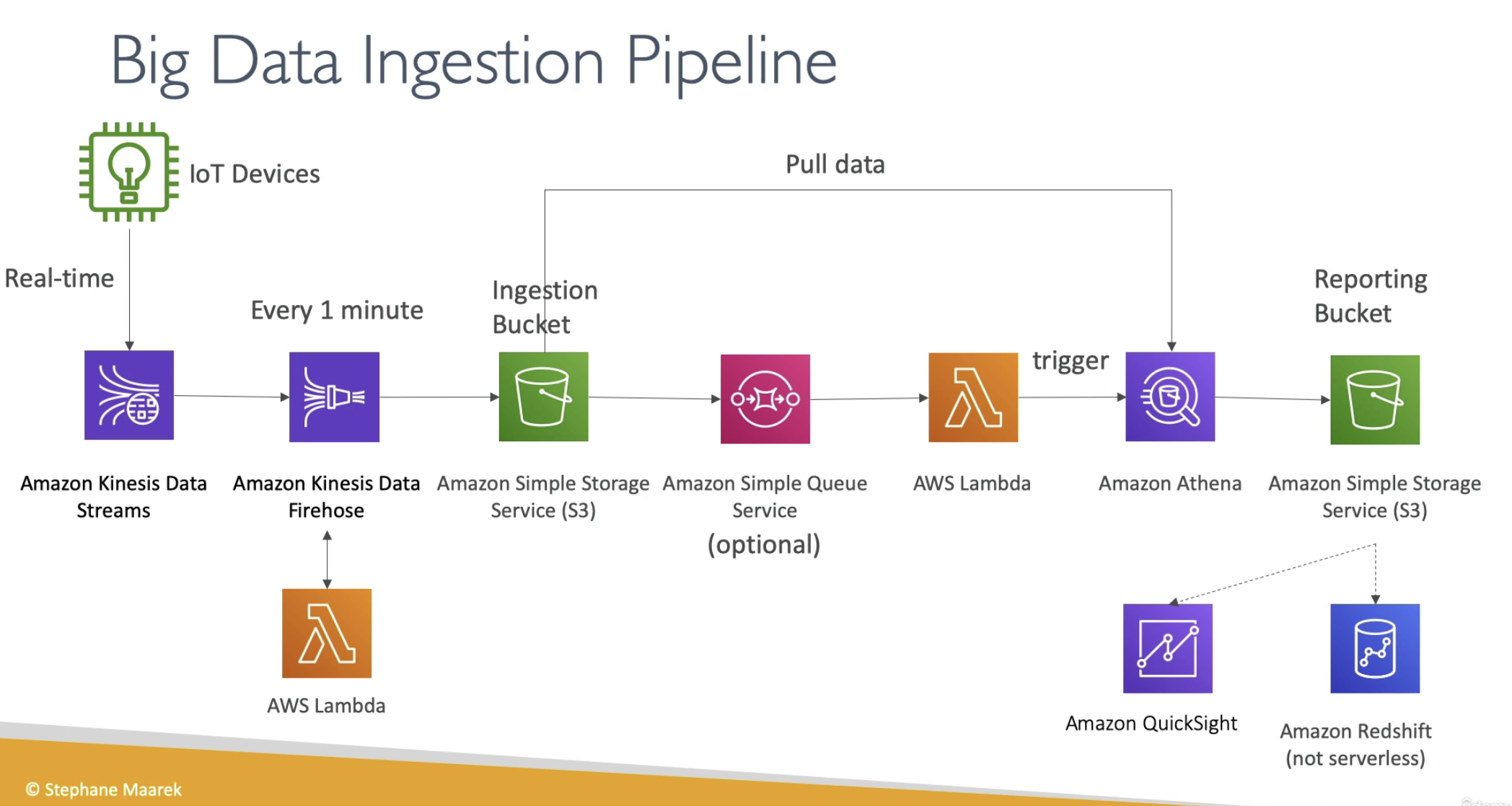
Kinesis
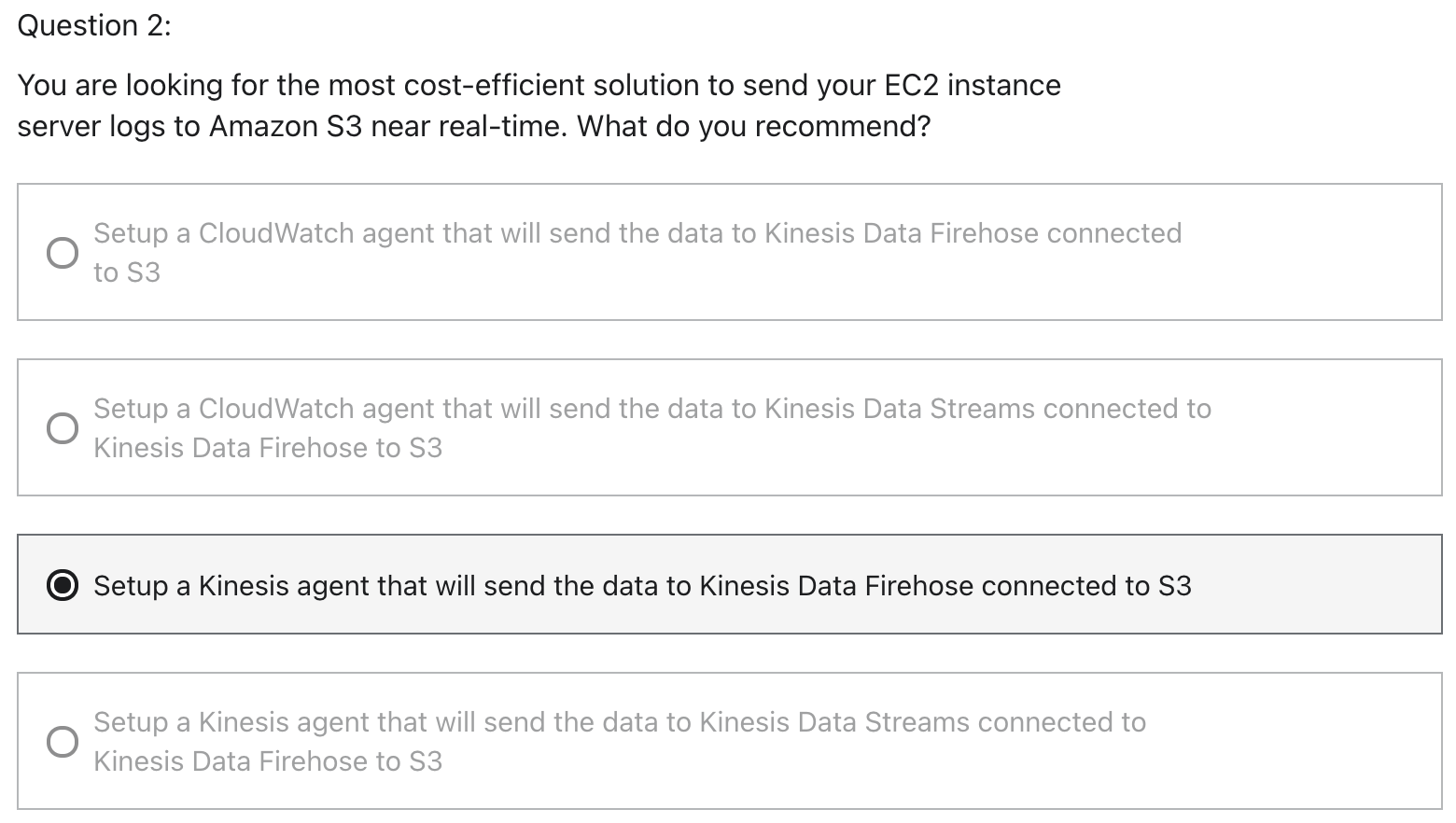
CloudWatch cannot send to Kinesis Data Firehose or Kinesis Data Streams
Near real-time: Kinesis Data Firehose
Kinesis agent can directly configured to send data to Kinesis Data Firehose
Firehose can connect to S3
Kinesis Data Firehose is near real-time
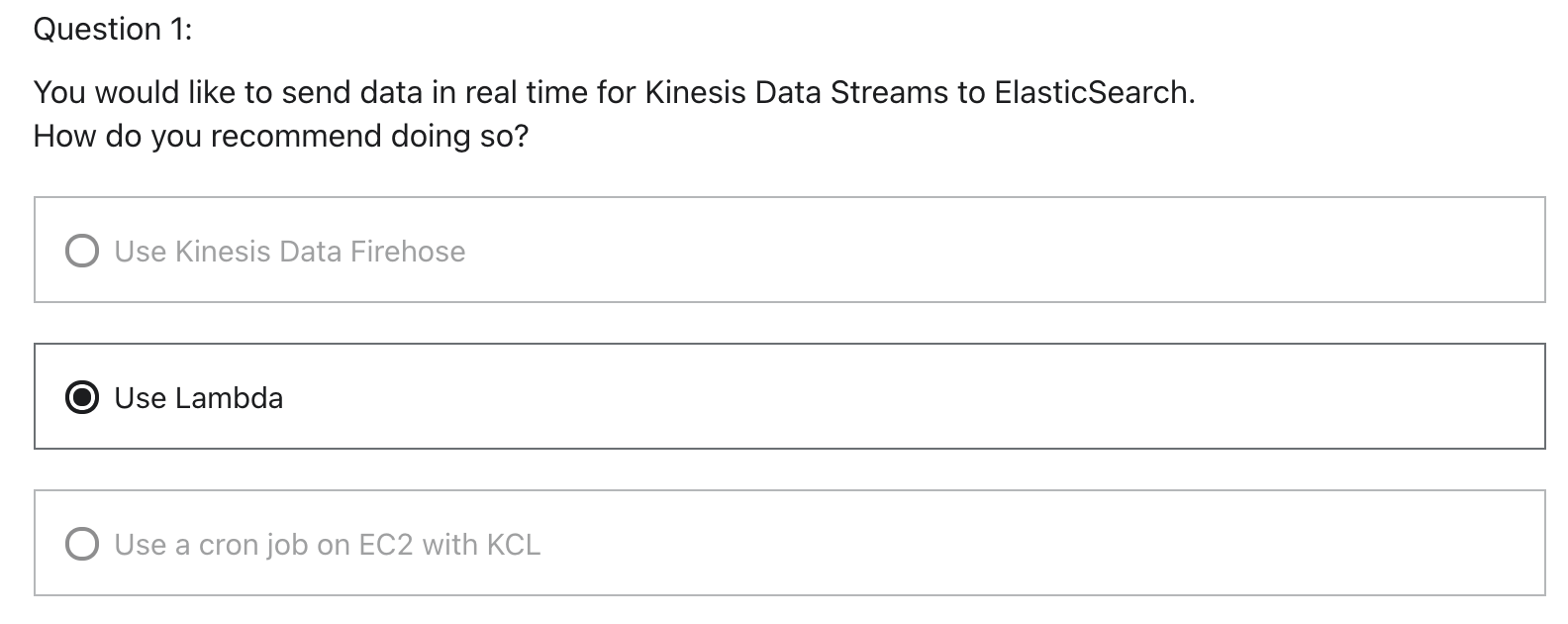
Using Lambda to send to ElasticSearch
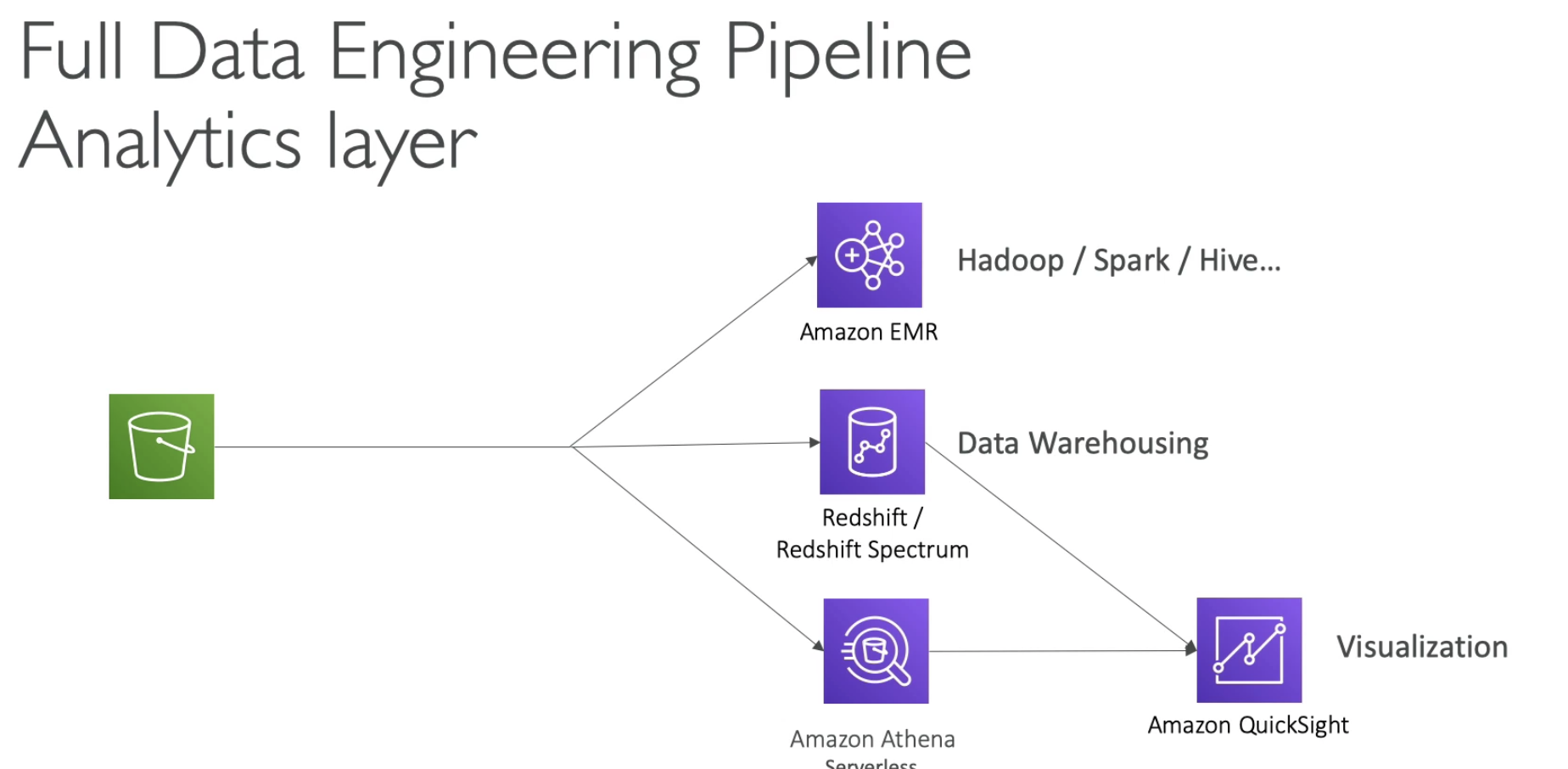
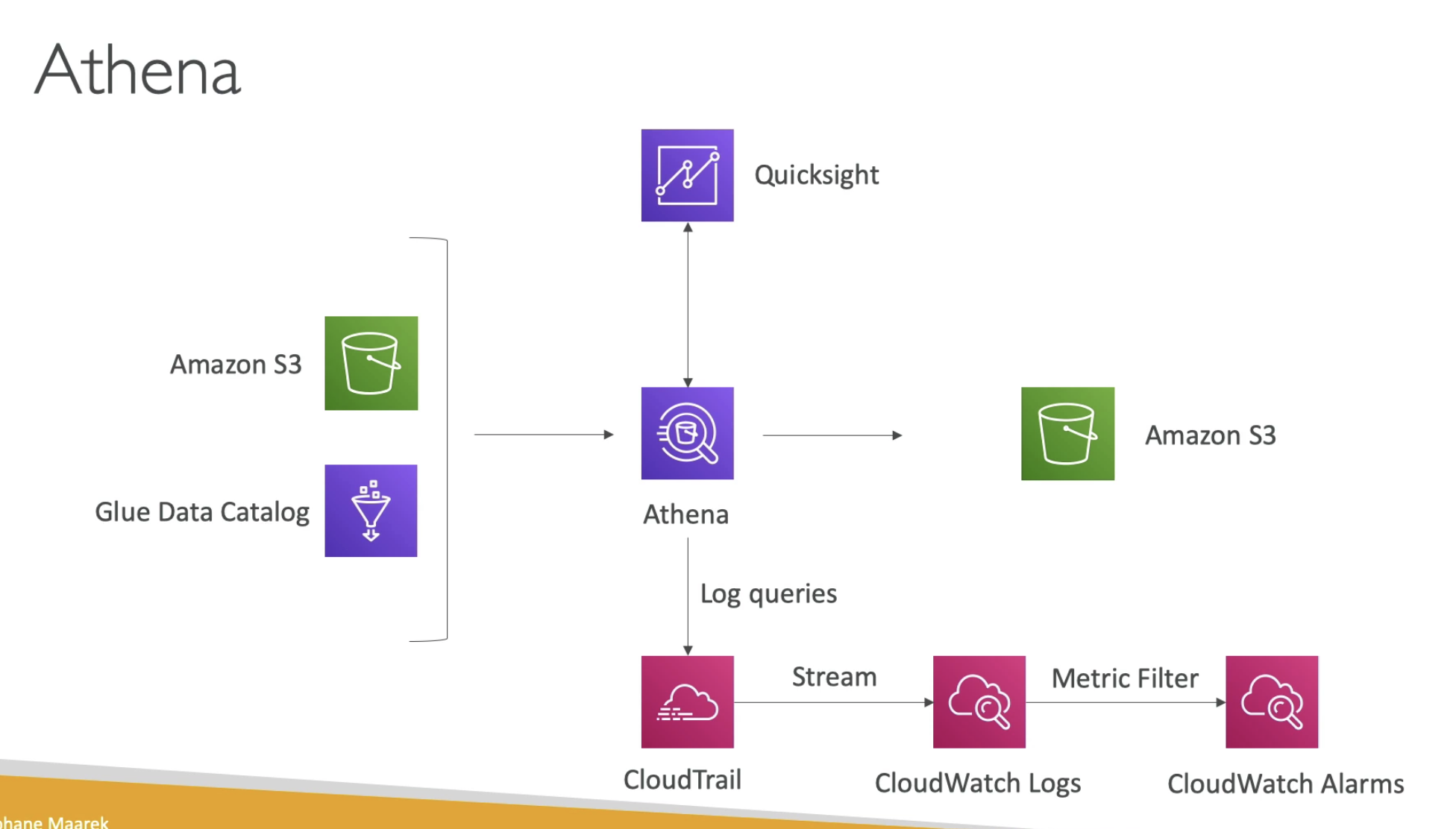
Athena
- Quicksight for visiulization dashboard
- CloudTrail can stream logs to CloudWatch

- EMR can choose to use Spot Fleet to control the cost
- Athena: data must stay in S3
- Redshift Spectrum for serverless queries on S3



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号