[SAA + SAP] 29. Disaster Recovery
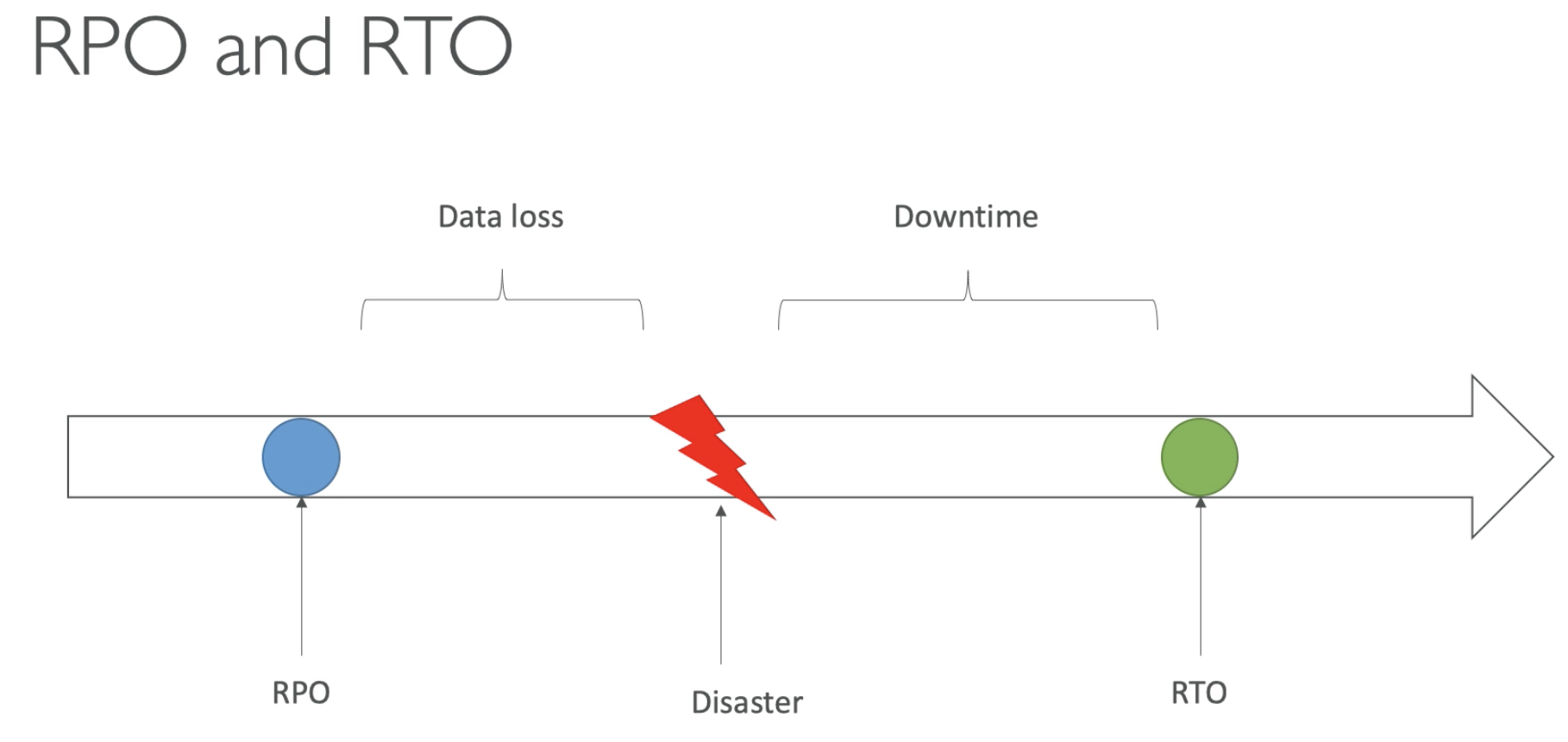
Two Terms
- RPO: Recovery Point Object
- RTO: Recovery Time Object
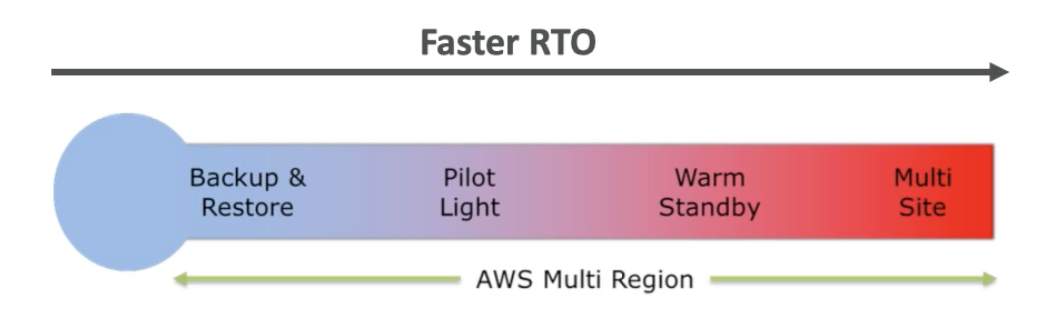
Disaster Recovery Strategies
- Backup and Restore
- Pilot Light
- Warm Standby
- Hot Site / Multi Site Approach
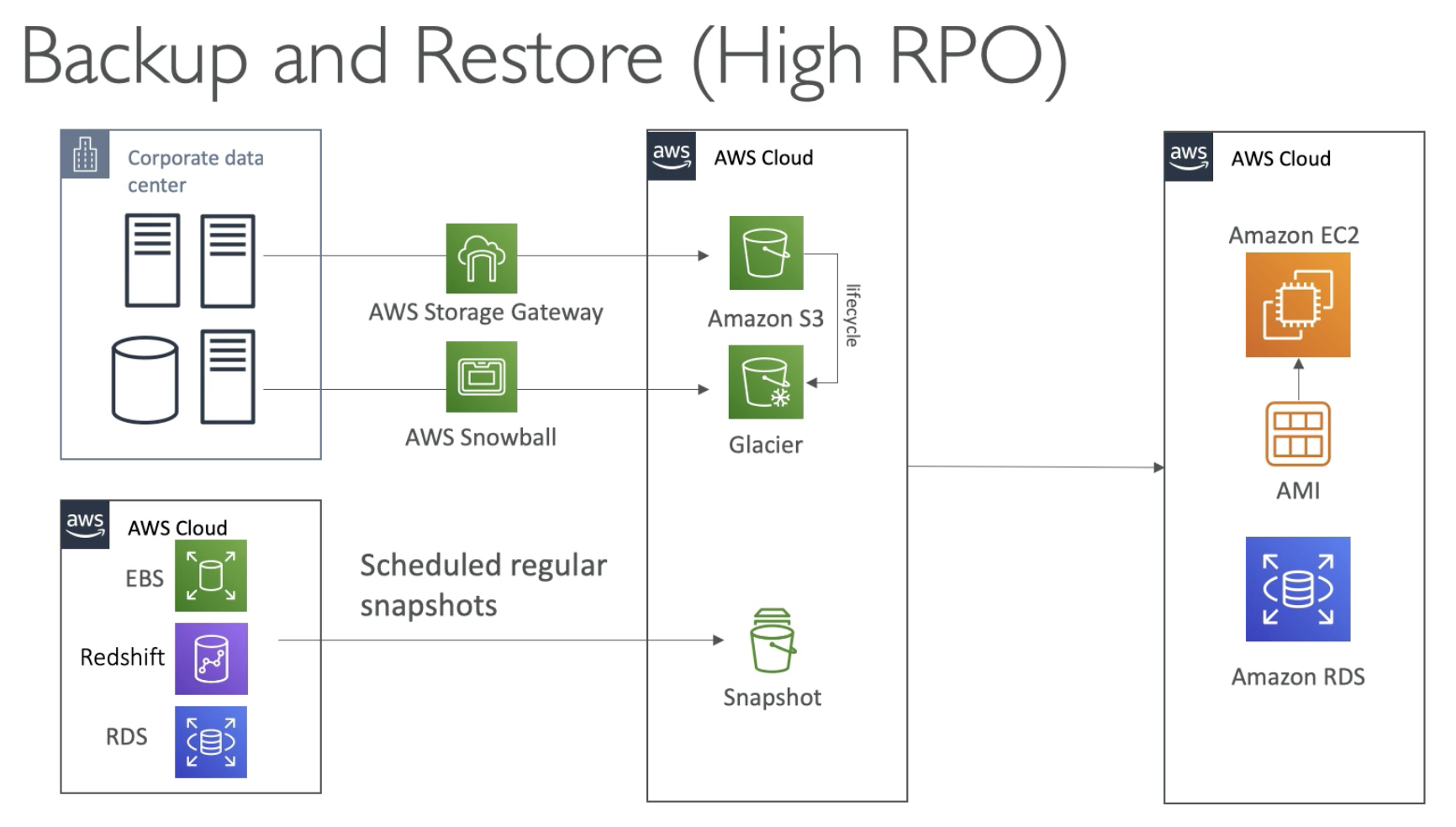
- You can backup your on-premise data into S3 / Glacier, for example, once a week through Snowball, Storgage Gateway or internet
- EBS, RDS, Redshift can be also backup into S3 as Snapshot
- For recovery:
- Create EC2 from AMI
- Get Snapshot of EBS from S3
- Restore snapshot of RDS
- High RTO
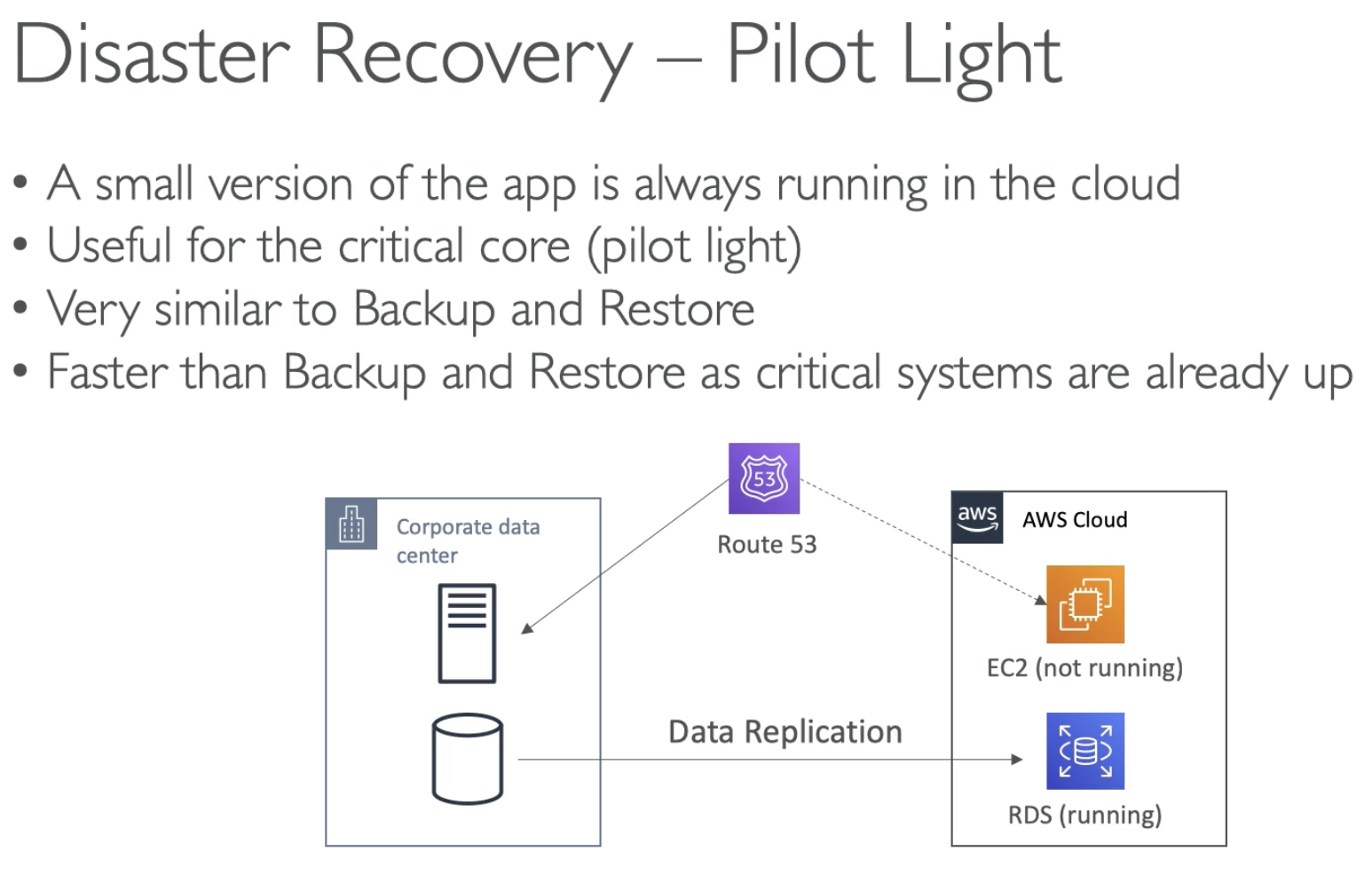
- Keep most critical part of your application running, for example, database
- Do sync data replication to RDS on the cloud
- Not infrasctures are not running in normal mode (EC2, ELB)
- Recovery:
- Using Route 53, route to new EC2
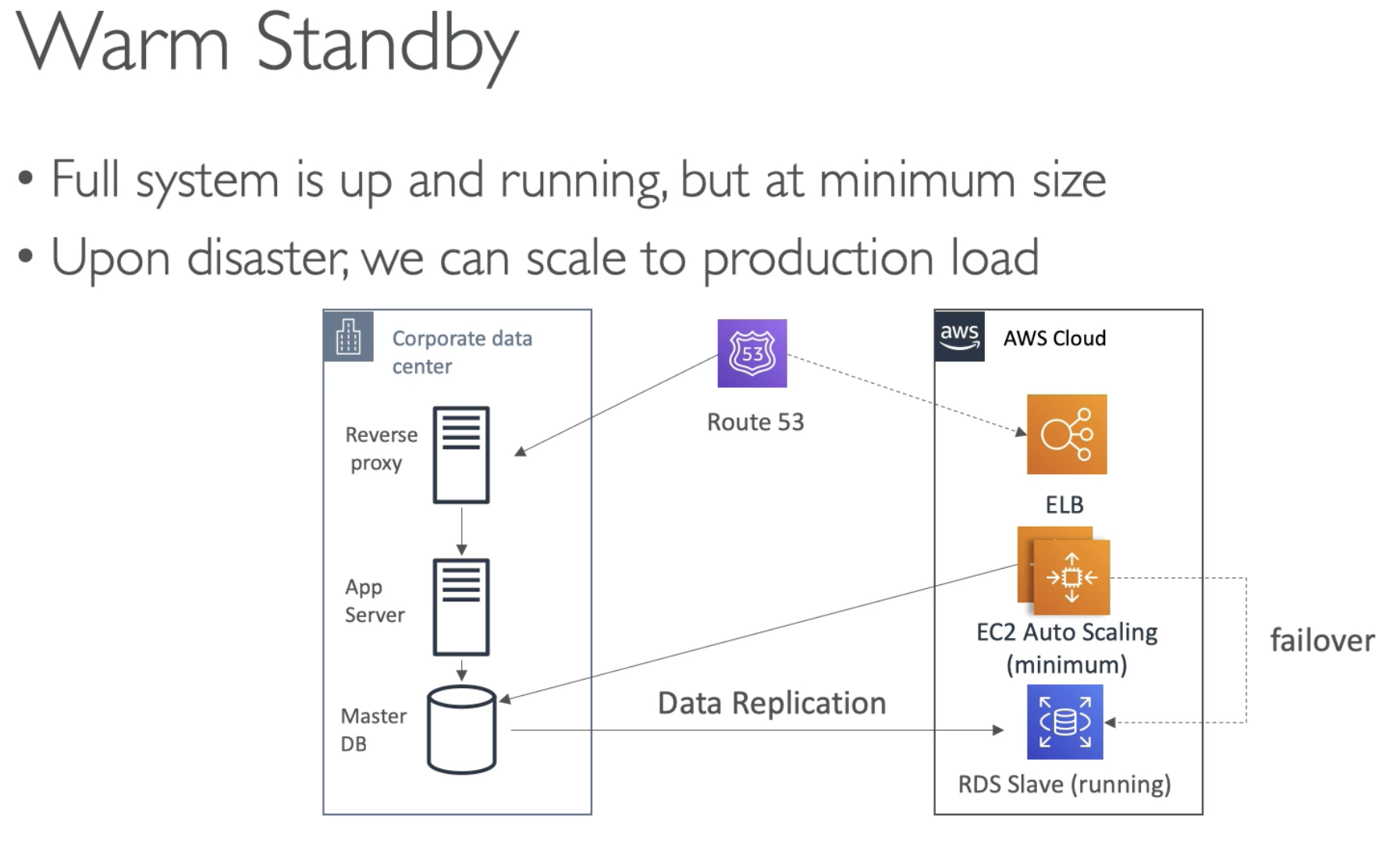
- Setup a full copy of an application
- Just set min capacity for it
- Recovery:
- Using Route 53 to point to standby ELB and modify its capacity
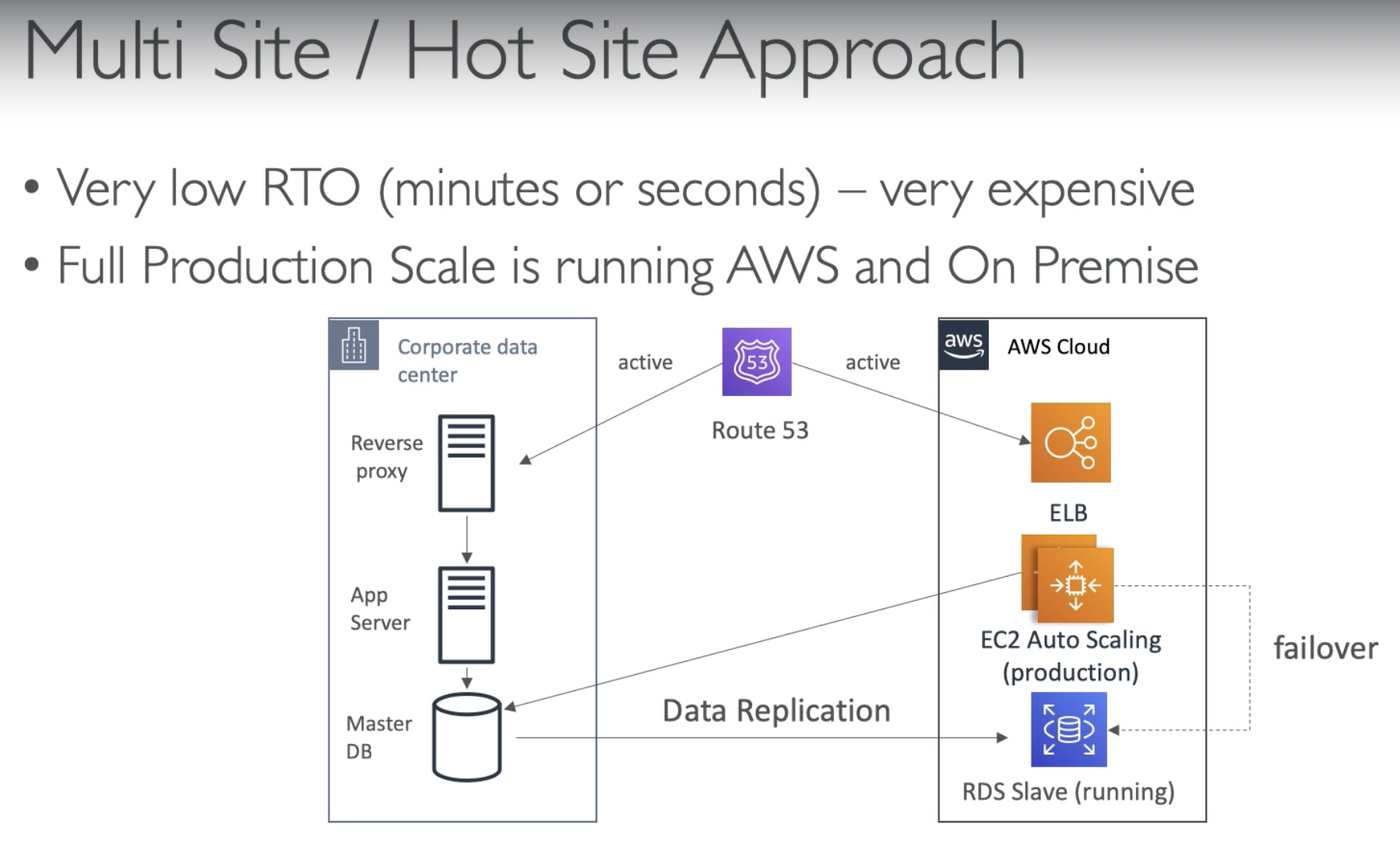
- Copy PROD application the same way as standby
- Fastest RTO
- Using Route 53 to switch DNS
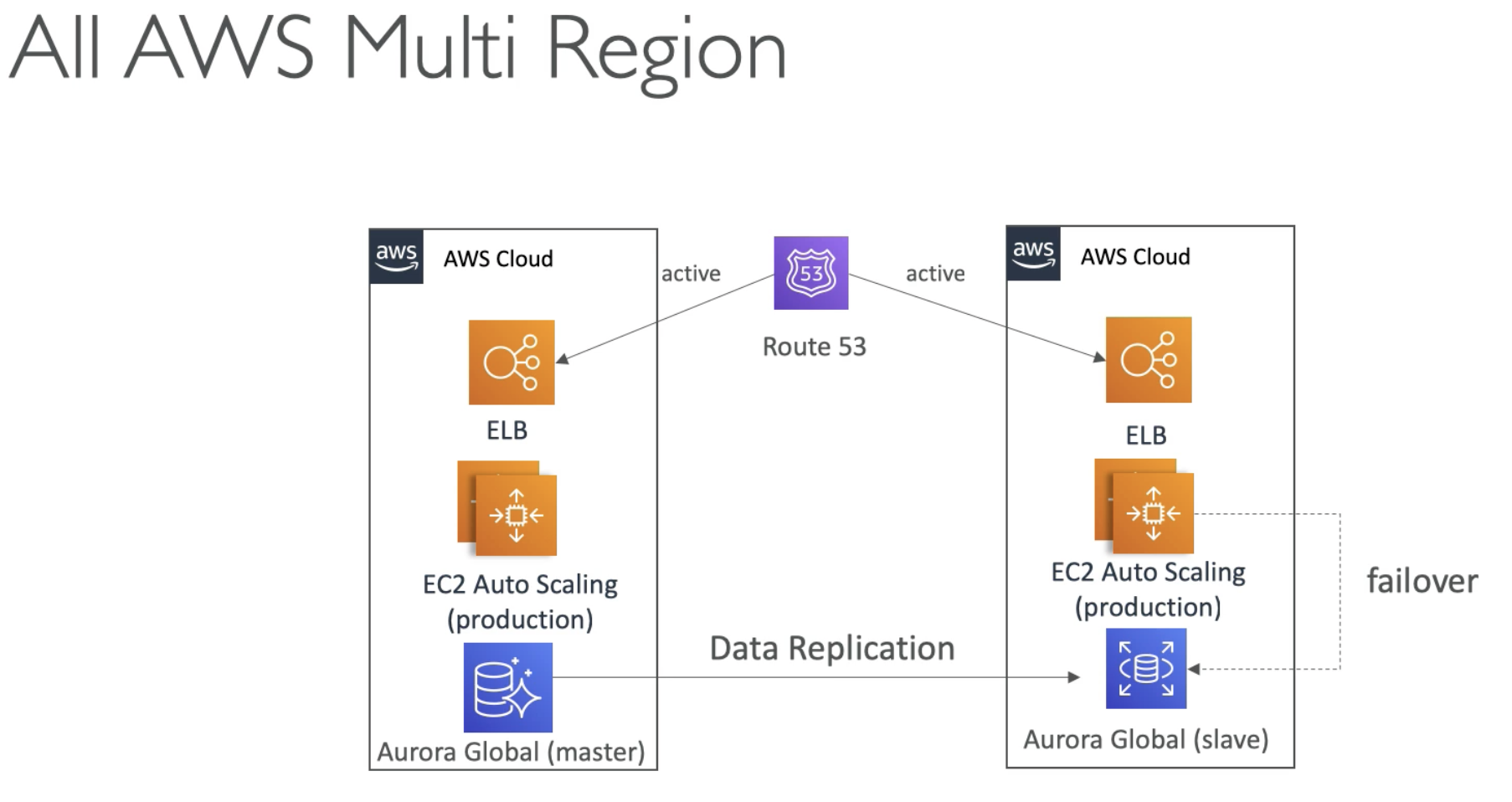
- RDS replciation cross Region
Some applications might have an additional requirement to deploy their components using multiple regions; this can be a business or regulatory requirement. Any of the preceding scenarios in this whitepaper can be deployed using separate AWS regions. The advantagesfor both production and DR scenariosinclude the following:
- You don’t need to negotiate contracts with another provider in another region
- You can use the same underlying AWS technologies across regions
- You can use the same tools or APIs







 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号