Android OpenGL ES(九)绘制线段Line Segment .
创建一个DrawLine Activity,定义四个顶点:
float vertexArray[] = { -0.8f, -0.4f * 1.732f, 0.0f, -0.4f, 0.4f * 1.732f, 0.0f, 0.0f, -0.4f * 1.732f, 0.0f, 0.4f, 0.4f * 1.732f, 0.0f, };
分别以三种模式GL_LINES,GL_LINE_STRIP,GL_LINE_LOOP 来绘制直线:
public void DrawScene(GL10 gl) { super.DrawScene(gl); ByteBuffer vbb = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(vertexArray.length*4); vbb.order(ByteOrder.nativeOrder()); FloatBuffer vertex = vbb.asFloatBuffer(); vertex.put(vertexArray); vertex.position(0); gl.glLoadIdentity(); gl.glTranslatef(0, 0, -4); gl.glEnableClientState(GL10.GL_VERTEX_ARRAY); gl.glVertexPointer(3, GL10.GL_FLOAT, 0, vertex); index++; index%=10; switch(index){ case 0: case 1: case 2: gl.glColor4f(1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f); gl.glDrawArrays(GL10.GL_LINES, 0, 4); break; case 3: case 4: case 5: gl.glColor4f(0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f); gl.glDrawArrays(GL10.GL_LINE_STRIP, 0, 4); break; case 6: case 7: case 8: case 9: gl.glColor4f(0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f); gl.glDrawArrays(GL10.GL_LINE_LOOP, 0, 4); break; } gl.glDisableClientState(GL10.GL_VERTEX_ARRAY); }
这里index 的目的是为了延迟一下显示(更好的做法是使用固定时间间隔)。前面说过GLSurfaceView 的渲染模式有两种,一种是连续不断的更新屏幕,另一种为on-demand ,只有在调用requestRender() 在更新屏幕。 缺省为RENDERMODE_CONTINUOUSLY 持续刷新屏幕。
OpenGLDemos 使用的是缺省的RENDERMODE_CONTINUOUSLY持续刷新屏幕 ,因此Activity的drawScene 会不断的执行。本例中屏幕上顺序以红,绿,蓝色显示LINES, LINE_STRIP,LINE_LOOP。
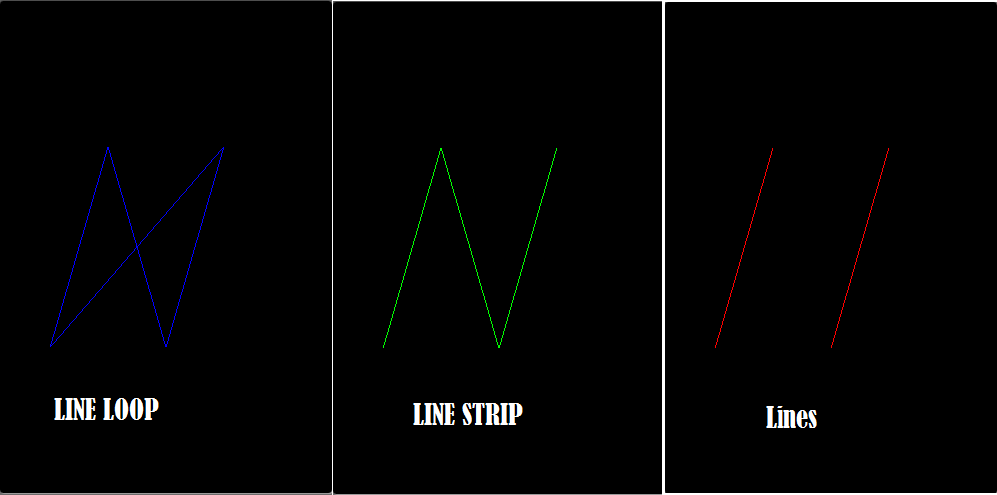
完整代码:
MainActivity.java
package com.example.gltest; import java.nio.ByteBuffer; import java.nio.ByteOrder; import java.nio.FloatBuffer; import javax.microedition.khronos.opengles.GL10; import android.opengl.GLSurfaceView; import android.os.Bundle; import android.app.Activity; import android.view.Menu; import android.view.Window; import android.view.WindowManager; public class MainActivity extends Activity implements IOpenGLDemo{ float vertexArray[] = { -0.8f, -0.4f * 1.732f, 0.0f, -0.4f, 0.4f * 1.732f, 0.0f, 0.0f, -0.4f * 1.732f, 0.0f, 0.4f, 0.4f * 1.732f, 0.0f, }; /** Called when the activity is first created. */ @Override public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); this.requestWindowFeature(Window.FEATURE_NO_TITLE); getWindow() .setFlags(WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_FULLSCREEN, WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_FULLSCREEN); mGLSurfaceView = new GLSurfaceView(this); mGLSurfaceView.setRenderer(new OpenGLRenderer(this)); setContentView(mGLSurfaceView); } // public void DrawScene(GL10 gl) { // gl.glClearColor(1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f); // // Clears the screen and depth buffer. // gl.glClear(GL10.GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT // | GL10.GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT); // // } public void DrawScene(GL10 gl) { //super.DrawScene(gl); ByteBuffer vbb = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(vertexArray.length*4); vbb.order(ByteOrder.nativeOrder()); FloatBuffer vertex = vbb.asFloatBuffer(); vertex.put(vertexArray); vertex.position(0); gl.glLoadIdentity(); gl.glTranslatef(0, 0, -4); gl.glEnableClientState(GL10.GL_VERTEX_ARRAY); gl.glVertexPointer(3, GL10.GL_FLOAT, 0, vertex); int index = 0; index ++; index%=10; switch(index){ case 0: case 1: case 2: gl.glColor4f(1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f); gl.glDrawArrays(GL10.GL_LINES, 0, 4); break; case 3: case 4: case 5: gl.glColor4f(0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f); gl.glDrawArrays(GL10.GL_LINE_STRIP, 0, 4); break; case 6: case 7: case 8: case 9: gl.glColor4f(0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f); gl.glDrawArrays(GL10.GL_LINE_LOOP, 0, 4); break; } gl.glDisableClientState(GL10.GL_VERTEX_ARRAY); } @Override protected void onResume() { // Ideally a game should implement // onResume() and onPause() // to take appropriate action when the //activity looses focus super.onResume(); mGLSurfaceView.onResume(); } @Override protected void onPause() { // Ideally a game should implement onResume() //and onPause() // to take appropriate action when the //activity looses focus super.onPause(); mGLSurfaceView.onPause(); } private GLSurfaceView mGLSurfaceView; }
OpenGLRenderer.java
package com.example.drawpointer; import javax.microedition.khronos.opengles.GL10; import android.opengl.EGLConfig; import android.opengl.GLSurfaceView.Renderer; import android.opengl.GLU; public class OpenGLRenderer implements Renderer { private final IOpenGLDemo openGLDemo; public OpenGLRenderer(IOpenGLDemo demo){ openGLDemo=demo; } public void onSurfaceCreated(GL10 gl, EGLConfig config) { // Set the background color to black ( rgba ). gl.glClearColor(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.5f); // Enable Smooth Shading, default not really needed. gl.glShadeModel(GL10.GL_SMOOTH); // Depth buffer setup. gl.glClearDepthf(1.0f); // Enables depth testing. gl.glEnable(GL10.GL_DEPTH_TEST); // The type of depth testing to do. gl.glDepthFunc(GL10.GL_LEQUAL); // Really nice perspective calculations. gl.glHint(GL10.GL_PERSPECTIVE_CORRECTION_HINT, GL10.GL_NICEST); } public void onDrawFrame(GL10 gl) { if(openGLDemo!=null){ openGLDemo.DrawScene(gl); } } public void onSurfaceChanged(GL10 gl, int width, int height) { // Sets the current view port to the new size. gl.glViewport(0, 0, width, height); // Select the projection matrix gl.glMatrixMode(GL10.GL_PROJECTION); // Reset the projection matrix gl.glLoadIdentity(); // Calculate the aspect ratio of the window GLU.gluPerspective(gl, 45.0f, (float) width / (float) height, 0.1f, 100.0f); // Select the modelview matrix gl.glMatrixMode(GL10.GL_MODELVIEW); // Reset the modelview matrix gl.glLoadIdentity(); } @Override public void onSurfaceCreated(GL10 arg0, javax.microedition.khronos.egl.EGLConfig arg1) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub } }
IOpenGLDemo.java
package com.example.gltest; import javax.microedition.khronos.opengles.GL10; public interface IOpenGLDemo { public void DrawScene(GL10 gl); }






