JAVA进阶9
间歇性混吃等死,持续性踌躇满志系列-------------第9天
1、使用throw语句抛出异常
在通常情况下,程序发生错误时系统会自动抛出异常,而有时希望程序自动抛出异常,可以使用throw语句来实现。

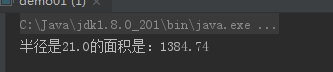
1 package code0320; 2 3 public class demo01 { 4 //定义常量(圆周率) 5 final static double PI = 3.14; 6 7 //根据半径计算圆周率面积的方法 8 public void computeArea(double r) throws Exception { 9 if (r <= 20.0) { 10 //使用throw语句抛出异常 11 throw new Exception("程序异常:\n 半径为:" + r + "\n 半径不能小于20."); 12 } else { 13 //计算圆的面积 14 double circleArea = PI * r * r; 15 System.out.println("半径是" + r + "的面积是:" + circleArea); 16 } 17 } 18 19 public static void main(String[] args) { 20 //创建对象 21 demo01 ex = new demo01(); 22 try { 23 //调用方法 24 ex.computeArea(14); 25 } catch (Exception e) { 26 //输出异常信息 27 System.out.println(e.getMessage()); 28 } 29 } 30 }
运行结果图

2、捕获单个异常
Java中捕获异常是通过try...catch...finally语句来完成的。其中try语句块是必须的,catch和finally语句块可以选择一个或者两个。try语句块是用来放置可能出现问题的语句,catch语句块用来放置异常发生后执行的代码。finally语句块用来放置无论是否发生异常都需要执行的代码。

1 package code0320; 2 3 public class demo01 { 4 public static void main(String[] args) { 5 //定义try语句块 6 try { 7 System.out.println("进入try语句块"); 8 //得到一个空的class对象 9 Class<?> clazz = Class.forName(""); 10 System.out.println("离开try语句块"); 11 }catch(ClassNotFoundException e){ 12 System.out.println("进入catch语句块"); 13 e.printStackTrace(); 14 System.out.println("离开catch语句块"); 15 }finally { 16 System.out.println("进入finally语句块"); 17 } 18 } 19 }
运行结果图

3、文件的创建与删除
可以使用File类创建一个文件对象,通常使用以下3种构造方法来创建文件对象。
①File(String pathname)
该构造方法通过将给定路径名字符串转换为抽象路径名来创建一个新的File实例。语法格式如下:
new File(String pathname)
pathname:是指路径名称(包含文件名)
FIle file = new File("D:/1.txt)
②File(String parent,String child)
该构造方法根据定义的父路径和子路径字符串(包含文件名)创建一个新的File对象。语法格式如下:
new File(String parent,String child)
parent:父路径字符串
child:子路径字符串
③File(File f,String child)
该构造方法根据parent抽象路径名和child路径名字符串创建一个新的File实例。语法格式如下:
new File(File f,String child)
f:父路径对象
child:子路径字符串
File file = new File("D:/MYWORD","word.txt");

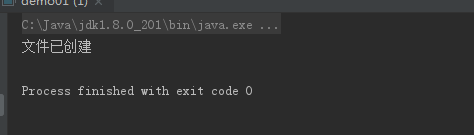
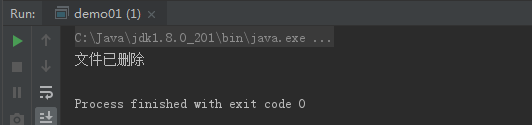
1 package code0320; 2 3 import java.io.File; 4 5 public class demo01 { 6 public static void main(String[] args) { 7 //创建文件对象 8 File file = new File("D:/myword","test.txt"); 9 //如果该文件存在 10 if (file.exists()){ 11 //将文件删除 12 file.delete(); 13 //输出的提示信息 14 System.out.println("文件已删除"); 15 }else{ 16 //如果文件不存在 17 try{ 18 //try语句块捕捉可能出现的异常 19 file.createNewFile();//创建改文件 20 //输出的提示信息 21 System.out.println("文件已创建"); 22 }catch (Exception e){ //catch处理该异常 23 //输出异常信息 24 e.printStackTrace(); 25 } 26 } 27 } 28 }
运行结果图
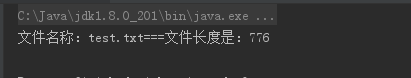
4、获取文件信息


1 package code0320; 2 3 import java.io.File; 4 5 public class demo01 { 6 public static void main(String[] args) { 7 //创建文件对象 8 File file = new File("D:/myword","test.txt"); 9 //判断该文件是否存在 10 if (file.exists()){ 11 String name = file.getName(); 12 long length = file.length(); 13 System.out.println("文件名称:"+name+"==="+"文件长度是:"+length); 14 }else{ 15 System.out.println("文件不存在"); 16 } 17 } 18 }
运行结果图
5、文件的输入/输出流

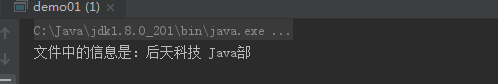
1 package code0320; 2 3 import java.io.File; 4 import java.io.FileInputStream; 5 import java.io.FileOutputStream; 6 7 public class demo01 { 8 public static void main(String[] args) { 9 //创建文件对象 10 File file = new File("D:/myword","test.txt"); 11 //捕捉异常 12 try { 13 //创建FileOutputStream对象 14 FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(file); 15 //创建byte型数组 16 byte buy[] = "后天科技 Java部".getBytes(); 17 //将数组信息写入到文件中 18 out.write(buy); 19 //将流关闭 20 out.close(); 21 }catch (Exception e){ 22 //输出异常信息 23 e.printStackTrace(); 24 } 25 try{ 26 //创建FileInputStream类对象 27 FileInputStream in = new FileInputStream(file); 28 //创建byte数组 29 byte byt[] = new byte[2048]; 30 //从文件中读取信息 31 int len = in.read(byt); 32 //将文件中的信息输出 33 System.out.println("文件中的信息是:"+new String(byt,0,len)); 34 //关闭流 35 in.close(); 36 }catch (Exception e){ 37 //输出异常信息 38 e.printStackTrace(); 39 } 40 } 41 }
运行结果图