JAVA进阶7
间歇性混吃等死,持续性踌躇满志系列-------------第7天
1、Map接口的常用方法

1 import java.util.HashMap; 2 import java.util.Map; 3 4 public class demo01 { 5 public static void main(String[] args) { 6 Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<String, String>(); 7 map.put("1", "apple"); 8 map.put("2", "pear"); 9 map.put("3", "orange"); 10 for (int i = 1; i <= 3; i++) { 11 System.out.println("第"+i+"元素是:"+map.get(""+i+"")); 12 } 13 } 14 }
运行结果图

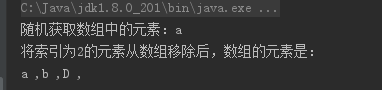
2、LinkedList类

1 import java.util.ArrayList; 2 import java.util.List; 3 4 //创建类 5 public class demo01 { 6 //主方法 7 public static void main(String[] args) { 8 // 创建集合对象 9 List list = new ArrayList(); 10 // 获得0-2之间的随机数 11 int i = (int) (Math.random()) * (list.size() - 1); 12 list.add("a"); //向集合中添加元素 13 list.add("b"); 14 list.add("C"); 15 list.add("D"); 16 System.out.println("随机获取数组中的元素:" + list.get(i)); 17 list.remove(2); //将指定索引位置的元素从集合中移除 18 System.out.println("将索引为2的元素从数组移除后,数组的元素是:"); 19 for (int j = 0; j < list.size(); j++) { 20 System.out.print(list.get(j) + " ,"); 21 } 22 } 23 }
运行结果图
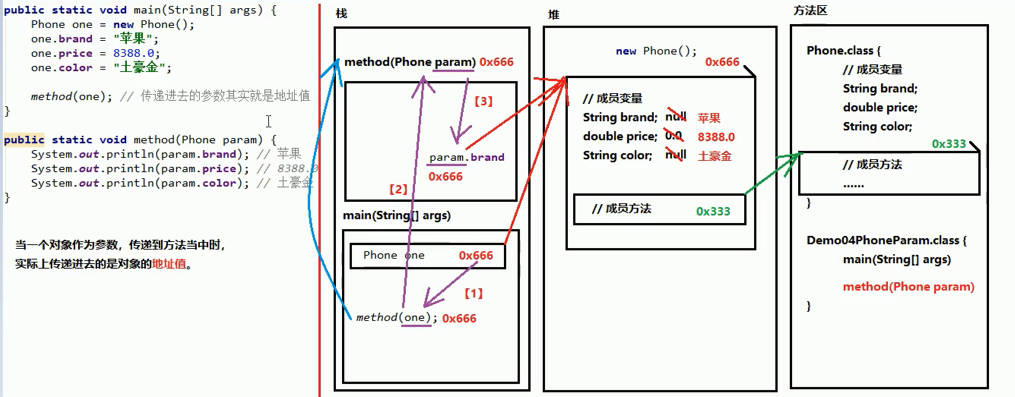
3、使用对象类型作为方法的参数

1 package cn.intcast.day06.demo01; 2 3 public class phonetwo { 4 public static void main(String[] args) { 5 phone one = new phone(); 6 one.brand = "三星"; 7 one.price = 5555.0; 8 one.color = "红色"; 9 method(one); //传递进去的参数其实就是地址值 10 } 11 public static void method(phone param){ 12 System.out.println(param.brand); 13 System.out.println(param.price); 14 System.out.println(param.color); 15 } 16 }
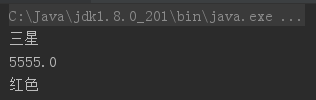
4、使用对象类型作为方法的返回值

1 package cn.intcast.day06.demo01; 2 3 public class phonetwo { 4 public static void main(String[] args) { 5 phone two = getphone(); 6 System.out.println(two.brand); 7 System.out.println(two.price); 8 System.out.println(two.color); 9 } 10 11 public static phone getphone() { 12 phone one = new phone(); 13 one.brand = "三星"; 14 one.price = 5555.0; 15 one.color = "红色"; 16 return one; 17 } 18 }
运行结果图
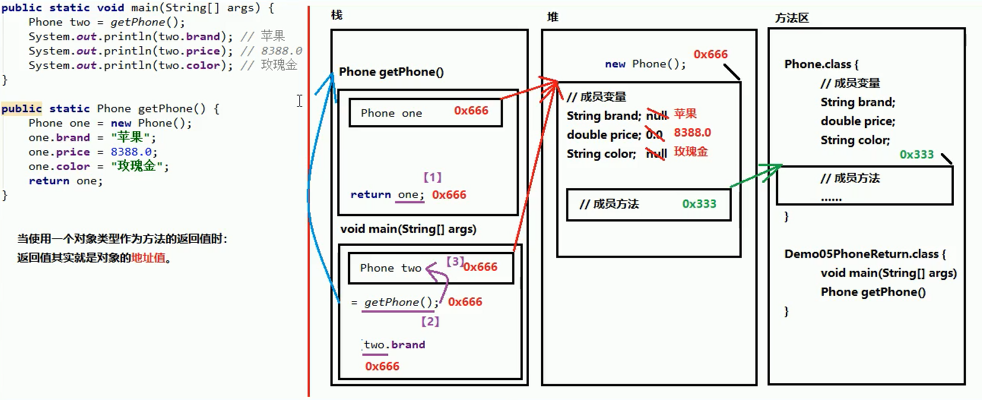
5、局部变量和成员变量的区别
①定义的位置不同
局部变量:在方法的内部
成员变量:在方法的外部,直接写在类中
②作用的范围不同
局部变量:只有方法当中才可以使用,出了方法就不能再用
成员变量:整个类全都可以通用
③默认值不同
局部变量:没有默认值,如果想使用,必须手动进行赋值
成员变量:如果没有赋值,会有默认值,规则与数组同
④内存位置不同
局部变量:位于栈内存
成员变量:位于堆内存
⑤生命周期不同
局部变量:随着方法进栈而诞生,随着方法出栈而消失
成员变量:随着对象创建而诞生,随着对象被垃圾回收而消失
6、private关键字

1 package cn.intcast.day06.demo01; 2 /* 3 * 对于boolean值的private 4 * 要用setXxx,和isXxx 5 * */ 6 public class Student { 7 private String name; 8 private int age; 9 private boolean male; 10 11 public void setMale(boolean b) { 12 male = b; 13 } 14 15 public boolean isMale() { 16 return male; 17 } 18 19 public void setName(String str) { 20 name = str; 21 } 22 23 public String getName() { 24 return name; 25 } 26 27 public void setAge(int num) { 28 if (num > 0 && num < 99) { 29 age = num; 30 } else { 31 System.out.println("数据不合理"); 32 } 33 } 34 35 public int getAge() { 36 return age; 37 } 38 39 }

1 package cn.intcast.day06.demo01; 2 3 public class dmeo07student { 4 public static void main(String[] args) { 5 Student stu = new Student(); 6 stu.setName("赵政"); 7 stu.setAge(22); 8 stu.setMale(true); 9 10 System.out.println("姓名:"+stu.getName()); 11 System.out.println("年龄:"+stu.getAge()); 12 System.out.println("是否是男生:"+stu.isMale()); 13 } 14 15 }
运行结果图
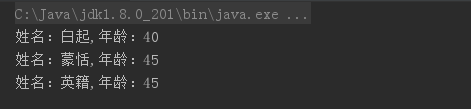
7、标准的java类


1 package cn.intcast.day06.demo01; 2 3 public class Student { 4 private String name; //姓名 5 private int age; //年龄 6 private boolean male; //性别 7 8 public Student() { 9 } 10 11 public Student(String name, int age) { 12 this.name = name; 13 this.age = age; 14 } 15 16 public String getName() { 17 return name; 18 } 19 20 public void setName(String name) { 21 this.name = name; 22 } 23 24 public int getAge() { 25 return age; 26 } 27 28 public void setAge(int age) { 29 this.age = age; 30 } 31 32 public boolean isMale() { 33 return male; 34 } 35 36 public void setMale(boolean male) { 37 this.male = male; 38 } 39 }

1 package cn.intcast.day06.demo01; 2 3 public class dmeo07student { 4 public static void main(String[] args) { 5 Student stu1 = new Student(); 6 stu1.setName("白起"); 7 stu1.setAge(40); 8 System.out.println("姓名:"+stu1.getName()+",年龄:"+stu1.getAge()); 9 Student stu2 = new Student("蒙恬",45); 10 System.out.println("姓名:"+stu2.getName()+",年龄:"+stu2.getAge()); 11 stu2.setName("英籍"); 12 System.out.println("姓名:"+stu2.getName()+",年龄:"+stu2.getAge()); 13 } 14 15 }
运行结果图