JAVA进阶3
间歇性混吃等死,持续性踌躇满志系列-------------第3天
1、局部内部类
局部内部类是指在类的方法中定义的内部类,它的作用范围也是在这个方法体内。

1 class SellOutClass{ 2 private String name; //私有成员变量 3 public SellOutClass(){ 4 name = "苹果"; //构造方法 5 } 6 public void sell(int price){ 7 class Apple{ //局部内部类 8 int innerPrice = 0; 9 public Apple(int price){ //构造方法 10 innerPrice = price; 11 } 12 public void price(){ //方法 13 System.out.println("现在开始销售"+name); 14 System.out.println("单价为:"+innerPrice+"元"); 15 } 16 } 17 Apple apple = new Apple(price); //实例化Apple类的对象 18 apple.price(); //调用局部内部类的方法 19 } 20 public static void main(String[] args){ 21 //实例化SellOutClass类的对象 22 SellOutClass sample = new SellOutClass(); 23 //调用SellOutClass类的sell()方法 24 sample.sell(200); 25 } 26 }
运行结果图

2、匿名内部类
由于匿名内部类没有名称,所以你匿名内部类使用默认构造方法来生成匿名内部类的对象,在匿名内部类定义结束后,需要加分号标识,这个分号并不代表定义内部类结束的标识,而代表创建匿名内部类的引用表达式的标识。
语法格式:
return new A(){
...//内部类体
}
例:在main()方法中编写匿名内部类去除字符串中的全部空格

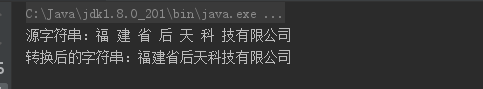
1 public class OutString{ 2 public static void main(String[] args){ 3 final String sourceStr = "福 建 省 后 天 科 技有限公司"; 4 //编写匿名内部类 5 IStringDear s = new IStringDear(){ 6 public String filterBlankChar(){ 7 String convertStr = sourceStr; 8 //替换全部空格 9 convertStr = convertStr.replaceAll(" ",""); 10 //返回转换后的字符串 11 return convertStr; 12 } 13 }; 14 //输出源字符串 15 System.out.println("源字符串:"+sourceStr); 16 //输出转换后的字符串 17 System.out.println("转换后的字符串:"+s.filterBlankChar()); 18 } 19 } 20 interface IStringDear{ 21 //声明过滤字符串中的空格的方法 22 public String filterBlankChar(); 23 }
运行结果图
3、在静态内部类中定义主方法,并访问内部类中的方法

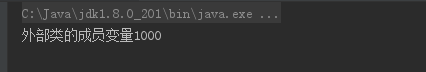
1 public class OutString{ 2 static int x = 1000; 3 static class Inner{ 4 static void doitInner(){ 5 //调用外部类的成员变量X 6 System.out.println("外部类的成员变量"+x); 7 } 8 //定义主方法 9 public static void main(String[] args){ 10 //访问内部类的方法 11 doitInner(); 12 } 13 } 14 }
运行结果图
4、标准的switch语句
注:多个case后面的数值不可以重复;
switch后面的小括号只能是下列的数据类型:
基本数据类型(byte/short/char/int)
引用数据类型 (String字符串/enum枚举);
swith语句格式可以很灵活,前后顺序可以颠倒,而且break语句还可以省略。匹配哪一个case就从哪一个位置向下执行。直到遇到break或者整体结束为止。

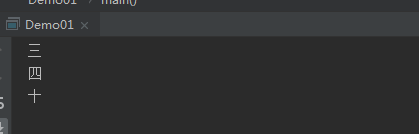
1 public class Demo01{ 2 public static void main(String[] args){ 3 int num = 2; 4 switch (num){ 5 case 1: 6 System.out.println("一"); 7 break; 8 case 2: 9 System.out.println("二"); 10 break; 11 case 3: 12 System.out.println("三"); 13 break; 14 case 4: 15 System.out.println("四"); 16 break; 17 default: 18 System.out.println("十"); 19 //最后一个break语句可以省略 20 break; 21 } 22 } 23 }
运行结果图