浅谈压缩感知(二十三):压缩感知重构算法之压缩采样匹配追踪(CoSaMP)
主要内容:
- CoSaMP的算法流程
- CoSaMP的MATLAB实现
- 一维信号的实验与结果
- 测量数M与重构成功概率关系的实验与结果
一、CoSaMP的算法流程
压缩采样匹配追踪(CompressiveSampling MP)是D. Needell继ROMP之后提出的又一个具有较大影响力的重构算法。CoSaMP也是对OMP的一种改进,每次迭代选择多个原子,除了原子的选择标准之外,它有一点不同于ROMP:ROMP每次迭代已经选择的原子会一直保留,而CoSaMP每次迭代选择的原子在下次迭代中可能会被抛弃。
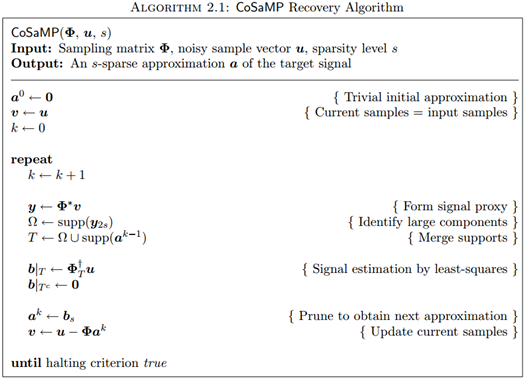


二、CS_CoSaMP的MATLAB实现(CS_CoSaMP.m)
function [ theta ] = CS_CoSaMP( y,A,K ) % CS_CoSaOMP % Detailed explanation goes here % y = Phi * x % x = Psi * theta % y = Phi*Psi * theta % 令 A = Phi*Psi, 则y=A*theta % K is the sparsity level % 现在已知y和A,求theta % Reference:Needell D,Tropp J A.CoSaMP:Iterative signal recovery from % incomplete and inaccurate samples[J].Applied and Computation Harmonic % Analysis,2009,26:301-321. [m,n] = size(y); if m<n y = y'; %y should be a column vector end [M,N] = size(A); %传感矩阵A为M*N矩阵 theta = zeros(N,1); %用来存储恢复的theta(列向量) pos_num = []; %用来迭代过程中存储A被选择的列序号 res = y; %初始化残差(residual)为y for kk=1:K %最多迭代K次 %(1) Identification product = A'*res; %传感矩阵A各列与残差的内积 [val,pos]=sort(abs(product),'descend'); Js = pos(1:2*K); %选出内积值最大的2K列 %(2) Support Merger Is = union(pos_num,Js); %Pos_theta与Js并集 %(3) Estimation %At的行数要大于列数,此为最小二乘的基础(列线性无关) if length(Is)<=M At = A(:,Is); %将A的这几列组成矩阵At else %At的列数大于行数,列必为线性相关的,At'*At将不可逆 if kk == 1 theta_ls = 0; end break; %跳出for循环 end %y=At*theta,以下求theta的最小二乘解(Least Square) theta_ls = (At'*At)^(-1)*At'*y; %最小二乘解 %(4) Pruning [val,pos]=sort(abs(theta_ls),'descend'); %(5) Sample Update pos_num = Is(pos(1:K)); theta_ls = theta_ls(pos(1:K)); %At(:,pos(1:K))*theta_ls是y在At(:,pos(1:K))列空间上的正交投影 res = y - At(:,pos(1:K))*theta_ls; %更新残差 if norm(res)<1e-6 %Repeat the steps until r=0 break; %跳出for循环 end end theta(pos_num)=theta_ls; %恢复出的theta end
三、一维信号的实验与结果
%压缩感知重构算法测试 clear all;close all;clc; M = 64; %观测值个数 N = 256; %信号x的长度 K = 12; %信号x的稀疏度 Index_K = randperm(N); x = zeros(N,1); x(Index_K(1:K)) = 5*randn(K,1); %x为K稀疏的,且位置是随机的 Psi = eye(N); %x本身是稀疏的,定义稀疏矩阵为单位阵x=Psi*theta Phi = randn(M,N); %测量矩阵为高斯矩阵 A = Phi * Psi; %传感矩阵 y = Phi * x; %得到观测向量y %% 恢复重构信号x tic theta = CS_CoSaMP( y,A,K ); x_r = Psi * theta; % x=Psi * theta toc %% 绘图 figure; plot(x_r,'k.-'); %绘出x的恢复信号 hold on; plot(x,'r'); %绘出原信号x hold off; legend('Recovery','Original') fprintf('\n恢复残差:'); norm(x_r-x) %恢复残差

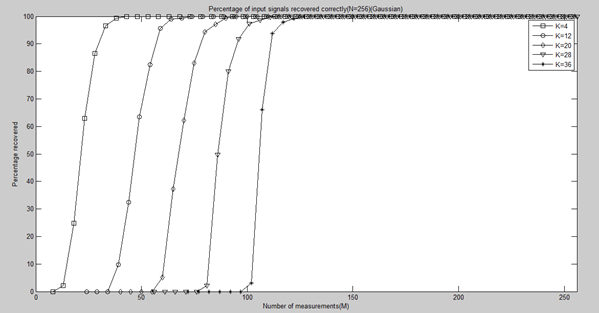
四、测量数M与重构成功概率关系的实验与结果
clear all;close all;clc; %% 参数配置初始化 CNT = 1000; %对于每组(K,M,N),重复迭代次数 N = 256; %信号x的长度 Psi = eye(N); %x本身是稀疏的,定义稀疏矩阵为单位阵x=Psi*theta K_set = [4,12,20,28,36]; %信号x的稀疏度集合 Percentage = zeros(length(K_set),N); %存储恢复成功概率 %% 主循环,遍历每组(K,M,N) tic for kk = 1:length(K_set) K = K_set(kk); %本次稀疏度 M_set = 2*K:5:N; %M没必要全部遍历,每隔5测试一个就可以了 PercentageK = zeros(1,length(M_set)); %存储此稀疏度K下不同M的恢复成功概率 for mm = 1:length(M_set) M = M_set(mm); %本次观测值个数 fprintf('K=%d,M=%d\n',K,M); P = 0; for cnt = 1:CNT %每个观测值个数均运行CNT次 Index_K = randperm(N); x = zeros(N,1); x(Index_K(1:K)) = 5*randn(K,1); %x为K稀疏的,且位置是随机的 Phi = randn(M,N)/sqrt(M); %测量矩阵为高斯矩阵 A = Phi * Psi; %传感矩阵 y = Phi * x; %得到观测向量y theta = CS_CoSaMP(y,A,K); %恢复重构信号theta x_r = Psi * theta; % x=Psi * theta if norm(x_r-x)<1e-6 %如果残差小于1e-6则认为恢复成功 P = P + 1; end end PercentageK(mm) = P/CNT*100; %计算恢复概率 end Percentage(kk,1:length(M_set)) = PercentageK; end toc save CoSaMPMtoPercentage1000 %运行一次不容易,把变量全部存储下来 %% 绘图 S = ['-ks';'-ko';'-kd';'-kv';'-k*']; figure; for kk = 1:length(K_set) K = K_set(kk); M_set = 2*K:5:N; L_Mset = length(M_set); plot(M_set,Percentage(kk,1:L_Mset),S(kk,:));%绘出x的恢复信号 hold on; end hold off; xlim([0 256]); legend('K=4','K=12','K=20','K=28','K=36'); xlabel('Number of measurements(M)'); ylabel('Percentage recovered'); title('Percentage of input signals recovered correctly(N=256)(Gaussian)');



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号