中国剩余定理(CRT / EXCRT)
中国剩余定理(CRT)
中国剩余定理是用于求解诸如:
$ $ $ $ $ $ $ $ 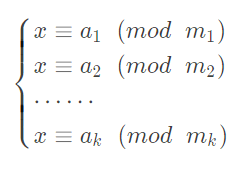
形式的同余方程组的定理。其中 \(m_1, m_2 ... m_k\) 是两两互质的整数。
解法
设:
统计答案:
栗子
今有物不知其数,三三数之剩二(除以三余二),五五数之剩三(除以五余三),七七数之剩二(除以七余二)。问物几何?
根据刚才的算法来解决此问题:
\(1.\) 从 \(3\) 和 \(5\) 的公倍数中找到被 \(7\) 除余 \(1\) 的最小数 \(15\),从 \(3\) 和 \(7\) 的公倍数中找出被 \(5\) 除余 \(1\) 的最小数 \(21\),从 \(5\) 和 \(7\) 的公倍数中找出被 \(3\) 除余 \(1\) 的最小数 \(70\)。
\(2.\) 用 \(15\) 乘以 \(2\)(除以 \(7\) 的余数),\(21\) 乘以 \(3\)(除以 \(5\) 的余数),\(70\) 乘以 \(2\)(除以 \(3\) 的余数)。三个乘积相加得到 \(15 * 2 + 21 * 3 + 70 * 2 = 233\)。
\(3.\) 用 \(233\) 除以 \(3, 5, 7\) 三个数的最小公倍数 \(105\),得到的余数 \(23\) 就是该问题的答案。
Code
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#define LL long long
using namespace std;
const int N = 233333;
LL n, x, y, ans = 0, Mul = 1, a[N], m[N], M[N], inv[N];
void exgcd(LL a, LL b)
{
if(b == 0) { x = 1, y = 0; return ; }
exgcd(b, a % b);
LL tx = x;
x = y, y = tx - (a / b) * y;
}
int main()
{
scanf("%lld", &n);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
scanf("%lld%lld", &m[i], &a[i]), Mul *= m[i];
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
M[i] = Mul / m[i];
exgcd(M[i], m[i]);
x = (x % m[i] + m[i]) % m[i];
ans += x * a[i] * M[i];
}
printf("%lld", ans % Mul);
return 0;
}
扩展中国剩余定理(EXCRT)
扩展中国剩余定理是用于求解诸如:
$ $ $ $ $ $ $ $ 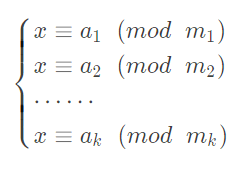
形式的同余方程组的定理。其中 \(m_1, m_2 ... m_k\) 是不一定两两互质的整数。
解法
假设已经求出前 \(k-1\) 个方程组成的同余方程组的解为 \(x\),且有
(其实这里的连乘不是连乘,而是取这些数的最小公倍数)
则前 \(k-1\) 个方程的通解为 \(x+iM\)(\(i\) 是整数)
考虑加入第 \(k\) 个方程:我们需要求一个正整数 \(t\),使得
转化后的该式右边可以看做常数,因此能使用 exgcd 求解。若对于某一个 \(k\),该方程无解,则这组数据无解。
注意做乘法时可能会爆,需要“龟速乘”。
Code
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#define LL long long
using namespace std;
const int N = 2333333;
LL n, x, y, M = 1, ans = 0, m[N], a[N];
LL gcd(LL x1, LL y1) { y1 == 0 ? x1 : gcd(y1, x1 % y1); }
void exgcd(LL a, LL b)
{
if(b == 0) { x = 1, y = 0; return ; }
exgcd(b, a % b);
LL tx = x;
x = y, y = tx - (a / b) * y;
}
LL mul(LL a, LL b, LL mod)
{
LL res = 0;
while(b)
{
if(b & 1) res = (res + a) % mod;
a = (a + a) % mod;
b >>= 1;
}
return res;
}
int main()
{
scanf("%lld", &n);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) scanf("%lld%lld", &m[i], &a[i]);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
x = y = 0;
LL A = M, B = m[i], C = ((a[i] - ans) % B + B) % B;
exgcd(A, B);
LL Gcd = gcd(A, B), bg = B / Gcd;
x = mul(x, C / Gcd, bg);
ans = ans + x * M;
M *= bg;
ans = (ans % M + M) % M;
}
printf("%lld", (ans % M + M) % M);
return 0;
}



【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】凌霞软件回馈社区,博客园 & 1Panel & Halo 联合会员上线
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步