JAVA_Collection容器
因为项目的需要,今天抽时间把JAVA中的容器复习了一下,为了以后的不时之需,现在把它记下来。
容器有其名,知其意,用来盛放数据的集合,JAVA中为我们提供了三种容器类:set、list、map,三种容器之间既有联系又有区别,首先它们均继承了Collection容器,区别在于:set容器存储数据类似于集合,里面的数据之间没有顺序,不能重复;list容器中的数据有序,并且数据可以重复;最后map容器是一种通过键值对进行的存储,所以map容器要求键值不能重复。
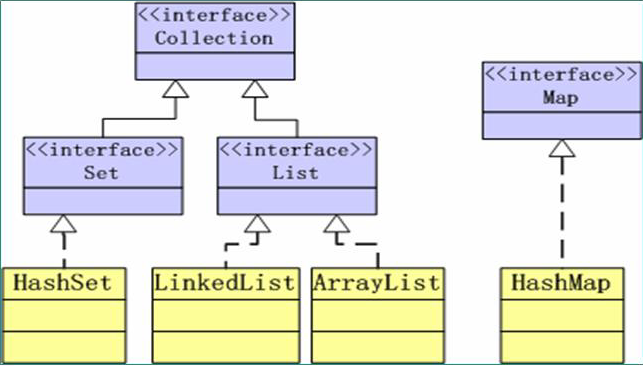
通过这个图相信大家一定能够对JAVA容器有一个很好地认识。
接下来让我们一起看几个例子:
第一个:HashSet、LinkedList、ArrayList、Interator的介绍
public class hashset { public static void main(String[] args) { Collection c = new HashSet(); c.add("one"); c.add("two"); c.add("three"); c.add("four"); c.add("five"); Iterator it = c.iterator(); while(it.hasNext()){ System.out.println(it.next()); } } }
输出结果:(HashSet存储里面的数据是无序的)
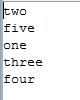
public class linkedlist { public static void main(String[] args) { Collection c = new LinkedList(); c.add("one"); c.add("two"); c.add("three"); c.add("four"); c.add("five"); Iterator it = c.iterator(); while(it.hasNext()){ System.out.println(it.next()); } } }
输出结果:
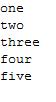
public class hashset { public static void main(String[] args) { Collection c = new HashSet(); c.add("one"); c.add("two"); c.add("three"); c.add("four"); c.add("five"); Iterator it = c.iterator(); while(it.hasNext()){ System.out.println(it.next()); } } }
输出结果:
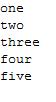
public class object_interator { public static void main(String [] args){ Collection c = new ArrayList(); //特别注意,add添加的均要为Object对象 c.add(new student("张生", "男")); c.add(new student("王二", "男")); c.add(new student("莉莉", "女")); c.add(new student("小明", "男")); Iterator it = c.iterator(); while(it.hasNext()){ student stu = (student)it.next();//特别注意it.next()获得的是一个Object对象,一定要转化为指定的对象,然后进行操作 System.out.println(stu);//默认调用其toString()方法 } } } //定义的一个student对象 class student{ public String name; public String sex; //无参构造方法 public student(){} //有参构造方法 public student(String name, String sex){ this.name = name; this.sex = sex; } public String getname(){ return name; } public String getsex(){ return sex; } //从写其toString()方法 public String toString(){ return "姓名:"+name+" 性别:"+sex; } }
下面简单介绍一下SDK1.5提出的增强for循环:
public class addFor { public static void main(String[] args) { int arr [] = {1,2,3,4,5}; for(int i=0; i<arr.length;i++){ System.out.println("传统的输出:"+arr[i]); } System.out.println(""); for(int i : arr){ System.out.println("增强的for循环输出:"+i); } System.out.println(""); Collection c = new ArrayList(); c.add(new String("aaa")); c.add(new String("bbb")); c.add(new String("ccc")); c.add(new String("ddd")); for(Object o : c){ System.out.println(o);//默认调用其toString()方法 } } }
对于List容器JAVA给出了一种处理内部数据的方法:Collections,下面简单给大家分享一下我的理解:
public class list_fix { public static void main(String [] args){ List li = new ArrayList(); for(int i = 0; i<=5; i++){ li.add("a"+i); } System.out.println("处理前:"+li); Collections.reverse(li);//逆序排列 System.out.println(li); Collections.shuffle(li);//随机排列 System.out.println(li); Collections.sort(li);//排序 System.out.println(li); int n = Collections.binarySearch(li, "a5");//基于二分法的查找 System.out.println("a5的位置:"+n); } }
输出结果:

到这里我想大家估计已经对容器有了一定的了解,如果你有更好的认识还望大家赐教。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号