微服务入门04 服务发现和消费
创建项目
这里创建一个名为MsgService的普通webApi项目
- 1.设置命令行读取配置文件 见02
- 2 consul服务注册 见03
- 3.创建一个心跳检测的controller 见03
- 4 创建一个测试用例的controller
[Route("api/[controller]")]
public class SMSController : ControllerBase
{
//发请求,报文体为{phoneNum:"110",msg:"aaaaaaaaaaaaa"},
[HttpPost(nameof(Send_MI))]
public void Send_MI(SendSMSRequest model)
{
Console.WriteLine($"通过小米短信接口向{model.PhoneNum}发送短信{model.Msg}");
}
[HttpPost(nameof(Send_LX))]
public void Send_LX(SendSMSRequest model)
{
Console.WriteLine($"通过联想短信接口向{model.PhoneNum}发送短信{model.Msg}");
}
[HttpPost(nameof(Send_HW))]
public void Send_HW(SendSMSRequest model)
{
Console.WriteLine($"通过华为短信接口向{model.PhoneNum}发送短信{model.Msg}");
}
}
启动项目
编译运行这个项目后 在bin下启动这个项目多个
我在这里启动了两个分别设置了5001 和5002两个端口
再把consul以开发模式运行 访问http://127.0.0.1:8500
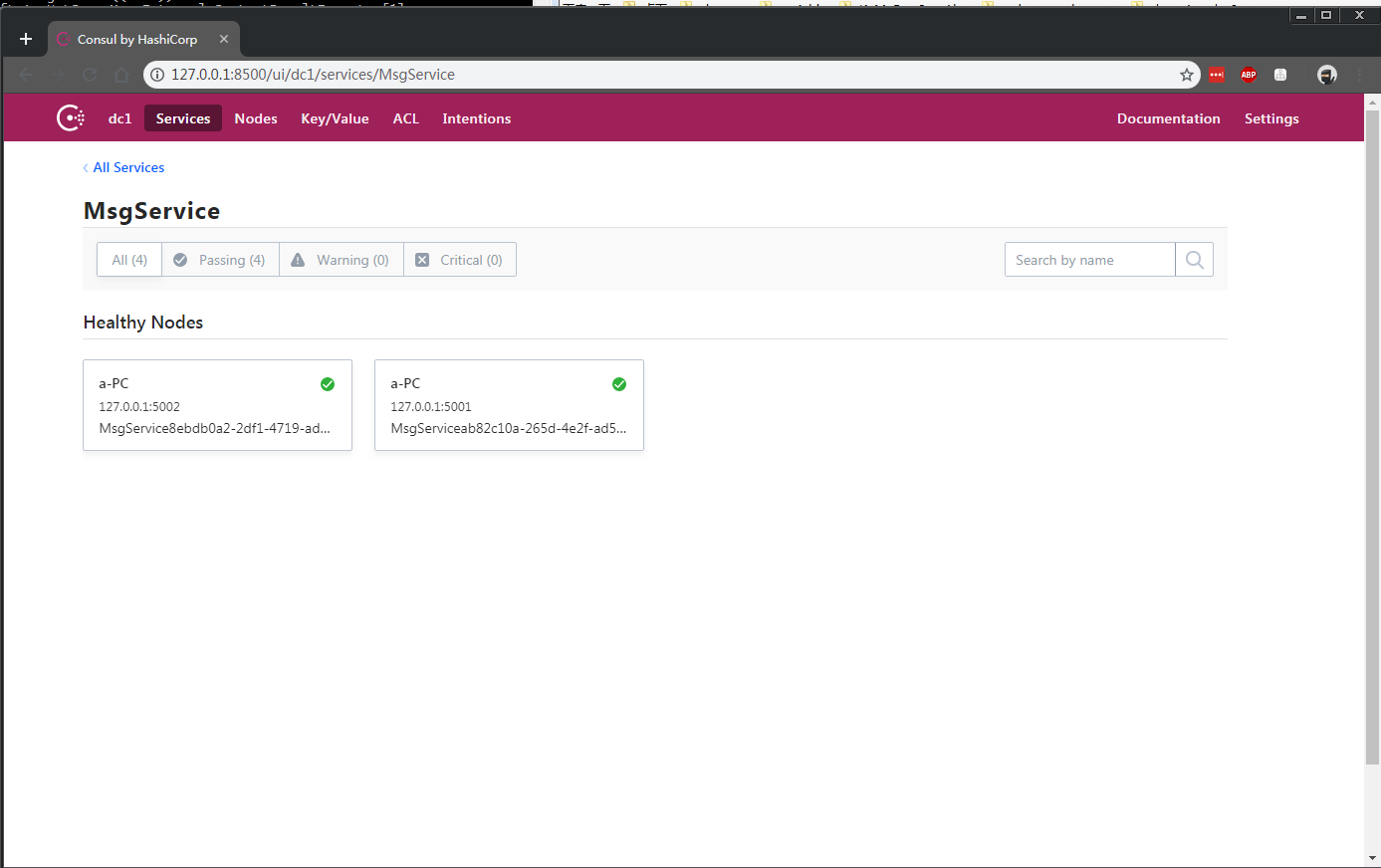
这时候这两个服务就被consul"发现"了
服务消费
这里用一个控制台程序演示
install-package consul
打印出所有的登记的consul
using (var consulClient = new ConsulClient(c => c.Address = new Uri("http://127.0.0.1:8500")))
{
var services = consulClient.Agent.Services().Result.Response;
foreach (var service in services.Values)
{
Console.WriteLine($"id={service.ID},name={service.Service},ip={service.Address},port={service.Port}");
}
}
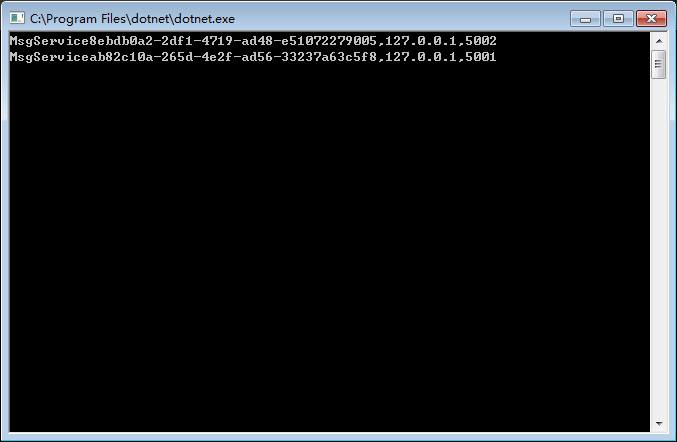
这里已经开启了两个msg服务,演示默认访问第一个msg
实际项目中可能是更多个msg一起运行,要访问哪个msg(每个msg服务都是相同的,可能每个msg服务都在不同的机器上) 就要考虑到负载均衡来分配由哪个msg服务来调度
var json = "{\"PhoneNum\":119,\"Msg\":\"aaaa\"}";
using (var consul = new ConsulClient((m) =>
{
m.Address = new Uri("http://127.0.0.1:8500");
}))
{
//所有注册到consul的service
var services = consul.Agent.Services().Result.Response;
var msgServices = services.Values.Where(m => m.Service.Equals("MsgService", StringComparison.OrdinalIgnoreCase));
var service = msgServices.ElementAt(0);
try
{
using (HttpClient http = new HttpClient())
using (var httpContent = new StringContent(json, Encoding.UTF8, "application/json"))
{
var result = http.PostAsync($"http://{service.Address}:{service.Port}/api/sms/send_lx", httpContent).Result;
Console.WriteLine(result.StatusCode);
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine(ex.ToString());
}
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号