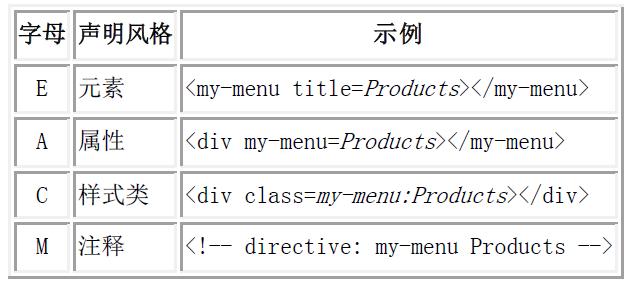
AngularJS1.X指令
<!DOCTYPE html> <html ng-app='myApp'> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <script src="https://cdn.staticfile.org/angular.js/1.4.6/angular.min.js"></script> </head> <body> <div ng-controller="listCtrl"> <input type="text" ng-model="t" /> <test title="{{t}}" > <span>我的angularjs</span> </test> </div> </body> <script> var myApp=angular.module('myApp',[]); myApp.controller('listCtrl',function($scope){ $scope.logchore="motorola"; }); myApp.directive('test',function(){ return { 'restrict':'E', scope:{ title:"@" }, template:'<div >{{title}}+内部</div>' } }); </script> </html>
<!DOCTYPE html> <html ng-app='myApp'> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <script src="https://cdn.staticfile.org/angular.js/1.4.6/angular.min.js"></script> </head> <body> <div ng-controller="listCtrl"> <input type="text" ng-model="t" /> <test title="t" > <p>{{title}}</p> <span>我的angularjs</span> </test> </div> </body> <script> var myApp=angular.module('myApp',[]); myApp.controller('listCtrl',function($scope){ $scope.logchore="motorola"; }); myApp.directive('test',function(){ return { 'restrict':'E', scope:{ title:"=" }, template:'<div >{{title}}+内部</div>' } }); </script> </html>
<!DOCTYPE html> <html ng-app='myApp'> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <script src="https://cdn.staticfile.org/angular.js/1.4.6/angular.min.js"></script> </head> <body> <div ng-controller="listCtrl"> <test flavor="logchore()" ></test> </div> </body> <script> var myApp=angular.module('myApp',[]); myApp.controller('listCtrl',function($scope){ $scope.logchore=function(){ alert('ok'); }; }); myApp.directive('test',function(){ return { 'restrict':'E', scope:{ flavor:"&" }, template:'<div ><button ng-click="flavor()"></button></div>' } }); </script> </html>
<!DOCTYPE html> <html ng-app='myApp'> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <script src="https://cdn.staticfile.org/angular.js/1.4.6/angular.min.js"></script> </head> <body> @father: <input type="text" ng-model="data" /> <me title="{{data}}">@</me> =father: <input type="text" ng-model="msg" /> <you title="msg">=</you> <div ng-controller="listCtrl"> <test flavor="logchore(str)"></test> </div> </body> <script> var app = angular.module("myApp", []); app.controller('listCtrl', function ($scope) { $scope.logchore = function (str) { alert(str); }; }); app.directive('me', function () { return { restrict: "E", //单向绑定,父元素可以改变子元素的model,子元素不能改变父元素的model scope: { title: '@' }, template: "<div>{{title}}@:<input type='text' ng-model='title'/></div>" } }); app.directive('you', function () { return { restrict: "E", scope: { title: "=" //双向绑定,父元素可以改变子元素的model,子元素可以改变父元素的model }, template: "<div>{{title}}=:<input type='text' ng-model='title'/></div>" } }) app.directive('test', function () { return { 'restrict': 'E', scope: { flavor: "&" }, //&是负责方法调用的,其中可以添加参数 template: '<div><input ng-model="v"/><button ng-click="flavor({str:v})">点击</button></div>' } }); </script> </html>
angular指令中@,=,&的区别
1、@(or @attr)
使用@符号可以进行单项的数据绑定,取值总是一个字符串,所以要用{{}}。
另外这也是一个单向的绑定,外部数据改变会反应到内部,但是内部数据变数据变化,外部不会变。
属性要用-连接,scope中写它的驼峰格式。
如果没有通过@attr指定属性名称,那么本地名称要与DOM属性的名称一致。
<!DOCTYPE html> <html ng-app="myApp"> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <title>AngularJS</title> </head> <body> <div ng-controller="parent"> <div> <input type="text" ng-model="name"/> </div> <my-name show-name="{{name}}"> </my-name> </div> </body> <script type="text/javascript" src="angular.min.js"></script> <script type="text/javascript"> var app = angular.module("myApp", []); app.controller("parent", function($scope){ $scope.name = "Jhon"; }).directive("myName", function(){ return { restrict:"EA", scope:{ showName: '@' // name: '@showName' }, template:'<input type="text" ng-model="showName"/>', // template:'<input type="text" ng-model="name"/>', } }); </script> </html>
2、= (or =attr)
使用=进行双向数据绑定,任何一方的值改变都会反应到另一方。因为是双向绑定,所以不要使用{{}},不然以下demo会报错。
属性要用-连接,scope中写它的驼峰格式。
如果没有通过@attr指定属性名称,那么本地名称要与DOM属性的名称一致。
<!DOCTYPE html> <html ng-app="myApp"> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <title>AngularJS</title> </head> <body> <div ng-controller="parent"> <div> <input type="text" ng-model="name"/> </div> <my-name show-name="name"> </my-name> </div> </body> <script type="text/javascript" src="angular.min.js"></script> <script type="text/javascript"> var app = angular.module("myApp", []); app.controller("parent", function($scope){ $scope.name = "Jhon"; }).directive("myName", function(){ return { restrict:"EA", scope:{ showName: '=' }, template:'<input type="text" ng-model="showName"/>' } }); </script> </html>
3、&(or &attr)
&用来绑定外部的函数。
属性要用-连接,scope中写它的驼峰格式。
如果没有通过@attr指定属性名称,那么本地名称要与DOM属性的名称一致。
<!DOCTYPE html> <html ng-app="myApp"> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <title>AngularJS</title> </head> <body> <div ng-controller="parent"> <div> <input type="text" ng-model="count"/> </div> <my-name show-name="increment()"> </my-name> </div> </body> <script type="text/javascript" src="angular.min.js"></script> <script type="text/javascript"> var app = angular.module("myApp", []); app.controller("parent", function($scope){ $scope.count = 0; $scope.increment = function(){ $scope.count++; }; }).directive("myName", function(){ return { restrict:"EA", scope:{ showName: '&' }, template:'<input type="button" ng-click="showName()" value="+1"/>' } }); </script> </html>




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号