实验1 现代C++编程初体验
任务1:
task1.cpp

// 现代C++标准库、算法库体验 // 本例用到以下内容: // 1. 字符串string, 动态数组容器类vector、迭代器 // 2. 算法库:反转元素次序、旋转元素 // 3. 函数模板、const引用作为形参 #include <iostream> #include <string> #include <vector> #include <algorithm> using namespace std; // 声明 // 模板函数声明 template<typename T> void output(const T &c); // 普通函数声明 void test1(); void test2(); void test3(); int main() { cout << "测试1: \n"; test1(); cout << "\n测试2: \n"; test2(); cout << "\n测试3: \n"; test3(); } // 函数实现 // 输出容器对象c中的元素 template <typename T> void output(const T &c) { for(auto &i: c) cout << i << " "; cout << endl; } // 测试1 // 组合使用算法库、迭代器、string反转字符串 void test1() { string s0{"0123456789"}; cout << "s0 = " << s0 << endl; string s1{s0}; reverse(s1.begin(), s1.end()); // 反转指定迭代器区间的元素 cout << "s1 = " << s1 << endl; string s2{s0}; reverse_copy(s0.begin(), s0.end(), s2.begin()); // 将指定迭代区间的元素拷贝 到指定迭代器开始的目标区间,并且在复制过程中反转次序 cout << "s2 = " << s2 << endl; } // 测试2 // 组合使用算法库、迭代器、vector反转动态数组对象vector内数据 void test2() { vector<int> v0{2, 0, 4, 9}; cout << "v0: "; output(v0); vector<int> v1{v0}; reverse(v1.begin(), v1.end()); cout << "v1: "; output(v1); vector<int> v2{v0}; reverse_copy(v0.begin(), v0.end(), v2.begin()); cout << "v2: "; output(v2); } // 测试3 // 组合使用算法库、迭代器、vector实现元素旋转移位 void test3() { vector<int> v0{0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9}; cout << "v0: "; output(v0); vector<int> v1{v0}; rotate(v1.begin(), v1.begin()+1, v1.end()); // 旋转指定迭代器区间 [v1.begin(), v1.end())之间的数据项,旋转后从迭代器v1.begin()+1位置的数据项开始 cout << "v1: "; output(v1); vector<int> v2{v0}; rotate(v2.begin(), v2.begin()+2, v2.end()); cout << "v2: "; output(v2); vector<int> v3{v0}; rotate(v3.begin(), v3.end()-1, v3.end()); cout << "v3: "; output(v3); vector<int> v4{v0}; rotate(v4.begin(), v4.end()-2, v4.end()); cout << "v4: "; output(v4); }
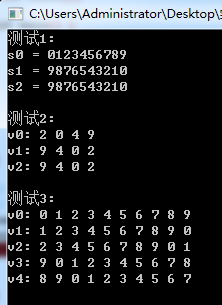
任务2:
task2.cpp

#include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <string> #include <algorithm> #include <numeric> #include <iomanip> using namespace std; // 函数声明 // 模板函数声明 template<typename T> void output(const T &c); // 普通函数声明 int rand_int_100(); void test1(); void test2(); int main() { cout << "测试1: \n"; test1(); cout << "\n测试2: \n"; test2(); } // 函数实现 // 输出容器对象c中的元素 template <typename T> void output(const T &c) { for(auto &i: c) cout << i << " "; cout << endl; } // 返回[0, 100]区间内的一个随机整数 int rand_int_100() { return rand() % 101; } // 测试1 // 对容器类对象指定迭代器区间进行赋值、排序 void test1() { vector<int> v0(10); // 创建一个动态数组对象v0, 对象大小为10 generate(v0.begin(), v0.end(), rand_int_100); // 产生[0, 100]之间的随机整数 赋值给指定迭代器区间[v0.begin(), v0.end())内的每个数据项 cout << "v0: "; output(v0); vector<int> v1{v0}; sort(v1.begin(), v1.end()); // 对指定迭代器区间[v1.begin(), v1.end())内数据 项进行升序排序 cout << "v1: "; output(v1); vector<int> v2{v0}; sort(v2.begin()+1, v2.end()-1); // 对指定迭代器区间[v1.begin()+1, v1.end()-1)内数据项进行升序排序 cout << "v2: "; output(v2); } // 测试2 // 对容器类对象指定迭代器区间进行赋值、计算最大值/最小值/均值 void test2() { vector<int> v0(10); generate(v0.begin(), v0.end(), rand_int_100); cout << "v0: "; output(v0); auto iter1 = min_element(v0.begin(), v0.end()); cout << "最小值: " << *iter1 << endl; auto iter2 = max_element(v0.begin(), v0.end()); cout << "最大值: " << *iter2 << endl; auto ans = minmax_element(v0.begin(), v0.end()); cout << "最小值: " << *(ans.first) << endl; cout << "最大值: " << *(ans.second) << endl; double avg1 = accumulate(v0.begin(), v0.end(), 0)/v0.size(); cout << "均值: " << fixed << setprecision(2) << avg1 << endl; cout << endl; vector<int> v1{v0}; cout << "v0: "; output(v0); sort(v1.begin(), v1.end()); double avg2 = accumulate(v1.begin()+1, v1.end()-1, 0)/(v1.size()-2); cout << "去掉最大值、最小值之后,均值: " << avg2 << endl; }
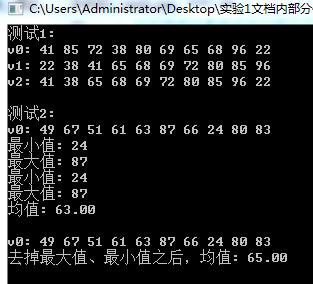
任务3:
task3.cpp

#include <iostream> #include <string> #include <algorithm> bool is_palindrome(std::string s); int main() { using namespace std; string s; while(cin >> s) // 多组输入,直到按下Ctrl+Z后结束测试 cout << boolalpha << is_palindrome(s) << endl; } bool is_palindrome(std::string s){ bool boolalpha=true; int len=s.size(); for(int i=0;i<len/2;i++){ if(s[i]!=s[len-i-1]){ boolalpha=false; return boolalpha; } } } // 函数is_palindrom定义 // 待补足 // ×××
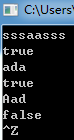
任务4:
task4.cpp

#include <iostream> #include <string> #include <algorithm> std::string dec2n(int x, int n = 2); int main() { using namespace std; int x; while (cin >> x) { cout << "十进制: " << x << endl; cout << "二进制: " << dec2n(x) << endl; cout << "八进制: " << dec2n(x, 8) << endl; cout << "十六进制: " << dec2n(x, 16) << endl << endl; } } std::string dec2n(int x, int n) { std::string t = ""; if (x == 0) { t = '0'; } if (n != 16) { while (x !=0) { t = std::to_string(x % n) + t; x = x / n; } } else { while (x!=0) { if (x % n >= 10) { t = char(x % n + 55) + t; } else { t = std::to_string(x % n) + t; } x = x / n; } } return t; } // 函数dec2n定义 // 待补足 // ×××
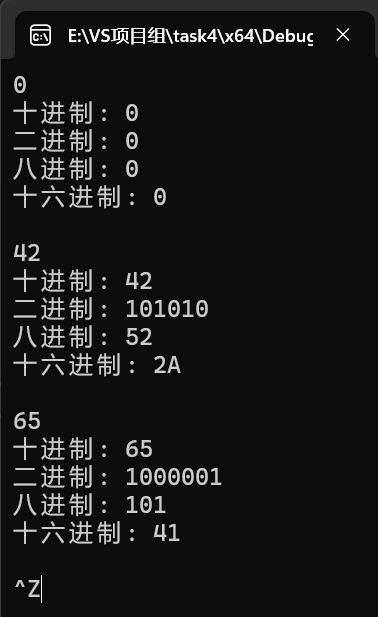
任务5:
task5.cpp

#include<iomanip> #include<iostream> #include<string> using namespace std; int main() { string s1 = "abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz"; string s2 = "ABCDEFGHIJKLNMOPQRSTUVWXYZ"; cout << " "; for (int i = 0; i <= 26; i++) cout << setw(2) << s1[i]; cout << endl; for (int i = 1; i <= 26; i++) { cout << setw(2) << i; for (int j = 0; j < 26; j++){ cout << setw(2) << s2[(j + i) % 26]; } cout << endl; } cout << endl; return 0; }
任务6:
task6.cpp

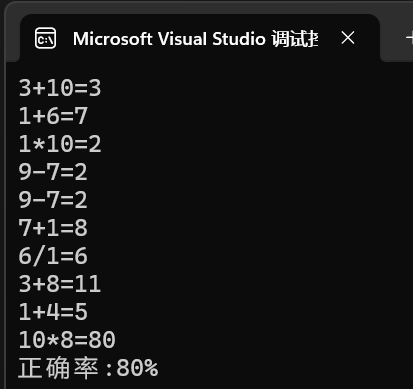
#include <iostream> #include <cstdlib> #include <ctime> using namespace std; int main() { int a, b, c, good, count; good = 0; count = 1; while (count <=10) { srand((unsigned)time(NULL)); int t = 1 + rand() % 4; a = 1 + rand() % 10; b = 1 + rand() % 10; if (t == 1) { cout << a << "+" << b << "="; cin >> c; if (a + b == c) good ++; count++; } else if (t == 2 && a > b) { cout << a << "-" << b << "="; cin >> c; if (a - b == c) good ++; count++; } else if (t == 3 && a % b == 0) { cout << a << "/" << b << "="; cin >> c; if (a / b == c) good ++; count++; } else if (t == 4) { cout << a << "*" << b << "="; cin >> c; if (a * b == c) good ++; count++; } } float rate; rate = good*10; cout << "正确率:" << rate << "%" << endl; }







【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
· 【自荐】一款简洁、开源的在线白板工具 Drawnix
· 没有Manus邀请码?试试免邀请码的MGX或者开源的OpenManus吧
· 园子的第一款AI主题卫衣上架——"HELLO! HOW CAN I ASSIST YOU TODAY
· 无需6万激活码!GitHub神秘组织3小时极速复刻Manus,手把手教你使用OpenManus搭建本