c++提高学习笔记——05-c++STLday11
在学习c++提高-STL总结了笔记,并分享出来。有问题请及时联系博主:Alliswell_WP,转载请注明出处。
05-c++STLday11
目录:
一、常用容器
1、上节作业——评委打分
2、stack栈容器
3、queue队列容器
4、list容器
测试API、测试:删除自定义数据类型
5、set容器
(1)测试API
(2)pair对组的创建方式——两种
(3)测试排序规则
6、map容器
测试API
7、STL容器使用时机
二、总结
一、常用容器
1、上节作业——评委打分
有5名选手:选手ABCDE,10个评委分别对每一名选手打分,去除最高分,去除评委中最低分,取平均分。
//1. 创建五名选手,放到vector中
//2. 遍历vector容器,取出来每一个选手,执行for循环,可以把10个评分打分存到deque容器中
//3. sort算法对deque容器中分数排序,pop_back pop_front去除最高和最低分
//4. deque容器遍历一遍,累加分数,累加分数/d.size()
//5. person.score = 平均分
1 /* 2 create by wp 3 2020.06.16 4 文件功能... 5 6 func()...干嘛的 参数1.... 7 */ 8 #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 9 #include<iostream> 10 using namespace std; 11 #include<vector> 12 #include<deque> 13 #include<algorithm> 14 #include<string> 15 #inlcude<ctime> 16 /* 17 有5名选手:选手ABCDE,10个评委分别对每一名选手打分,去除最高分,去除评委中最低分,取平均分。 18 //1. 创建五名选手,放到vector中 19 //2. 遍历vector容器,取出来每一个选手,执行for循环,可以把10个评分打分存到deque容器中 20 //3. sort算法对deque容器中分数排序,pop_back pop_front去除最高和最低分 21 //4. deque容器遍历一遍,累加分数,累加分数/d.size() 22 //5. person.score = 平均分 23 */ 24 25 class Person 26 { 27 public: 28 Person(string name, int score) 29 { 30 this->m_Name = name; 31 this->m_Score = score; 32 } 33 34 string m_Name;//人名 35 int m_Score;//分数 36 }; 37 38 void createPerson(vector<Person>& v) 39 { 40 string nameSeed = "ABCDE"; 41 for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++) 42 { 43 string name = "选手"; 44 name += nameSeed[i]; 45 46 int score = 0; 47 Person p(name, score); 48 49 v.push_back(p); 50 } 51 52 53 } 54 55 void setScore(vector<Person>& v) 56 { 57 for(vector<Person>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++) 58 { 59 //对5个人进行打分 60 deque<int>d; 61 for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++) 62 { 63 int score = rand() % 41 + 60;//60~100 64 65 d.push_back(score); 66 } 67 /* 68 //先测试看下打分 69 for(deque<int>::iterator dit = d.begin(); dit != d.end(); dit++) 70 { 71 cout << *dit << " "; 72 } 73 cout << endl; 74 */ 75 76 //排序 77 sort(d.begin(), d.end()); 78 79 //去除最高和最低 80 d.pop_back();//最高 81 d.pop_front(); 82 83 int sum = 0; 84 for(deque<int>::iterator dit = d.begin(); dit != d.end(); dit++) 85 { 86 sum += *dit; 87 } 88 89 //平均分 90 int avg = sum / d.size(); 91 92 it->m_Score = avg; 93 } 94 95 } 96 97 void showScore(vector<Person>& v) 98 { 99 for(vector<Person>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++) 100 { 101 cout << "姓名:" << it->m_Name << "最终平均分:" << it->m_Score << endl; 102 } 103 104 } 105 106 void test01() 107 { 108 //为方便测试,最后设置随机数种子 109 srand(unsigned int)time(NULL); 110 111 //创建容器,存放选手 112 vector<Person>v; 113 114 //创建5名选手 115 createPerson(v); 116 117 /* 118 //测试 119 for(vector<Person>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++) 120 { 121 cout << "姓名:" << (*it).m_Name << endl; 122 } 123 */ 124 125 //打分 126 SetScore(v); 127 128 //展示平均分 129 showScore(v); 130 } 131 132 int main() 133 { 134 test01(); 135 136 system("pause"); 137 return EXIT_SUCCESS; 138 }
2、stack栈容器
stack容器基本概念
stack是一种先进后出(First In Last Out,FILO)的数据结构,它只有一个出口,形式如图所示。stack容器允许新增元素,移除元素,取得栈顶元素,但是除了最顶端外,没有任何其他方法可以存取stack的其他元素。换言之,stack不允许有遍历行为。
有元素推入栈的操作称为:push,将元素推出stack的操作称为pop.



stack没有迭代器
Stack所有元素的进出都必须符合”先进后出”的条件,只有stack顶端的元素,才有机会被外界取用。Stack不提供遍历功能,也不提供迭代器。
测试API:
1 #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 2 #include<iostream> 3 using namespace std; 4 //包含stack头文件 5 #include<stack> 6 7 /* 8 //stack构造函数 9 stack<T> stkT;//stack采用模板类实现, stack对象的默认构造形式: 10 stack(const stack &stk);//拷贝构造函数 11 12 //stack赋值操作 13 stack& operator=(const stack &stk);//重载等号操作符 14 15 //stack数据存取操作 16 push(elem);//向栈顶添加元素 17 pop();//从栈顶移除第一个元素 18 top();//返回栈顶元素 19 20 //stack大小操作 21 empty();//判断堆栈是否为空 22 size();//返回堆栈的大小 23 24 */ 25 26 27 void test01() 28 { 29 stack<int>s; 30 //放入数据 push 31 s.push(10); 32 s.push(30); 33 s.push(20); 34 s.push(40); 35 36 while(s.size() != 0) 37 { 38 cout << "栈顶为:" << s.top() << endl;//40 20 30 10 39 //弹出栈顶元素 40 s.pop(); 41 } 42 cout << "size = " << s.size() << endl; 43 44 } 45 46 int main() 47 { 48 test01(); 49 50 system("pause"); 51 return EXIT_SUCCESS; 52 }
3、queue队列容器
queue容器基本概念
Queue是一种先进先出(First In First Out,FIFO)的数据结构,它有两个出口,queue容器允许从一端新增元素,从另一端移除元素。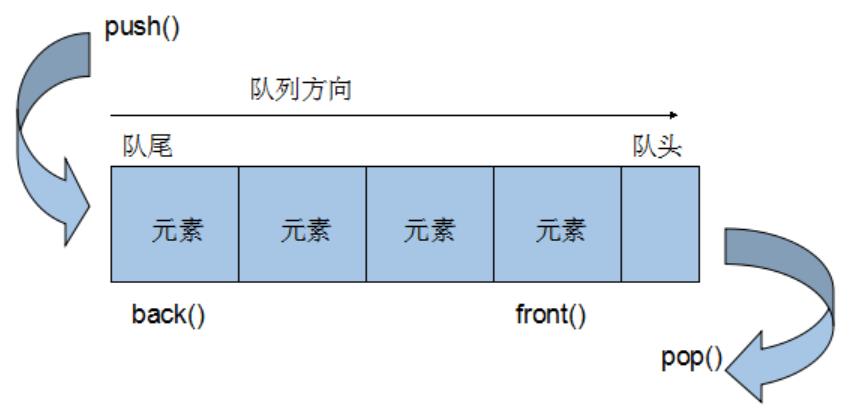

queue没有迭代器
Queue所有元素的进出都必须符合”先进先出”的条件,只有queue的顶端元素,才有机会被外界取用。Queue不提供遍历功能,也不提供迭代器。
测试API:
1 #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 2 #include<iostream> 3 using namespace std; 4 //包含队列头文件 5 #include<queue> 6 7 /* 8 //queue构造函数 9 queue<T> queT;//queue采用模板类实现,queue对象的默认构造形式: 10 queue(const queue &que);//拷贝构造函数 11 12 //queue存取、插入和删除操作 13 push(elem);//往队尾添加元素 14 pop();//从队头移除第一个元素 15 back();//返回最后一个元素 16 front();//返回第一个元素 17 18 //queue赋值操作 19 queue& operator=(const queue &que);//重载等号操作符 20 21 //queue大小操作 22 empty();//判断队列是否为空 23 size();//返回队列的大小 24 25 */ 26 27 void test01() 28 { 29 queue<int>q; 30 q.push(10);//往队尾添加元素 31 q.push(30); 32 q.push(20); 33 q.push(40); 34 35 while(!q.empty()) 36 { 37 cout << "队头:" << q.front() << endl;//10 40 30 40 20 40 40 40 38 cout << "队尾:" << q.back() << endl; 39 //弹出队头 40 q.pop(); 41 } 42 cout << "size:" << q.size() << endl; 43 } 44 45 int main() 46 { 47 test01(); 48 49 system("pause"); 50 return EXIT_SUCCESS; 51 }
4、list容器
list容器基本概念
链表是一种物理存储单元上非连续、非顺序的存储结构,数据元素的逻辑顺序是通过链表中的指针链接次序实现的。链表由一系列结点(链表中每一个元素称为结点)组成,结点可以在运行时动态生成。每个结点包括两个部分:一个是存储数据元素的数据域,另一个是存储下一个结点地址的指针域。
相较于vector的连续线性空间,list就显得负责许多,它的好处是每次插入或者删除一个元素,就是配置或者释放一个元素的空间。因此,list对于空间的运用有绝对的精准,一点也不浪费。而且,对于任何位置的元素插入或元素的移除,list永远是常数时间。
List和vector是两个最常被使用的容器。
List容器是一个双向链表。

>采用动态存储分配,不会造成内存浪费和溢出
>链表执行插入和删除操作十分方便,修改指针即可,不需要移动大量元素
>链表灵活,但是空间和时间额外耗费较大
list容器的迭代器
List容器不能像vector一样以普通指针作为迭代器,因为其节点不能保证在同一块连续的内存空间上。List迭代器必须有能力指向list的节点,并有能力进行正确的递增、递减、取值、成员存取操作。所谓”list正确的递增,递减、取值、成员取用”是指,递增时指向下一个节点,递减时指向上一个节点,取值时取的是节点的数据值,成员取用时取的是节点的成员。
由于list是一个双向链表,迭代器必须能够具备前移、后移的能力,所以list容器提供的是Bidirectional Iterators.
List有一个重要的性质,插入操作和删除操作都不会造成原有list迭代器的失效。这在vector是不成立的,因为vector的插入操作可能造成记忆体重新配置,导致原有的迭代器全部失效,甚至List元素的删除,也只有被删除的那个元素的迭代器失效,其他迭代器不受任何影响。
list容器的数据结构
list容器不仅是一个双向链表,而且还是一个循环的双向链表。
测试API:
1 #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 2 #include<iostream> 3 using namespace std; 4 #include<list> 5 #include<algorithm> 6 #include<string> 7 8 //list是双向循环链表 9 void test01() 10 { 11 list<int> myList; 12 for (int i = 0; i < 10; i ++){ 13 myList.push_back(i); 14 } 15 16 list<int>::_Nodeptr node = myList._Myhead->_Next; 17 18 for (int i = 0; i < myList._Mysize * 2;i++){ 19 cout << "Node:" << node->_Myval << endl; 20 node = node->_Next; 21 if (node == myList._Myhead){ 22 node = node->_Next; 23 } 24 } 25 26 } 27 28 /* 29 //list构造函数 30 list<T> lstT;//list采用采用模板类实现,对象的默认构造形式: 31 list(beg,end);//构造函数将[beg, end)区间中的元素拷贝给本身。 32 list(n,elem);//构造函数将n个elem拷贝给本身。 33 list(const list &lst);//拷贝构造函数。 34 35 //list数据元素插入和删除操作 36 push_back(elem);//在容器尾部加入一个元素 37 pop_back();//删除容器中最后一个元素 38 push_front(elem);//在容器开头插入一个元素 39 pop_front();//从容器开头移除第一个元素 40 insert(pos,elem);//在pos位置插elem元素的拷贝,返回新数据的位置。 41 insert(pos,n,elem);//在pos位置插入n个elem数据,无返回值。 42 insert(pos,beg,end);//在pos位置插入[beg,end)区间的数据,无返回值。 43 clear();//移除容器的所有数据 44 erase(beg,end);//删除[beg,end)区间的数据,返回下一个数据的位置。 45 erase(pos);//删除pos位置的数据,返回下一个数据的位置。 46 remove(elem);//删除容器中所有与elem值匹配的元素。 47 48 */ 49 50 void printList(list<int>& L) 51 { 52 for(list<int>::iterator it = L.begin(); it != L.end(); it++) 53 { 54 cout << *it << " "; 55 } 56 cout << endl; 57 } 58 59 void test02() 60 { 61 list<int>L(10, 10); 62 list<int>L2(L.begin(), L.end()); 63 64 printList(L); 65 printList(L2); 66 L2.push_back(100); 67 68 //逆向打印 69 for(list<int>::reverse_iterator it = L2.rbegin(); it != L2.rend(); it++) 70 { 71 cout << *it << " "; 72 } 73 cout << endl; 74 75 //list迭代器不支持随机访问 76 list<int>::iterator itBegin = L2.begin(); 77 //itBegin = itBegin + 1; 78 79 //插入数据 80 list<int>L3; 81 L3.push_back(10); 82 L3.push_back(30); 83 L3.push_back(20); 84 L3.push_front(100); 85 L3.push_front(300); 86 L3.push_front(200); 87 88 printList(L3);//200 300 100 10 30 20 89 90 //删除两端的数据 91 L3.pop_front();//头删 92 L3.pop_back();//尾删 93 printList(L3);//300 100 10 30 94 95 L3.insert(L3.begin(), 1000); 96 printList(L3);//1000 300 100 10 30 97 98 //remove(elem);//删除容器中所有与elem值匹配的元素 99 L3.push_back(10);//1000 300 100 10 30 10 100 L3.remove(10);//参数,直接放值 101 102 printList(L3);//1000 300 100 30 103 } 104 105 /* 106 //list大小操作 107 size();//返回容器中元素的个数 108 empty();//判断容器是否为空 109 resize(num);//重新指定容器的长度为num, 110 若容器变长,则以默认值填充新位置。 111 如果容器变短,则末尾超出容器长度的元素被删除。 112 resize(num, elem);//重新指定容器的长度为num, 113 若容器变长,则以elem值填充新位置。 114 如果容器变短,则末尾超出容器长度的元素被删除。 115 116 //list赋值操作 117 assign(beg, end);//将[beg, end)区间中的数据拷贝赋值给本身。 118 assign(n, elem);//将n个elem拷贝赋值给本身。 119 list& operator=(const list &lst);//重载等号操作符 120 swap(lst);//将lst与本身的元素互换。 121 122 //list数据的存取 123 front();//返回第一个元素。 124 back();//返回最后一个元素。 125 126 */ 127 128 void test03() 129 { 130 list<int>L3; 131 L3.push_back(10); 132 L3.push_back(30); 133 L3.push_back(20); 134 L3.push_front(100); 135 L3.push_front(300); 136 L3.push_front(200); 137 138 cout << "大小:" << L3.size() << endl; 139 if(L3.empty()) 140 { 141 cout << "L3为空" << endl; 142 } 143 else 144 { 145 cout << "L3不为空" << endl; 146 } 147 148 L3.resize(10); 149 printList(L3);//200 300 100 10 30 20 0 0 0 0 150 151 L3.resize(3); 152 printList(L3);//200 300 100 153 154 list<int> L4; 155 L4.assign(L3.begin(), L3.end()); 156 157 cout << "front:" << L4.front() << endl;//200 158 cout << "back:" << L4.back() << endl;//100 159 160 } 161 162 /* 163 //list反转排序 164 reverse();//反转链表,比如lst包含1,3,5元素,运行此方法后,lst就包含5,3,1元素。 165 sort(); //list排序 166 */ 167 bool myCompare(int v1, int v2) 168 { 169 return v1 > v2; 170 } 171 172 void test04() 173 { 174 list<int>L; 175 176 L.push_back(10); 177 L.push_back(20); 178 L.push_back(40); 179 L.push_back(30); 180 181 L.reverse(); 182 printList(L);//30 40 20 10 183 184 //所有不支持随机访问的迭代器,不可以用系统提供的算法 185 //如果不支持用系统提供算法,那么这个类内部会提供 186 //sort(L.begin(), L.end()); 187 L.sort();//从小到大 188 189 printList(L); 190 191 //从大到小 192 L.sort(myCompare); 193 printList(L); 194 } 195 196 //自定义数据类型 197 class Person 198 { 199 public: 200 Person(string name, int age, int height) 201 { 202 this->m_Name = time; 203 this->m_Age = age; 204 this->m_Height = height; 205 } 206 207 208 string m_Name; 209 int m_Age; 210 int m_Height;//身高 211 }; 212 213 //Person排序规则:如果年龄相同,按照身高升序排序 214 bool myComparePerson(Person& p1, Person& p2) 215 { 216 /* 217 if(p1.m_Age > p2.m_Age) 218 { 219 return true; 220 } 221 return false; 222 */ 223 224 if(p1.m_Age == p2.m_Age) 225 { 226 return p1.m_Height < p2.m_Height; 227 } 228 else 229 { 230 return p1.m_Age > p2.m_Age; 231 } 232 } 233 234 void test05() 235 { 236 list<Person>L; 237 238 Person p1("亚瑟", 10, 165); 239 Person p2("德玛西亚", 20, 170); 240 Person p3("火枪", 17, 177); 241 Person p4("德雷福斯", 19, 120); 242 Person p5("MT", 18, 200); 243 Person p6("狗蛋", 18, 166); 244 Person p7("狗剩", 18, 210); 245 246 L.push_back(p1); 247 L.push_back(p2); 248 L.push_back(p3); 249 L.push_back(p4); 250 L.push_back(p5); 251 L.push_back(p6); 252 L.push_back(p7); 253 254 //需求:打印数据时候,按照年龄的降序输出 255 //对于自定义数据类型,必须要指定排序规则 256 L.sort(myComparePerson); 257 258 for(list<Person>::iterator it = it = L.begin(); it != L.end(); it++) 259 { 260 cout << "姓名:" << it->m_Name << "年龄:" << *it.m_Age << "身高:" << it->m_Height << endl; 261 } 262 } 263 264 265 266 267 int main() 268 { 269 test01(); 270 271 system("pause"); 272 return EXIT_SUCCESS; 273 }
测试:删除自定义数据类型
1 #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 2 #include<iostream> 3 using namespace std; 4 #include<list> 5 #include<algorithm> 6 #include<string> 7 8 9 //自定义数据类型 10 class Person 11 { 12 public: 13 Person(string name, int age, int height) 14 { 15 this->m_Name = time; 16 this->m_Age = age; 17 this->m_Height = height; 18 } 19 20 //重载 == 让remove可以删除自定义的Person类型 21 bool operator==(const Person& p)//必须加const 22 { 23 if(this->m_Name == p.m_Name && this->m_Age == p.m_Age && this->m_Height == p.m_Height) 24 { 25 return true; 26 } 27 return false; 28 } 29 30 31 string m_Name; 32 int m_Age; 33 int m_Height;//身高 34 }; 35 36 //Person排序规则:如果年龄相同,按照身高升序排序 37 bool myComparePerson(Person& p1, Person& p2) 38 { 39 /* 40 if(p1.m_Age > p2.m_Age) 41 { 42 return true; 43 } 44 return false; 45 */ 46 47 if(p1.m_Age == p2.m_Age) 48 { 49 return p1.m_Height < p2.m_Height; 50 } 51 else 52 { 53 return p1.m_Age > p2.m_Age; 54 } 55 } 56 57 void test01() 58 { 59 list<Person>L; 60 61 Person p1("亚瑟", 10, 165); 62 Person p2("德玛西亚", 20, 170); 63 Person p3("火枪", 17, 177); 64 Person p4("德雷福斯", 19, 120); 65 Person p5("MT", 18, 200); 66 Person p6("狗蛋", 18, 166); 67 Person p7("狗剩", 18, 210); 68 69 L.push_back(p1); 70 L.push_back(p2); 71 L.push_back(p3); 72 L.push_back(p4); 73 L.push_back(p5); 74 L.push_back(p6); 75 L.push_back(p7); 76 77 //需求:打印数据时候,按照年龄的降序输出 78 //对于自定义数据类型,必须要指定排序规则 79 L.sort(myComparePerson); 80 81 for(list<Person>::iterator it = it = L.begin(); it != L.end(); it++) 82 { 83 cout << "姓名:" << it->m_Name << "年龄:" << *it.m_Age << "身高:" << it->m_Height << endl; 84 } 85 86 cout << "----------" << endl; 87 //删除 狗蛋 88 L.remove(p6); 89 for(list<Person>::iterator it = it = L.begin(); it != L.end(); it++) 90 { 91 cout << "姓名:" << it->m_Name << "年龄:" << *it.m_Age << "身高:" << it->m_Height << endl; 92 } 93 94 } 95 96 97 98 99 int main() 100 { 101 test01(); 102 103 system("pause"); 104 return EXIT_SUCCESS; 105 }
5、set容器
set/multiset容器基本概念
set容器基本概念
Set的特性是。所有元素都会根据元素的键值自动被排序。Set的元素不像map那样可以同时拥有实值和键值,set的元素即是键值又是实值。Set不允许两个元素有相同的键值。
我们可以通过set的迭代器改变set元素的值吗?不行,因为set元素值就是其键值,关系到set元素的排序规则。如果任意改变set元素值,会严重破坏set组织。换句话说,set的iterator是一种const_iterator.
set拥有和list某些相同的性质,当对容器中的元素进行插入操作或者删除操作的时候,操作之前所有的迭代器,在操作完成之后依然有效,被删除的那个元素的迭代器必然是一个例外。
multiset容器基本概念
multiset特性及用法和set完全相同,唯一的差别在于它允许键值重复。set和multiset的底层实现是红黑树,红黑树为平衡二叉树的一种。
树的简单知识:
二叉树就是任何节点最多只允许有两个字节点。分别是左子结点和右子节点。
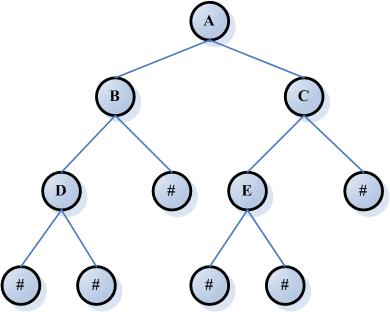
二叉树示意图
二叉搜索树,是指二叉树中的节点按照一定的规则进行排序,使得对二叉树中元素访问更加高效。二叉搜索树的放置规则是:任何节点的元素值一定大于其左子树中的每一个节点的元素值,并且小于其右子树的值。因此从根节点一直向左走,一直到无路可走,即得到最小值,一直向右走,直至无路可走,可得到最大值。那么在儿茶搜索树中找到最大元素和最小元素是非常简单的事情。下图为二叉搜索树:
上面我们介绍了二叉搜索树,那么当一个二叉搜索树的左子树和右子树不平衡的时候,那么搜索依据上图表示,搜索9所花费的时间要比搜索17所花费的时间要多,由于我们的输入或者经过我们插入或者删除操作,二叉树失去平衡,造成搜索效率降低。
所以我们有了一个平衡二叉树的概念,所谓的平衡不是指的完全平衡。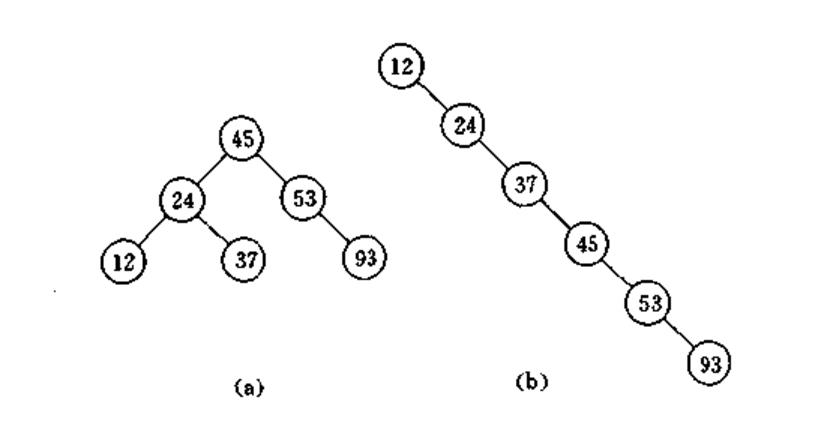
RB-tree(红黑树)为二叉树的一种。
(1)测试API:
1 #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 2 #include<iostream> 3 using namespace std; 4 #include<set> 5 /* 6 //set构造函数 7 set<T> st;//set默认构造函数: 8 mulitset<T> mst; //multiset默认构造函数: 9 set(const set &st);//拷贝构造函数 10 11 //set赋值操作 12 set& operator=(const set &st);//重载等号操作符 13 swap(st);//交换两个集合容器 14 15 //set大小操作 16 size();//返回容器中元素的数目 17 empty();//判断容器是否为空 18 19 //set插入和删除操作 20 insert(elem);//在容器中插入元素。 21 clear();//清除所有元素 22 erase(pos);//删除pos迭代器所指的元素,返回下一个元素的迭代器。 23 erase(beg, end);//删除区间[beg,end)的所有元素 ,返回下一个元素的迭代器。 24 erase(elem);//删除容器中值为elem的元素。 25 26 */ 27 void printSet(set<int>& s) 28 { 29 for(set<int>::iterator it = s.begin(); it != s.end(); it++) 30 { 31 cout << *it << " "; 32 } 33 cout << endl; 34 } 35 36 37 void test01() 38 { 39 set<int>s1; 40 41 //关联式容器,key进行排序,从小到大 42 s1.intsert(5); 43 s1.intsert(1); 44 s1.intsert(9); 45 s1.intsert(3); 46 s1.intsert(7); 47 48 printSet(s1);//1 3 5 7 9 49 50 if(s1.empty()) 51 { 52 cout << "空" << endl; 53 } 54 else 55 { 56 cout << "size = " << s1.size() << endl; 57 } 58 59 s1.erase(s1.begin());// 3 5 7 9 60 printSet(s1); 61 s1.erase(3);//5 7 9 62 printSet(s1); 63 64 } 65 66 /* 67 //set查找操作 68 find(key);//查找键key是否存在,若存在,返回该键的元素的迭代器;若不存在,返回set.end(); 69 count(key);//查找键key的元素个数 70 lower_bound(keyElem);//返回第一个key>=keyElem元素的迭代器。 71 upper_bound(keyElem);//返回第一个key>keyElem元素的迭代器。 72 equal_range(keyElem);//返回容器中key与keyElem相等的上下限的两个迭代器。 73 74 */ 75 void test02() 76 { 77 set<int>s1; 78 s1.intsert(5); 79 s1.intsert(1); 80 s1.intsert(9); 81 s1.intsert(3); 82 s1.intsert(7); 83 84 //对于set,没有value,key就是value 85 86 set<int>::iterator pos = s1.find(3); 87 //判断是否找到 88 if(pos != s1.end()) 89 { 90 cout << "找到了,值为:" << *pos << endl; 91 } 92 else 93 { 94 cout << "未找到" << endl; 95 } 96 97 //count(key);//查找键key的元素个数,对于set而言,结果0或者1 98 int num = s1.count(1); 99 cout << "2的个数为:" << num << endl; 100 101 //lower_bound(keyElem);//返回第一个key>=keyElem元素的迭代器 102 set<int>::iterator it = s1.lower_bound(3);//10就是未找到 103 if(it != s1.end()) 104 { 105 cout << "找到了,lower_bound(3)的值为:" << *it << endl; 106 } 107 else 108 { 109 cout << "未找到" << endl; 110 } 111 //upper_bound(keyElem);//返回第一个key>keyElem元素的迭代器 112 set<int>::iterator it2 = s1.lower_bound(3); 113 if(it2 != s1.end()) 114 { 115 cout << "找到了,lower_bound(3)的值为:" << *it2 << endl; 116 } 117 else 118 { 119 cout << "未找到" << endl; 120 } 121 //equal_range(keyElem);//返回容器中key与keyElem相等的上下限的两个迭代器 122 //上下限就是 lower_bound upper_bound 123 pair<set<int>::iterator, set<int>::iterator> ret = s1.equal_range(3); 124 //获取第一个值 125 if(ret.first != s1.end()) 126 { 127 cout << "找到equal_range中的lower_bound的值:" << *(ret.first) << endl; 128 } 129 else 130 { 131 cout << "未找到" << endl; 132 } 133 //获取第二个值 134 if(ret.second != s1.end()) 135 { 136 cout << "找到equal_range中的upper_bound的值:" << *(ret.second) << endl; 137 } 138 else 139 { 140 cout << "未找到" << endl; 141 } 142 143 } 144 145 int main() 146 { 147 test01(); 148 149 system("pause"); 150 return EXIT_SUCCESS; 151 }
(2)pair对组的创建方式——两种
对组(pair)将一对值组合成一个值,这一对值可以具有不同的数据类型,两个值可以分别用pair的两个公有属性first和second访问。
类模板:template <class T1, class T2> struct pair.
测试:
1 #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 2 #include<iostream> 3 #include<string> 4 using namespace std; 5 6 //创建对组,使用对组pair不需要引用头文件 7 void test01() 8 { 9 //第一种括号 10 pair<string, int>p(string("Tom"), 100); 11 12 //取值 13 cout << "姓名:" << p.first << endl; 14 cout << "年龄:" << p.second << endl; 15 16 //第二种创建 17 pair<string, int> p2 = make_pair("Jerry", 200); 18 cout << "姓名:" << p2.first << endl; 19 cout << "年龄:" << p2.second << endl; 20 21 } 22 23 int main() 24 { 25 test01(); 26 27 system("pause"); 28 return EXIT_SUCCESS; 29 }
(3)测试排序规则:
1 #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 2 #include<iostream> 3 using namespace std; 4 #include<set> 5 #include<string> 6 7 void printSet(set<int>& s) 8 { 9 for(set<int>::iterator it = s.begin(); it != s.end(); it++) 10 { 11 cout << *it << " "; 12 } 13 cout << endl; 14 } 15 16 //set容器,不允许插入重复的键值 17 void test01() 18 { 19 set<int>s1; 20 21 pair<set<int>::iterator, bool> ret = s1.intsert(10); 22 23 24 if(ret.second) 25 { 26 cout << "插入成功" << endl; 27 } 28 else 29 { 30 cout << "插入失败" << endl; 31 } 32 s1.intsert(10); 33 34 35 if(ret.second) 36 { 37 cout << "第二次插入成功" << endl; 38 } 39 else 40 { 41 cout << "第二次插入失败" << endl; 42 } 43 44 printSet(s1);//10
//multiset允许插入重复的值
multiset<int>mul;
mul.insert(10);
mul.insert(10);
45 } 46 47 //指定set排序规则,从大到小 48 //仿函数 49 class myCompare 50 { 51 public: 52 //重载() 53 bool operator()(int v1, int v2) 54 { 55 return v1 > v2; 56 } 57 58 59 }; 60 61 //set容器排序 62 void test02() 63 { 64 set<int, myCompare>s1; 65 66 s1.insert(5); 67 s1.insert(1); 68 s1.insert(9); 69 s1.insert(3); 70 s1.insert(7); 71 72 //printSet(s1); 73 74 //从大到小排序 75 //在插入之前就指定排序规则 76 77 for(set<int, myCompare>::iterator it = s1.begin(); it != s1.end(); it++) 78 { 79 cout << *it << " "; 80 } 81 cout << endl; 82 83 } 84 85 //自定义数据类型 86 class Person 87 { 88 public: 89 Person(string name, int age) 90 { 91 this->m_Name = name; 92 this->m_Age = age; 93 } 94 95 string m_Name; 96 int m_Age; 97 }; 98 99 class myComparePerson 100 { 101 public: 102 bool operator()(const Person& p1, const Person& p2)//必须加入const 103 { 104 if(p1.m_Age > p2.m_Age)//降序 105 { 106 return true; 107 } 108 return false; 109 } 110 111 112 }; 113 114 void test03() 115 { 116 set<Person, myComparePerson> s1; 117 118 Person p1("大娃", 100); 119 Person p2("二娃", 90); 120 Person p3("六娃", 10); 121 Person p4("爷爷", 1000); 122 123 s1.insert(p1); 124 s1.insert(p2); 125 s1.insert(p3); 126 s1.insert(p4); 127 128 //插入自定义数据类型,一开始就指定排序规则 129 130 //显示 131 for(set<Person, myComparePerson>::iterator it = s1.begin(); it != s1.end(); it++) 132 { 133 cout << "姓名:" << (*it).m_Name << "年龄:" << (*it).m_Age << endl; 134 } 135 } 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 int main() 143 { 144 test01(); 145 146 system("pause"); 147 return EXIT_SUCCESS; 148 }
6、map容器
map/multimap基本概念
Map的特性是,所有元素都会根据元素的键值自动排序。Map所有的元素都是pair,同时拥有实值和键值,pair的第一元素被视为键值,第二元素被视为实值,map不允许两个元素有相同的键值。
我们可以通过map的迭代器改变map的键值吗?答案是不行,因为map的键值关系到map元素的排列规则,任意改变map键值将会严重破坏map组织。如果想要修改元素的实值,那么是可以的。
Map和list拥有相同的某些性质,当对它的容器元素进行新增操作或者删除操作时,操作之前的所有迭代器,在操作完成之后依然有效,当然被删除的那个元素的迭代器必然是个例外。
Multimap和map的操作类似,唯一区别multimap键值可重复。
Map和multimap都是以红黑树为底层实现机制。
测试API:
1 #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 2 #include<iostream> 3 using namespace std; 4 //引入头文件 5 #include<map> 6 7 /* 8 //map构造函数 9 map<T1, T2> mapTT;//map默认构造函数: 10 map(const map &mp);//拷贝构造函数 11 12 //map赋值操作 13 map& operator=(const map &mp);//重载等号操作符 14 swap(mp);//交换两个集合容器 15 16 //map大小操作 17 size();//返回容器中元素的数目 18 empty();//判断容器是否为空 19 20 //map插入数据元素操作 21 map.insert(...); //往容器插入元素,返回pair<iterator,bool> 22 map<int, string> mapStu; 23 // 第一种 通过pair的方式插入对象 24 mapStu.insert(pair<int, string>(3, "小张")); 25 // 第二种 通过pair的方式插入对象 26 mapStu.inset(make_pair(-1, "校长")); 27 // 第三种 通过value_type的方式插入对象 28 mapStu.insert(map<int, string>::value_type(1, "小李")); 29 // 第四种 通过数组的方式插入值 30 mapStu[3] = "小刘"; 31 mapStu[5] = "小王"; 32 33 */ 34 35 36 void test01() 37 { 38 map<int, int>m; 39 //插入值 40 //4种方式 41 //第一种 42 m.insert(pair<int, int>(1, 10)); 43 //第二种 推荐 44 m.insert(make_pair(2,20)); 45 //第三种 46 m.insert(map<int, int>::value_type(3, 30)); 47 //第四种,如果保证key存在,那么可以通过[]访问 48 m[4] = 40; 49 50 for(map<int, int>::iterator it = m.begin(); it != m.end(); it++) 51 { 52 cout << "key = " << it->first << "value = " << it->second << endl; 53 } 54 55 //cout << m[5] << endl; 56 57 for(map<int, int>::iterator it = m.begin(); it != m.end(); it++) 58 { 59 cout << "key = " << it->first << "value = " << it->second << endl; 60 } 61 62 cout << m[4] << endl; 63 64 if(m.empty()) 65 { 66 cout << "空" << endl; 67 } 68 else 69 { 70 cout << "size = " << m.size() << endl; 71 } 72 73 } 74 75 /* 76 //map删除操作 77 clear();//删除所有元素 78 erase(pos);//删除pos迭代器所指的元素,返回下一个元素的迭代器。 79 erase(beg,end);//删除区间[beg,end)的所有元素 ,返回下一个元素的迭代器。 80 erase(keyElem);//删除容器中key为keyElem的对组。 81 82 //map查找操作 83 find(key);//查找键key是否存在,若存在,返回该键的元素的迭代器;/若不存在,返回map.end(); 84 count(keyElem);//返回容器中key为keyElem的对组个数。对map来说,要么是0,要么是1。对multimap来说,值可能大于1。 85 lower_bound(keyElem);//返回第一个key>=keyElem元素的迭代器。 86 upper_bound(keyElem);//返回第一个key>keyElem元素的迭代器。 87 equal_range(keyElem);//返回容器中key与keyElem相等的上下限的两个迭代器。 88 89 */ 90 91 void test02() 92 { 93 map<int, int>m; 94 m.insert(pair<int, int>(1, 10)); 95 m.insert(make_pair(2,20)); 96 m.insert(map<int, int>::value_type(3, 30)); 97 m[4] = 40; 98 99 m.erase(1); 100 for(map<int, int>::iterator it = m.begin(); it != m.end(); it++) 101 { 102 cout << "key = " << it->first << "value = " << it->second << endl; 103 } 104 105 map<int, int>::iterator pos = m.find(2); 106 if(pos != m.end()) 107 { 108 cout << "找到,key:" << pos->first << "value:" << pos->second << endl; 109 } 110 else 111 { 112 cout << "未找到" << endl; 113 } 114 115 int num = m.count(3);//map的count要么0,要么1 116 cout << "num = " << endl; 117 118 //lower_bound(keyElem);//返回第一个key>=keyElem元素的迭代器 119 map<int, int>::iterator ret = m.lower_bound(3); 120 if(ret != m.end()) 121 { 122 cout << "lower_bound中key:" << ret->first << "value:" << ret->second << endl; 123 } 124 else 125 { 126 cout << "未找到" << endl; 127 } 128 129 //upper_bound(keyElem);//返回第一个key>keyElem元素的迭代器 130 map<int, int>::iterator ret = m.upper_bound(3); 131 if(ret != m.end()) 132 { 133 cout << "upper_bound中key:" << ret->first << "value:" << ret->second << endl; 134 } 135 else 136 { 137 cout << "未找到" << endl; 138 } 139 140 //equal_range(keyElem);//返回容器中key与keyElem相等的上下限的两个迭代器 141 pair<map<int, int>::iterator, map<int, int>::iterator> ret2 = m.equal_range(3); 142 143 if(ret2.first != m.end()) 144 { 145 cout << "找到了equal_range中的lower_bound的key" << ret2.first->first << "value:" << ret2.first->second << endl; 146 } 147 else 148 { 149 cout << "未找到" << endl; 150 } 151 152 if(ret2.second != m.end()) 153 { 154 cout << "找到了equal_range中的upper_bound的key" << ret2.second->first << "value:" << ret2.second->second << endl; 155 } 156 else 157 { 158 cout << "未找到" << endl; 159 } 160 161 } 162 163 //指定排序规则 164 class myCompare 165 { 166 public: 167 bool operator()(int v1, int v2) 168 { 169 return v1 > v2; 170 } 171 }; 172 173 174 void test03() 175 { 176 //从大到小排序 177 map<int, int, myCompare>m; 178 m.insert(pair<int, int>(1, 10)); 179 m.insert(make_pair(2,20)); 180 m.insert(map<int, int>::value_type(3, 30)); 181 m[4] = 40; 182 183 for(map<int, int, myCompare>::iterator it = m.begin(); it != m.end(); it++) 184 { 185 cout << "key = " << it->first << "value = " << it->second << endl; 186 } 187 188 } 189 190 191 192 int main() 193 { 194 test01(); 195 196 system("pause"); 197 return EXIT_SUCCESS; 198 }
7、STL容器使用时机
|
|
vector |
deque |
list |
set |
multiset |
map |
multimap |
|
典型内存结构 |
单端数组 |
双端数组 |
双向链表 |
二叉树 |
二叉树 |
二叉树 |
二叉树 |
|
可随机存取 |
是 |
是 |
否 |
否 |
否 |
对key而言:不是 |
否 |
|
元素搜寻速度 |
慢 |
慢 |
非常慢 |
快 |
快 |
对key而言:快 |
对key而言:快 |
|
元素安插移除 |
尾端 |
头尾两端 |
任何位置 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
》vector的使用场景:比如软件历史操作记录的存储,我们经常要查看历史记录,比如上一次的记录,上上次的记录,但却不会去删除记录,因为记录是事实的描述。
》deque的使用场景:比如排队购票系统,对排队者的存储可以采用deque,支持头端的快速移除,尾端的快速添加。如果采用vector,则头端移除时,会移动大量的数据,速度慢。
vector与deque的比较:
一:vector.at()比deque.at()效率高,比如vector.at(0)是固定的,deque的开始位置 却是不固定的。
二:如果有大量释放操作的话,vector花的时间更少,这跟二者的内部实现有关。
三:deque支持头部的快速插入与快速移除,这是deque的优点。
》list的使用场景:比如公交车乘客的存储,随时可能有乘客下车,支持频繁的不确实位置元素的移除插入。
》set的使用场景:比如对手机游戏的个人得分记录的存储,存储要求从高分到低分的顺序排列。
》map的使用场景:比如按ID号存储十万个用户,想要快速要通过ID查找对应的用户。二叉树的查找效率,这时就体现出来了。如果是vector容器,最坏的情况下可能要遍历完整个容器才能找到该用户。
二、总结
1 stack栈容器
1.1 先进后出
1.2 栈顶 top
1.3 压栈 push
1.4 弹出栈顶 pop
1.5 大小 size
1.6 为空 empty
2 queue 队列容器
2.1 先进先出
2.2 队头 front 队尾 back
2.3 入队 push
2.4 弹出队头 pop
2.5 大小 size
2.6 为空 empty
3 List容器
3.1 赋值、构造、大小、为空、删除 、添加
3.2 移除 remove( 10 ) 删除容器中所有与10 匹配的元素
3.3 双向循环链表
3.4 迭代器是不支持随机访问的
3.5 反转排序
3.5.1 reverse 反转
3.5.2 排序 成员函数 sort
3.5.3 默认排序 从小到大
3.5.4 自定义数据类型,必须指定排序规则
3.5.5 高级
3.6 remove删除list容器中自定义数据类型
4 set容器
4.1 关联式容器
4.2 插入数据自动排序 按照key
4.3 insert 插入值
4.4 erase 参数可以传值 或者 迭代器
4.5 find() 返回值 迭代器 找不到返回的 end()
4.6 count 计数 对于set而言 结果 就是 0 或者1
4.7 lower_bound(keyElem);//返回第一个key>=keyElem元素的迭代器。
4.8 upper_bound(keyElem);//返回第一个key>keyElem元素的迭代器。
4.9 equal_range(keyElem);//返回容器中key与keyElem相等的上下限的两个迭代器。
4.10 对组 pair
4.10.1 第一个值 first
4.10.2 第二个值 second
4.10.3 默认括号
4.10.4 make_pair()
4.11 set插入返回值是 对组 < 迭代器, 是否成功标示>
4.12 指定set排序规则,利用仿函数
4.13 set插入自定义数据类型
5 map容器
5.1 每个元素 都是一个pair
5.2 对于map而言 key是不可以重复
5.3 multimap可以
5.4 4中插入方式
5.5 count 统计 map 0 或1 multimap可能大于1
5.6 排序规则自己指定
在学习c++提高-STL总结了笔记,并分享出来。有问题请及时联系博主:Alliswell_WP,转载请注明出处。
posted on 2020-06-16 09:11 Alliswell_WP 阅读(134) 评论(0) 收藏 举报


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号