Azure AD(五)使用多租户应用程序模式让任何 Azure Active Directory 用户登录
一,引言
距离上次分享关于 “Azure AD" 的知识过去差不多2个多月了, 今天最近刚好也是学习,分享一下关于Azure AD 使用多租户应用程序模式让任何 Azure Active Directory 用户登录,之前仅仅都是在当初租户的用户或者受邀来宾来访问和使用我们的api资源的。今天我们将以下关于只要拥有微软 的工作/学校账号的用户都可以使用我们受AD保护的 API 资源。接下来就开始我们今天的分享
--------------------我是分割线--------------------
1,Azure AD(一)入门认识
2,Azure AD(二)调用受Microsoft 标识平台保护的 ASP.NET Core Web API 上
3,Azure AD(二)调用受Microsoft 标识平台保护的 ASP.NET Core Web API 下
4,Azure AD(三)知识补充-Azure资源的托管标识
5,Azure AD(四)知识补充-服务主体
6,Azure AD(五)使用多租户应用程序模式让任何 Azure Active Directory 用户登录
二,正文
1,修改受保护资源的应用的账号类型
首先我们登陆Azure Portal 上,并且切换一下当前活动的目录(也就是当前所在的租户)
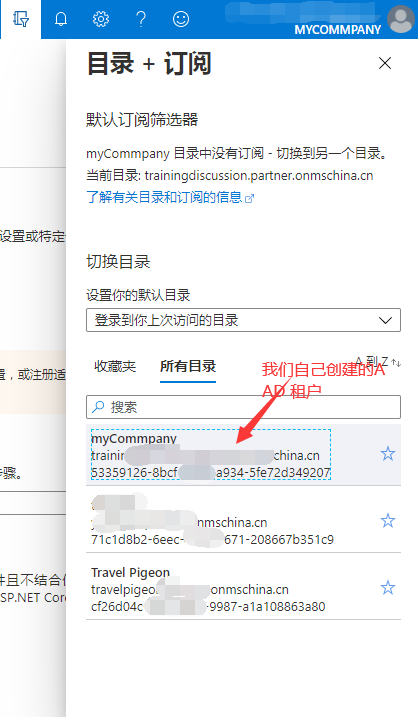
在之前在AAD中注册好的应用注册---”WebApi“,点击进入WebApi的设置
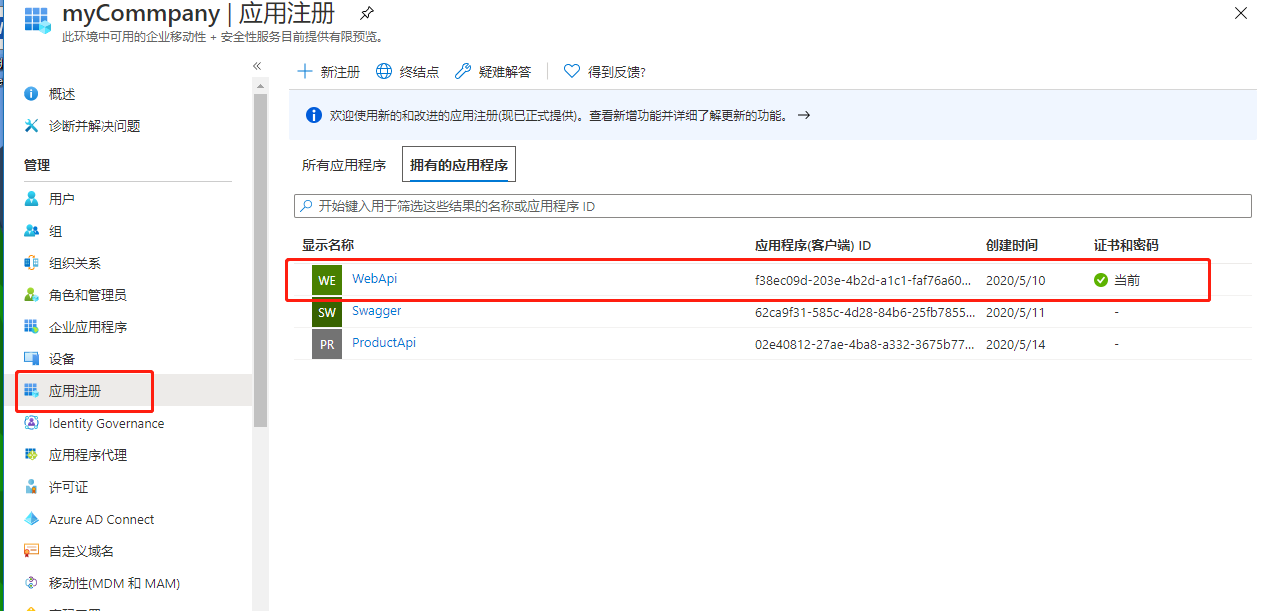
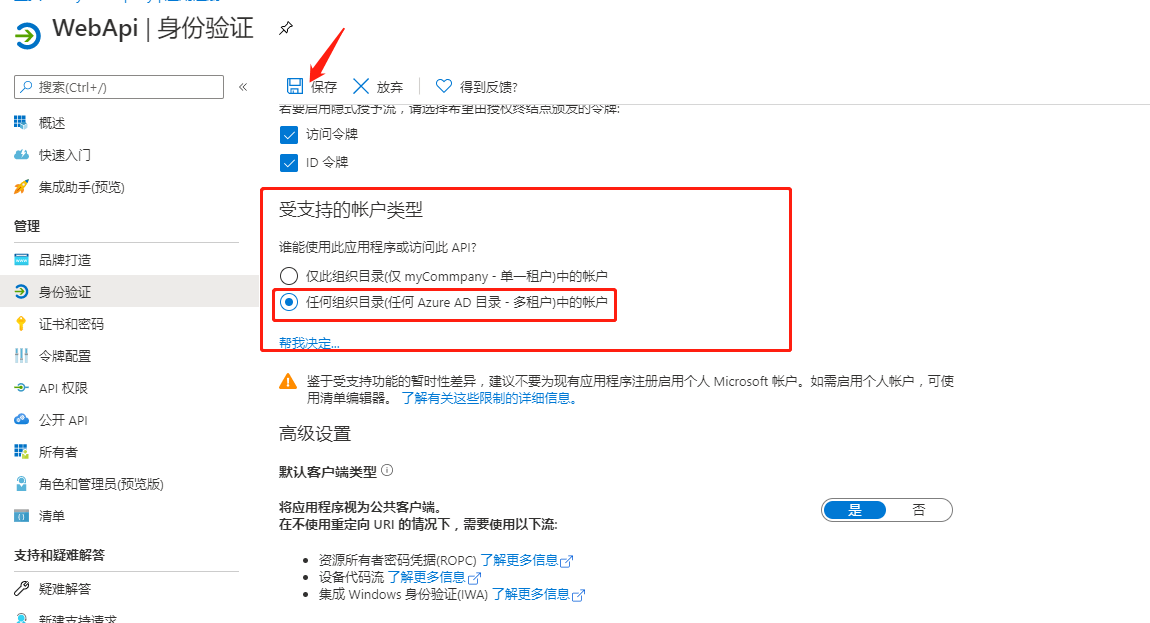
点击图中圈中的受支持的账户类型---仅我的组织

修改 受支持的账号类型 为 ”任何组合目录(任何 Azure AD 目录 - 都租户)中的账户“,点击 ”保存“
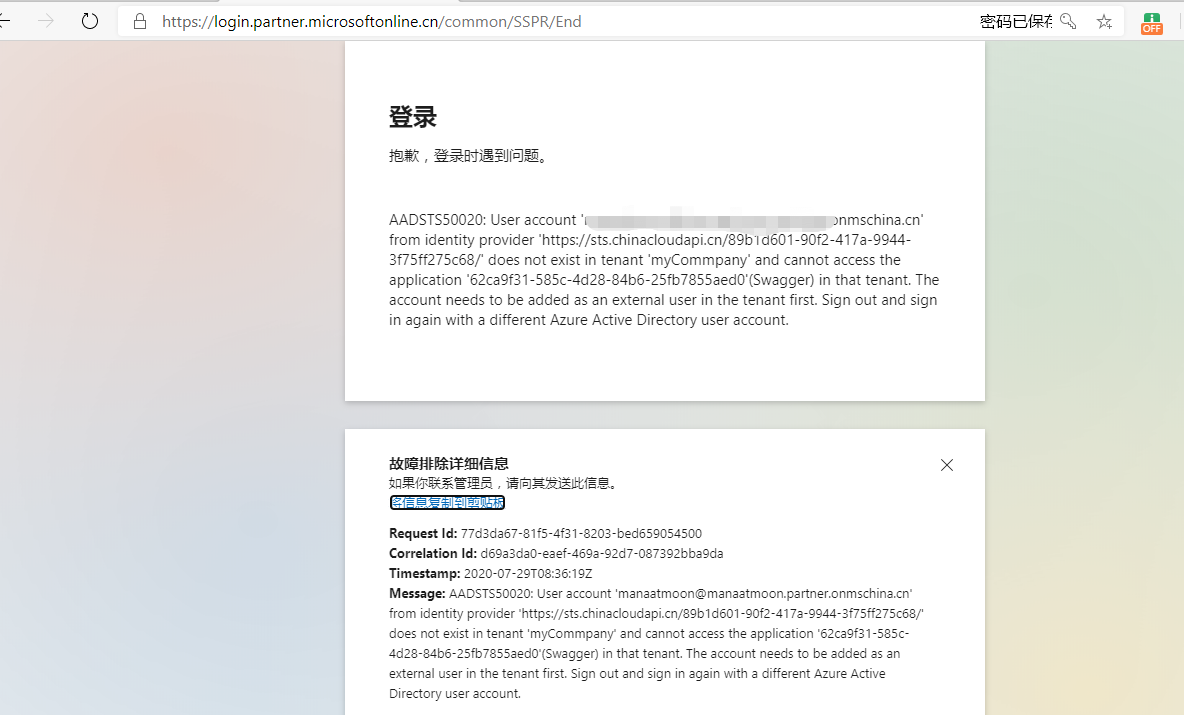
我们使用其他租户的账号登陆认证,提示 当前登陆账号不在当前登陆的租户内
2,修改代码配置
微软官方文档给出,当使用多租户模式的时候,
(1)代码需要更为为向/common 发出请求
在单租户应用程序中,登录请求将发送到租户的登录终结点。 以 trainingdiscussion.partner.onmschina.cn 为例,终结点将是:https://login.chinacloudapi.cn/trainingdiscussion.partner.onmschina.cn。 发送到租户终结点的请求可以让该租户中的用户(或来宾)登录该租户中的应用程序。
使用多租户应用程序时,应用程序事先并不知道用户来自哪个租户,因此无法将请求发送到租户的终结点。 取而代之的是,请求将发送到在所有 Azure AD 租户之间多路复用的终结点:https://login.chinacloudapi.cn/common
当 Microsoft 标识平台在 /common 终结点上收到请求时,会使用户登录,因而可以发现用户来自哪个租户。 /Common 终结点可与 Azure AD 支持的所有身份验证协议配合使用: OpenID Connect、OAuth 2.0、SAML 2.0 和 WS 联合身份验证。
/common 终结点不是租户,也不是颁发者,而只是一个多路复用器。 使用 /common 时,需要更新应用程序中用于验证令牌的逻辑。然后,对应用程序做出的登录响应会包含代表该用户的令牌。 令牌中的颁发者值告知应用程序该用户来自哪个租户。 从 /common 终结点返回响应时,令牌中的颁发者值将与用户的租户相对应。
(2)将代码更新为处理多个颁发者值
单租户应用程序通常采用类似于下面的终结点值:https://login.chinacloudapi.cn/trainingdiscussion.partner.onmschina.cn
并使用该值构造元数据 URL(在本例中为 OpenID Connect),例如:https://login.chinacloudapi.cn/trainingdiscussion.partner.onmschina.cn/.well-known/openid-configuration
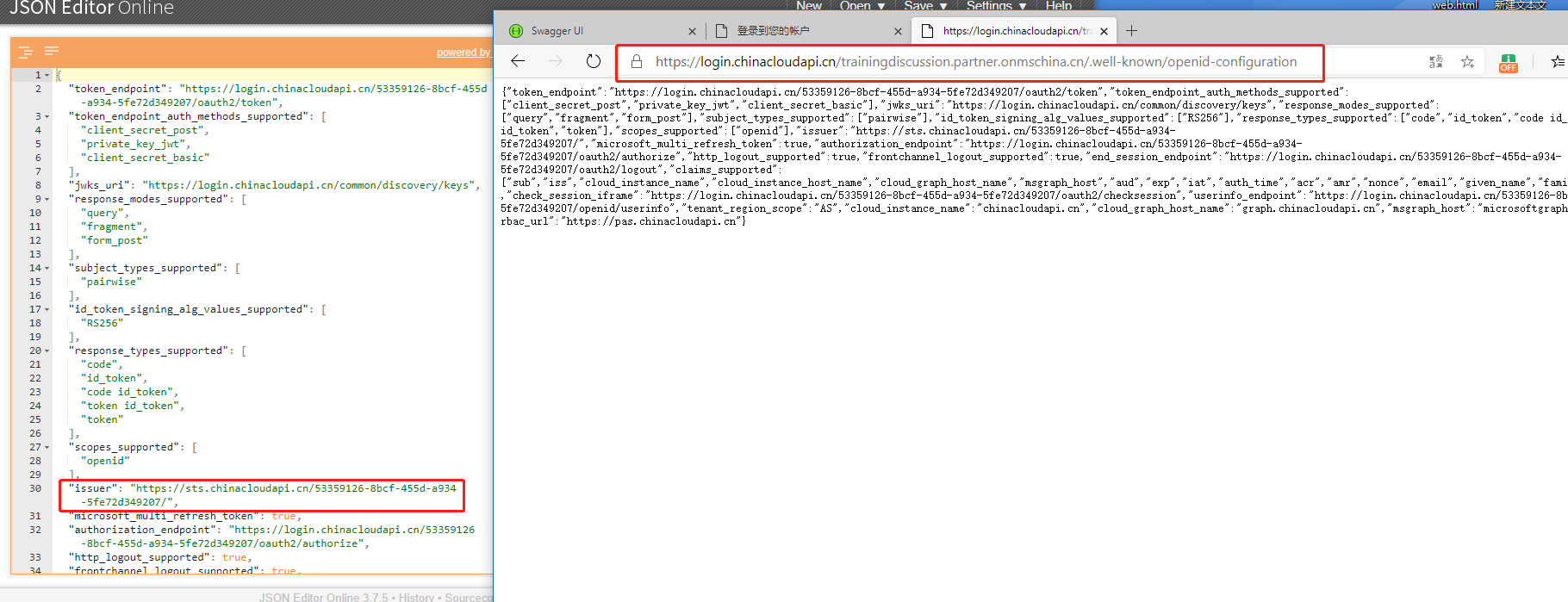
以下载用于验证令牌的两项关键信息:租户的签名密钥和颁发者值。 每个 Azure AD 租户使用以下格式的唯一颁发者值:https://sts.chinacloudapi.cn/53359126-8bcf-455d-a934-5fe72d349207/
下图中,是我当前AAD 租户中注册的 Web Api 的OpenID Connect 元数据文档
Authentication 配置
services.AddAuthentication("Bearer") .AddJwtBearer(o => { o.Audience = Appsettings.app(new string[] { "AzureAD", "ClientId" }); o.RequireHttpsMetadata = false; o.SaveToken = true; o.Authority = Appsettings.app(new string[] { "AzureAD", "Authority" }); o.TokenValidationParameters = new Microsoft.IdentityModel.Tokens.TokenValidationParameters() { ValidateIssuerSigningKey = true, ValidIssuer = Appsettings.app(new string[] { "AzureAD", "Issuer" }), ValidateLifetime = true, }; });
Swagger服务的配置
services.AddSwaggerGen(c => { c.SwaggerDoc("v1", new OpenApiInfo { Title = "My API", Version = "v1" }); c.AddSecurityDefinition("oauth2", new OpenApiSecurityScheme { Description = "JWT授权(数据将在请求头中进行传输) 直接在下框中输入Bearer {token}(注意两者之间是一个空格)\"", Type = SecuritySchemeType.OAuth2, In = ParameterLocation.Header,//jwt默认存放Authorization信息的位置(请求头中) Flows = new OpenApiOAuthFlows() { Implicit = new OpenApiOAuthFlow { //AuthorizationUrl = new Uri($"https://login.chinacloudapi.cn/{ Appsettings.app(new string[] { "AzureAD", "TenantId" })}/oauth2/authorize") AuthorizationUrl = new Uri($"https://login.chinacloudapi.cn/common/oauth2/authorize") } } }); // 在header中添加token,传递到后台 c.OperationFilter<SecurityRequirementsOperationFilter>(); });
开启中间件
#region Swagger app.UseSwagger(); app.UseSwaggerUI(c => { //根据版本名称倒序 遍历展示 var ApiName = Appsettings.app(new string[] { "Startup", "ApiName" }); c.SwaggerEndpoint($"/swagger/v1/swagger.json", $"{ApiName} v1"); c.OAuthClientId(Appsettings.app(new string[] { "Swagger", "ClientId" })); //c.OAuthClientSecret(Appsettings.app(new string[] { "Swagger", "ClientSecret" })); c.OAuthRealm(Appsettings.app(new string[] { "AzureAD", "ClientId" })); c.OAuthAppName("My API V1"); c.OAuthScopeSeparator(" "); c.OAuthAdditionalQueryStringParams(new Dictionary<string, string>() { { "resource", Appsettings.app(new string[] { "AzureAD", "ClientId" }) } }); }); #endregion IdentityModelEventSource.ShowPII = true; // here app.UseAuthentication();
完整代码:

public class Startup { public Startup(IConfiguration configuration, IWebHostEnvironment environment) { Configuration = configuration; Environment = environment; } public IConfiguration Configuration { get; } public IWebHostEnvironment Environment { get; } // This method gets called by the runtime. Use this method to add services to the container. public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services) { services.AddSingleton(new Appsettings(Environment.ContentRootPath)); //services.AddAuthentication(AzureADDefaults.JwtBearerAuthenticationScheme) // .AddAzureADBearer(options => Configuration.Bind("AzureAd", options)); services.AddAuthentication("Bearer") .AddJwtBearer(o => { o.Audience = Appsettings.app(new string[] { "AzureAD", "ClientId" }); o.RequireHttpsMetadata = false; o.SaveToken = true; o.Authority = Appsettings.app(new string[] { "AzureAD", "Authority" }); o.TokenValidationParameters = new Microsoft.IdentityModel.Tokens.TokenValidationParameters() { ValidateIssuerSigningKey = false, ValidIssuer = Appsettings.app(new string[] { "AzureAD", "Issuer" }), ValidateLifetime = true, }; }); services.AddSwaggerGen(c => { c.SwaggerDoc("v1", new OpenApiInfo { Title = "My API", Version = "v1" }); c.AddSecurityDefinition("oauth2", new OpenApiSecurityScheme { Description = "JWT授权(数据将在请求头中进行传输) 直接在下框中输入Bearer {token}(注意两者之间是一个空格)\"", Type = SecuritySchemeType.OAuth2, In = ParameterLocation.Header,//jwt默认存放Authorization信息的位置(请求头中) Flows = new OpenApiOAuthFlows() { Implicit = new OpenApiOAuthFlow { //AuthorizationUrl = new Uri($"https://login.chinacloudapi.cn/{ Appsettings.app(new string[] { "AzureAD", "TenantId" })}/oauth2/authorize") AuthorizationUrl = new Uri($"https://login.chinacloudapi.cn/common/oauth2/authorize") } } }); // 在header中添加token,传递到后台 c.OperationFilter<SecurityRequirementsOperationFilter>(); }); services.AddControllers(); } // This method gets called by the runtime. Use this method to configure the HTTP request pipeline. public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IWebHostEnvironment env) { if (env.IsDevelopment()) { app.UseDeveloperExceptionPage(); } #region Swagger app.UseSwagger(); app.UseSwaggerUI(c => { //根据版本名称倒序 遍历展示 var ApiName = Appsettings.app(new string[] { "Startup", "ApiName" }); c.SwaggerEndpoint($"/swagger/v1/swagger.json", $"{ApiName} v1"); c.OAuthClientId(Appsettings.app(new string[] { "Swagger", "ClientId" })); //c.OAuthClientSecret(Appsettings.app(new string[] { "Swagger", "ClientSecret" })); c.OAuthRealm(Appsettings.app(new string[] { "AzureAD", "ClientId" })); c.OAuthAppName("My API V1"); c.OAuthScopeSeparator(" "); c.OAuthAdditionalQueryStringParams(new Dictionary<string, string>() { { "resource", Appsettings.app(new string[] { "AzureAD", "ClientId" }) } }); }); #endregion IdentityModelEventSource.ShowPII = true; // here app.UseAuthentication(); app.UseRouting(); app.UseAuthorization(); app.UseEndpoints(endpoints => { endpoints.MapControllers(); }); } }

{ "Logging": { "LogLevel": { "Default": "Information", "Microsoft": "Warning", "Microsoft.Hosting.Lifetime": "Information" } }, "AllowedHosts": "*", "AzureAd": { "Instance": "https://login.chinacloudapi.cn/common", "Domain": "trainingdiscussion.partner.onmschina.cn", "TenantId": "common", "ClientId": "f38ec09d-203e-4b2d-a1c1-faf76a608528", "CallbackPath": "/signin-oidc", "Authority": "https://login.chinacloudapi.cn/organizations/v2.0/", "Issuer": "https://sts.chinacloudapi.cn/53359126-8bcf-455d-a934-5fe72d349207/" }, "Swagger": { "ClientId": "62ca9f31-585c-4d28-84b6-25fb7855aed0", "ClientSecret": "" // ?fxV/=/pwlRjwQgoIdLRlPNlWBBQ8939 } }
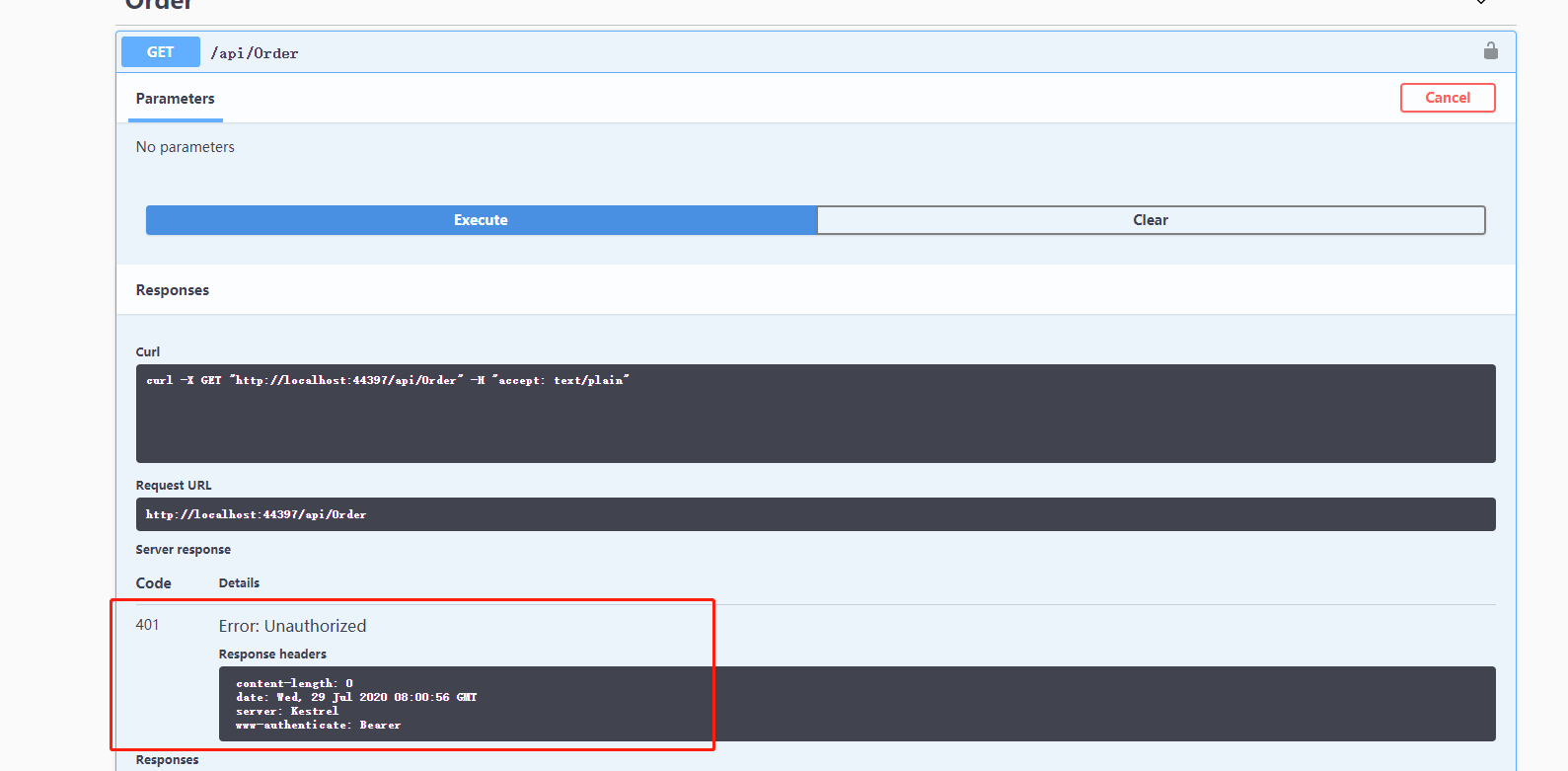
3,运行项目,进行测试
我们进行测试 order 接口,提示 返回码 401,无权限。
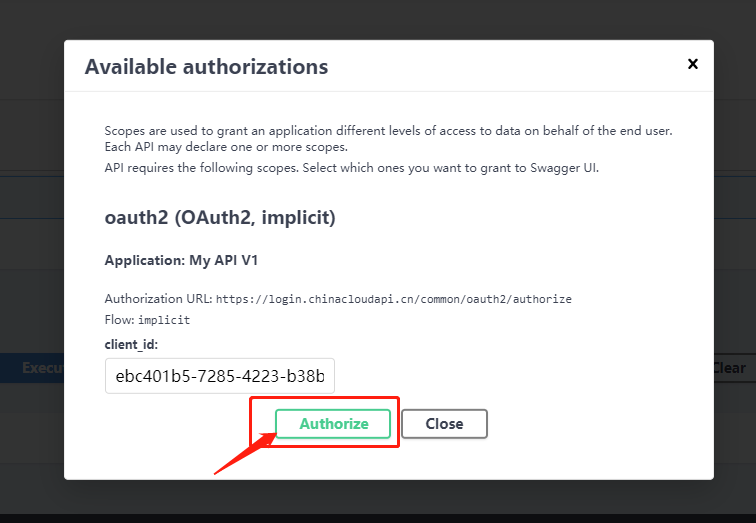
我们点击页面上的 ”Authorize“ 进行验证
这里,我们输入其他azure租户的用户的账号信息进行登陆验证(因为这号牵扯个人隐私,所以目前不展示),点击下一步
输入 账号密码信息,点击登陆
登陆验证通过后,我们再次进行验证操作
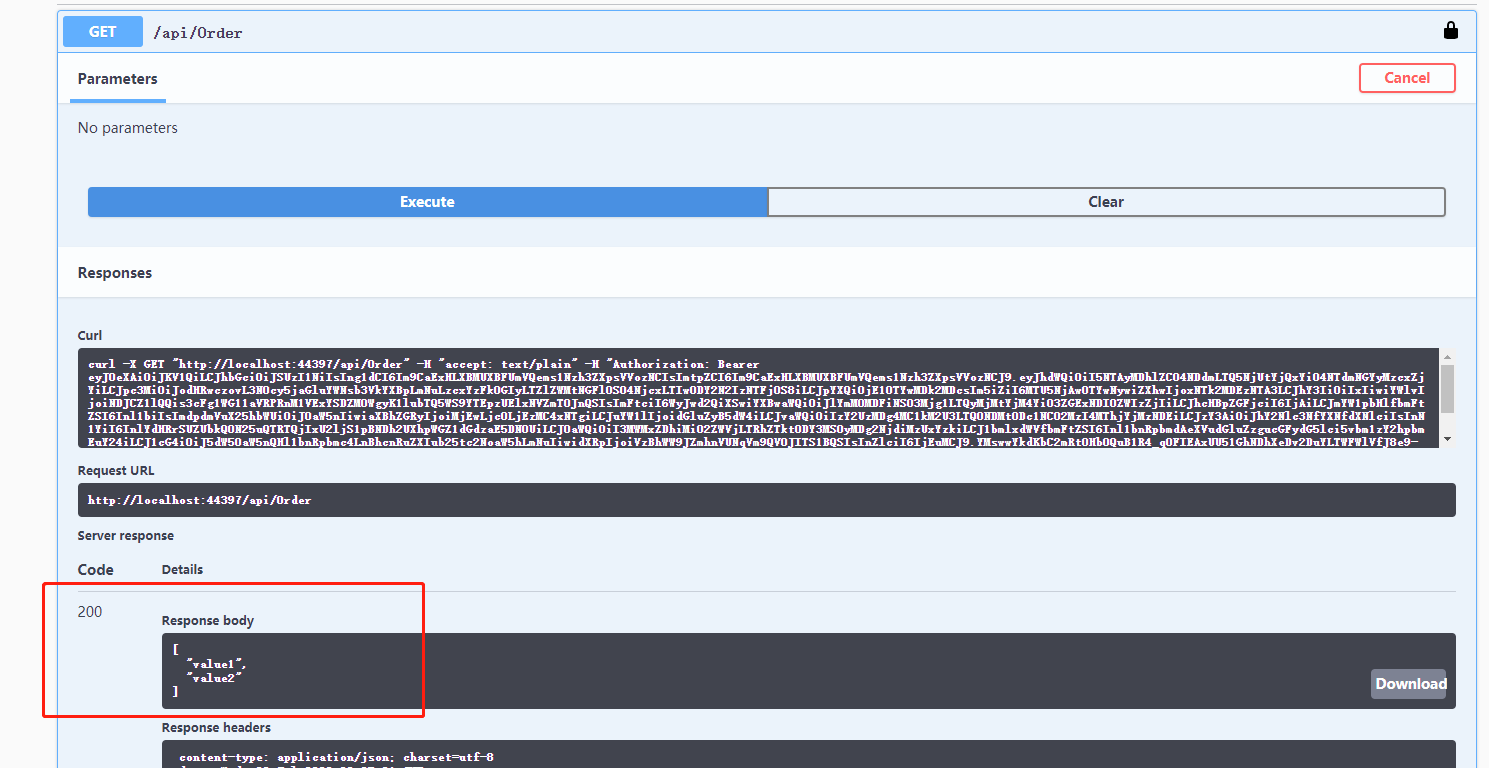
我们再次进行测试,ok,成功
🎉🎉🎉🎉🎉!!! 成功!,大家可以都试试哈
三,结尾
今天的文章大概介绍了多租户模式登陆/访问我们的受Azure AD保护的api资源,以及通过 Swagger中使用隐式授权模式来访问Api资源。
代码稍等,我会整理一下,上传到github中
作者:Allen
版权:转载请在文章明显位置注明作者及出处。如发现错误,欢迎批评指正。




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号