php分享二十九:命名空间
1:命名空间的命名不区分大小写
2:namespace必须在所有代码之前,除了declare语法以外(不过他之前可以有注释,空行等)
3:只有以下类型的代码受命名空间的影响,它们是:类(包括抽象类和traits)、接口、函数和常量。
4:如果你需要定义一个常量只在当前命名空间中,定义的时候要加上命名空间前缀,否则定义的是存在于全局命名空间的常量
例子:
The following code will define the constant "MESSAGE" in the global namespace (i.e. "\MESSAGE").
namespace test;
define('MESSAGE', 'Hello world!');
The following code will define two constants in the "test" namespace.
namespace test;
define('test\HELLO', 'Hello world!');
define(__NAMESPACE__ . '\GOODBYE', 'Goodbye cruel world!');
<?php
namespace NS;
define(__NAMESPACE__ .'\foo','111');
define('foo','222');
echo foo; // 111.
echo \foo; // 222.
echo \NS\foo // 111.
echo NS\foo // fatal error. assumes \NS\NS\foo.
?>
5:The namespace hierarchy will normally mirror the directory hierarchy where the class files are located, but this is not a strict requirement. You could, for example, have several class flles with different namespaces in the same directory.
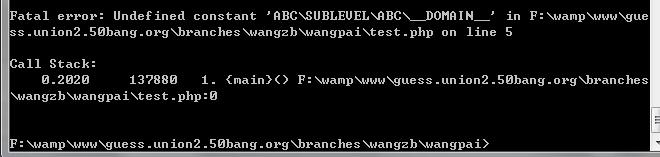
6: \ABC\__DOMAIN__ 和 ABC\__COMAIN__的区别
\ABC\__DOMAIN__指的是以根命名空间为起点的,而不加\默认以当前所在文件的命名空间为起点, 解析时会默认加上当前文件的命名空间
这个同文件系统的相对路径和绝对路径
baseTest.php
<?php namespace ABC; const __DOMAIN__ = 'example.com';
test.php
<?php namespace ABC\SUBLEVEL; require 'baseTest.php'; echo \ABC\__DOMAIN__; //输出example.com (测试一:加\)
测试二(不加\)
<?php namespace ABC\SUBLEVEL; require 'baseTest.php'; const __DOMAIN__ = 'self.com'; echo ABC\__DOMAIN__; //输出example.com
7:注意在命名空间中用exception类时
<?php
namespace Foo;
try {
// Something awful here
// That will throw a new exception from SPL
}
catch (Exception as $ex) {
// We will never get here
// This is because we are catchin Foo\Exception
}
?>
Instead use fully qualified name for the exception to catch it
<?php
namespace Foo;
try {
// something awful here
// That will throw a new exception from SPL
}
catch (\Exception as $ex) {
// Now we can get here at last
}
?>
8:一个文件中的内容的命名空间与include包含无关,只跟当前的文件有关
如果没有定义任何命名空间,所有的类与函数的定义都是在全局空间,与 PHP 引入命名空间概念前一样。在名称前加上前缀 \ 表示该名称是全局空间中的名称,即使该名称位于其它的命名空间中时也是如此。
Included files will default to the global namespace.
<?php
//test.php
namespace test {
include 'test1.inc';
echo '-',__NAMESPACE__,'-<br />';
}
?>
<?php
//test1.inc
echo '-',__NAMESPACE__,'-<br />';
?>
Results of test.php:
--
-test-
9:
在一个命名空间中,当 PHP 遇到一个非限定的类、函数或常量名称时,它使用不同的优先策略来解析该名称。类名称总是解析到当前命名空间中的名称。因此在访问系统内部或不包含在命名空间中的类名称时,必须使用完全限定名称
对于函数和常量来说,如果当前命名空间中不存在该函数或常量,PHP 会退而使用全局空间中的函数或常量。
<?php
namespace A\B\C;
class Exception extends \Exception {}
$a = new Exception('hi'); // $a 是类 A\B\C\Exception 的一个对象
$b = new \Exception('hi'); // $b 是类 Exception 的一个对象
$c = new ArrayObject; // 致命错误, 找不到 A\B\C\ArrayObject 类
?>
<?php
namespace A\B\C;
const E_ERROR = 45;
function strlen($str)
{
return \strlen($str) - 1;
}
echo E_ERROR, "\n"; // 输出 "45"
echo INI_ALL, "\n"; // 输出 "7" - 使用全局常量 INI_ALL
echo strlen('hi'), "\n"; // 输出 "1"
if (is_array('hi')) { // 输出 "is not array"
echo "is array\n";
} else {
echo "is not array\n";
}
?>
10:相同的命名空间不能出现在一个文件中,但是包含进来的相同命名空间则没问题
file1.php
<?php
namespace my\stuff;
class MyClass {}
?>
another.php
<?php
namespace another;
class thing {}
?>
file2.php
<?php namespace my\stuff; include 'file1.php'; include 'another.php'; use another\thing as MyClass; $a = new MyClass; // instantiates class "thing" from namespace another ?>
There is no name conflict, even though the class MyClass exists within the my\stuff namespace, because the MyClass definition is in a separate file. However, the next example causes a fatal error on name conflict because MyClass is defined in the same file as the use statement.
<?php
namespace my\stuff;
use another\thing as MyClass;
class MyClass {} // fatal error: MyClass conflicts with import statement
$a = new MyClass;
?>
11:嵌套的命名空间不允许
<?php
namespace my\stuff {
namespace nested {
class foo {}
}
}
?>
However, it is easy to simulate nested namespaces like so:
<?php
namespace my\stuff\nested {
class foo {}
}
?>
12:动态命名空间的名字需要主要反斜线的转义
<?php $a = new "dangerous\name"; // \n is a newline inside double quoted strings! $obj = new $a; $a = new 'not\at\all\dangerous'; // no problems here. $obj = new $a; ?>
注意:Inside a single-quoted string, the backslash escape sequence is much safer to use, but it is still recommended practice to escape backslashes in all strings as a best practice.
13:常量如果没有定义,则返回notice错误,默认常量的值设置成和它的名字一样
命名空间如果没有定义,则返回fatal错误
<?php namespace bar; $a = FOO; // produces notice - undefined constants "FOO" assumed "FOO"; $a = \FOO; // fatal error, undefined namespace constant FOO $a = Bar\FOO; // fatal error, undefined namespace constant bar\Bar\FOO $a = \Bar\FOO; // fatal error, undefined namespace constant Bar\FOO ?>




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号