UVM中测试用例的启动
UVM使用的是一种树形结构。但是在一个实际应用的UVM验证平台中,通常来说,树根是一个基于uvm_test派生的类。真正的测试用例都是基于base_test派生的一个类。
//base_test.sv
4 class base_test extends uvm_test;
5
6 my_env env;
7
8 function new(string name = "base_test", uvm_component parent = null);
9 super.new(name,parent);
10 endfunction
11
12 extern virtual function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase);
13 extern virtual function void report_phase(uvm_phase phase);
14 `uvm_component_utils(base_test)
15 endclass
16
18 function void base_test::build_phase(uvm_phase phase);
19 super.build_phase(phase);
20 env = my_env::type_id::create("env", this);
21 uvm_config_db#(uvm_object_wrapper)::set(this,
22 "env.i_agt.sqr.main_phase",
23 "default_sequence",
24 my_sequence::type_id::get());
25 endfunction
26
27 function void base_test::report_phase(uvm_phase phase);
28 uvm_report_server server; //
29 int err_num;
30 super.report_phase(phase);
31
32 server = get_report_server();//
33 err_num = server.get_severity_count(UVM_ERROR);//获取UVM_ERROR的数量
34
35 if (err_num != 0) begin
36 $display("TEST CASE FAILED");
37 end
38 else begin
39 $display("TEST CASE PASSED");
40 end
41 endfunction
base_test派生自uvm_test,使用uvm_component_utils宏来注册到factory中。在build_phase中实例化my_env,并设置sequencer的
default_sequence。需要注意的是,这里设置了default_sequence,其他地方就不需要再设置了。
除了实例化env外,base_test中做的事情在不同的公司各不相同。上面的代码中出现了report_phase,在report_phase中根据
UVM_ERROR的数量来打印不同的信息。一些日志分析工具可以根据打印的信息来判断DUT是否通过了某个测试用例的检查。
report_phase也是UVM内建的一个phase,它在main_phase结束之后执行。
除了上述操作外,还通常在base_test中做如下事情:第一,设置整个验证平台的超时退出时间;第二,通过config_db设置验
证平台中某些参数的值。
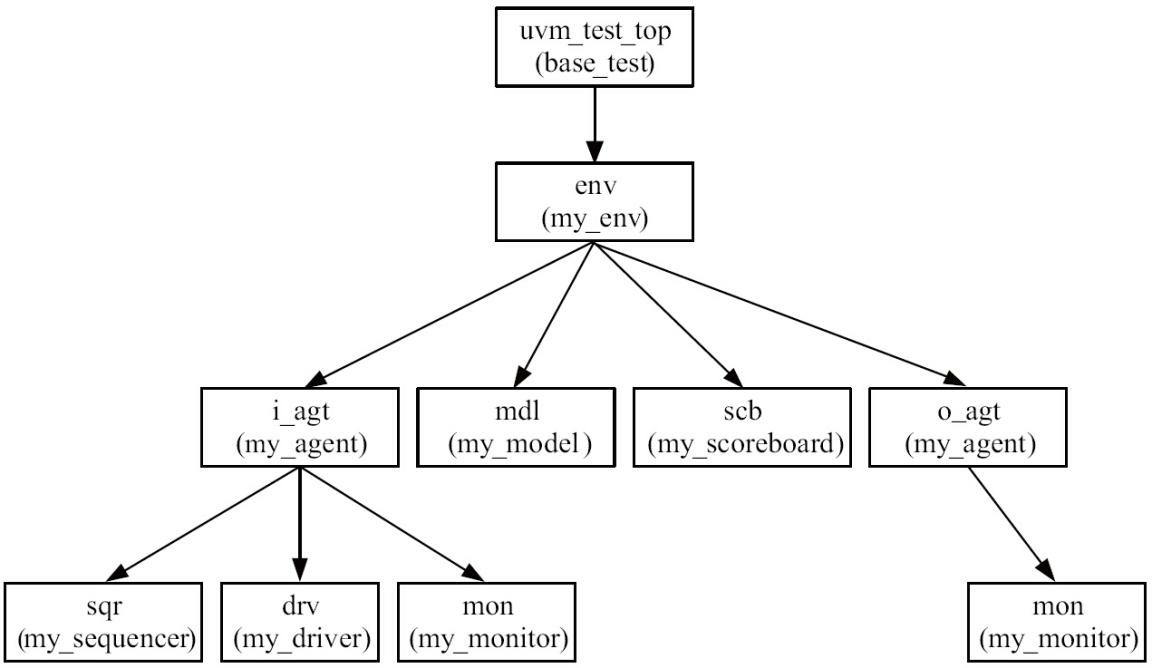
在把my_env放入base_test中之后,UVM树的层次结构变为如图2-11所示的形式。
top_tb中run_test的参数变成了base_test,并且config_db中设置virtual interface的路径参数要做如下改变:
文件:src/ch2/section2.5/2.5.1/top_tb.sv
49 initial begin
50 run_test("base_test");
51 end
52
53 initial begin
54 uvm_config_db#(virtual my_if)::set(null, "uvm_test_top.env.i_agt.drv", "vif",
input_if);
55 uvm_config_db#(virtual my_if)::set(null, "uvm_test_top.env.i_agt.mon","vif", input_if);
56 uvm_config_db#(virtual my_if)::set(null, "uvm_test_top.env.o_agt.mon","vif", output_if);
57 end
要测试一个DUT是否按照预期工作,需要对其施加不同的激励,这些激励被称为测试向量或pattern。一种激励作为一个测试用例,不同的激励就是不同的测试用例。测试用例的数量是衡量验证人员工作成果的最直接目标。
伴随着验证的进行,测试用例的数量一直在增加,在增加的过程中,很重要的一点是保证后加的测试用例不影响已经建好的测试用例。在前面所有的例子中,通过设置default_sequence的形式启动my_sequence。假如现在有另外一个my_sequence2,如何在不影响my_sequence的前提下将其启动呢?最理想的办法是在命令行中指定参数来启动不同的测试用例。
无论是在my_env中设置default_sequence,还是在base_test中或者top_tb中设置,都必须修改相关的设置代码才能启动my_sequence2,这与预期相去甚远。为了解决这个问题,先来看两个不同的测试用例。my_case0的定义如下:
文件:src/ch2/section2.5/2.5.2/my_case0.sv
3 class case0_sequence extends uvm_sequence #(my_transaction);
4 my_transaction m_trans;
…
10 virtual task body();
11 if(starting_phase != null)
12 starting_phase.raise_objection(this);
13 repeat (10) begin
14 `uvm_do(m_trans)
15 end
16 #100;
17 if(starting_phase != null)
18 starting_phase.drop_objection(this);
19 endtask
…
22 endclass
23
24
25 class my_case0 extends base_test;
26
27 function new(string name = "my_case0", uvm_component parent = null);
28 super.new(name,parent);
29 endfunction
30 extern virtual function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase);
31 `uvm_component_utils(my_case0)
32 endclass
33
34
35 function void my_case0::build_phase(uvm_phase phase);
36 super.build_phase(phase);
37
38 uvm_config_db#(uvm_object_wrapper)::set(this,
39 "env.i_agt.sqr.main_phase",
40 "default_sequence",
41 case0_sequence::type_id::get());
42 endfunction
my_case1的定义如下:
//my_case1.sv
3 class case1_sequence extends uvm_sequence #(my_transaction);
4 my_transaction m_trans;
…
10 virtual task body();
11 if(starting_phase != null)
12 starting_phase.raise_objection(this);
13 repeat (10) begin
14 `uvm_do_with(m_trans, { m_trans.pload.size() == 60;})
15 end
16 #100;
17 if(starting_phase != null)
18 starting_phase.drop_objection(this);
19 endtask
…
22 endclass
23
24 class my_case1 extends base_test;
25
26 function new(string name = "my_case1", uvm_component parent = null);
27 super.new(name,parent);
28 endfunction
29
30 extern virtual function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase);
31 `uvm_component_utils(my_case1)
32 endclass
33
34
35 function void my_case1::build_phase(uvm_phase phase);
36 super.build_phase(phase);
37
38 uvm_config_db#(uvm_object_wrapper)::set(this,
39 "env.i_agt.sqr.main_phase",
40 "default_sequence",
41 case1_sequence::type_id::get());
42 endfunction
在case1_sequence中出现了uvm_do_with宏,它是uvm_do系列宏中的一个,用于在随机化时提供对某些字段的约束。
要启动my_case0,需要在top_tb中更改run_test的参数:
initial begin
run_test("my_case0");
end
而要启动my_case1,也需要更改:
initial begin
run_test("my_case1");
end
当my_case0运行的时候需要修改代码,重新编译后才能运行;当my_case1运行时也需如此,这相当不方便。事实上,UVM提供对不加参数的run_test的支持:
//top_tb.sv
50 initial begin
51 run_test();
52 end
在这种情况下,UVM会利用UVM_TEST_NAME从命令行中寻找测试用例的名字,创建它的实例并运行。如下所示的代码可以启动my_case0:
<sim command>
… +UVM_TEST_NAME=my_case0
而如下所示的代码可以启动my_case1:
<sim command>
… +UVM_TEST_NAME=my_case1
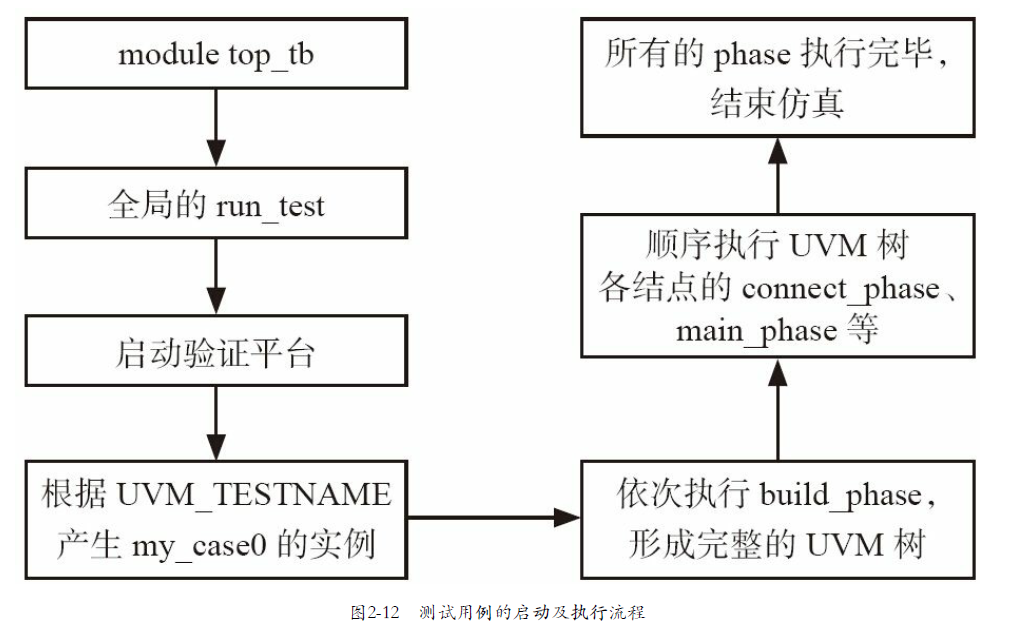
整个启动及执行的流程如图2-12所示。
启动后,整棵UVM树的结构如图2-13所示。
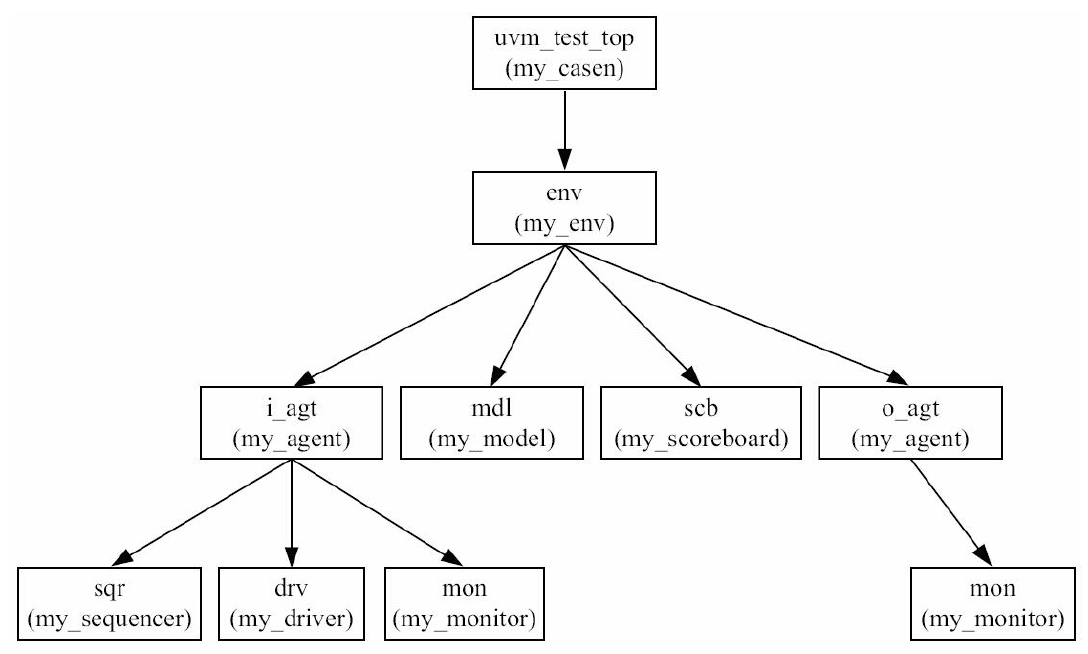
唯一区别在于树根的类型从base_test变成了my_casen。

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号