Binary Trees Aizu - ALDS1_7_B
Binary Tree
A rooted binary tree is a tree with a root node in which every node has at most two children.
Your task is to write a program which reads a rooted binary tree T and prints the following information for each node u of T:
node ID of u
parent of u
sibling of u
the number of children of u
depth of u
height of u
node type (root, internal node or leaf)
If two nodes have the same parent, they are siblings. Here, if u and v have the same parent, we say u is a sibling of v (vice versa).
The height of a node in a tree is the number of edges on the longest simple downward path from the node to a leaf.
Here, the given binary tree consists of n nodes and evey node has a unique ID from 0 to n-1.
Input
The first line of the input includes an integer n, the number of nodes of the tree.
In the next n lines, the information of each node is given in the following format:
id left right
id is the node ID, left is ID of the left child and right is ID of the right child. If the node does not have the left (right) child, the left(right) is indicated by -1.
Output
Print the information of each node in the following format:
node id: parent = p , sibling = s , degree = deg, depth = dep, height = h, type
p is ID of its parent. If the node does not have a parent, print -1.
s is ID of its sibling. If the node does not have a sibling, print -1.
deg, dep and h are the number of children, depth and height of the node respectively.
type is a type of nodes represented by a string (root, internal node or leaf. If the root can be considered as a leaf or an internal node, print root.
Please follow the format presented in a sample output below.
Constraints
1 ≤ n ≤ 25
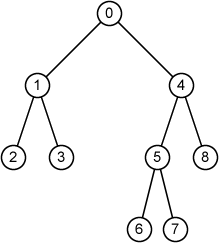
Sample Input 1
9
0 1 4
1 2 3
2 -1 -1
3 -1 -1
4 5 8
5 6 7
6 -1 -1
7 -1 -1
8 -1 -1
Sample Output 1
node 0: parent = -1, sibling = -1, degree = 2, depth = 0, height = 3, root
node 1: parent = 0, sibling = 4, degree = 2, depth = 1, height = 1, internal node
node 2: parent = 1, sibling = 3, degree = 0, depth = 2, height = 0, leaf
node 3: parent = 1, sibling = 2, degree = 0, depth = 2, height = 0, leaf
node 4: parent = 0, sibling = 1, degree = 2, depth = 1, height = 2, internal node
node 5: parent = 4, sibling = 8, degree = 2, depth = 2, height = 1, internal node
node 6: parent = 5, sibling = 7, degree = 0, depth = 3, height = 0, leaf
node 7: parent = 5, sibling = 6, degree = 0, depth = 3, height = 0, leaf
node 8: parent = 4, sibling = 5, degree = 0, depth = 2, height = 0, leaf
Reference
Introduction to Algorithms, Thomas H. Cormen, Charles E. Leiserson, Ronald L. Rivest, and Clifford Stein. The MIT Press.
Code
/*
^....0
^ .1 ^1^
.. 01
1.^ 1.0
^ 1 ^ ^0.1
1 ^ ^..^
0. ^ 0^
.0 1 .^
.1 ^0 .........001^
.1 1. .111100....01^
00 11^ ^1. .1^
1.^ ^0 0^
.^ ^0..1
.1 1..^
1 .0 ^ ^
00. ^^0.^
^ 0 ^^110.^
0 0 ^ ^^^10.01
^^ 10 1 1 ^^^1110.1
01 10 1.1 ^^^1111110
010 01 ^^ ^^^1111^1.^ ^^^
10 10^ 0^ 1 ^^111^^^0.1^ 1....^
11 0 ^^11^^^ 0.. ....1^ ^ ^
1. 0^ ^11^^^ ^ 1 111^ ^ 0.
10 00 11 ^^^^^ 1 0 1.
0^ ^0 ^0 ^^^^ 0 0.
0^ 1.0 .^ ^^^^ 1 1 .0
^.^ ^^ 0^ ^1 ^^^^ 0. ^.1
1 ^ 11 1. ^^^ ^ ^ ..^
^..^ ^1 ^.^ ^^^ .0 ^.0
0..^ ^0 01 ^^^ .. 0..^
1 .. .1 ^.^ ^^^ 1 ^ ^0001
^ 1. 00 0. ^^^ ^.0 ^.1
. 0^. ^.^ ^.^ ^^^ ..0.0
1 .^^. .^ 1001 ^^ ^^^ . 1^
. ^ ^. 11 0. 1 ^ ^^ 0.
0 ^. 0 ^0 1 ^^^ 0.
0.^ 1. 0^ 0 .1 ^^^ ..
.1 1. 00 . .1 ^^^ ..
1 1. ^. 0 .^ ^^ ..
0. 1. .^ . 0 .
.1 1. 01 . . ^ 0
^.^ 00 ^0 1. ^ 1 1
.0 00 . ^^^^^^ .
.^ 00 01 ..
1. 00 10 1 ^
^.1 00 ^. ^^^ .1
.. 00 .1 1..01 ..
1.1 00 1. ..^ 10
^ 1^ 00 ^.1 0 1 1
.1 00 00 ^ 1 ^
. 00 ^.^ 10^ ^^
1.1 00 00 10^
..^ 1. ^. 1.
0 1 ^. 00 00 .^
^ ^. ^ 1 00 ^0000^ ^ 01
1 0 ^. 00.0^ ^00000 1.00.1 11
. 1 0 1^^0.01 ^^^ 01
.^ ^ 1 1^^ ^.^
1 1 0.
.. 1 ^
1 1
^ ^ .0
1 ^ 1
.. 1.1 ^0.0
^ 0 1..01^^100000..0^
1 1 ^ 1 ^^1111^ ^^
0 ^ ^ 1 1000^
.1 ^.^ . 00
.. 1.1 0. 0
1. . 1. .^
1. 1 1. ^0
^ . ^.1 00 01
^.0 001. .^
*/
// Virtual_Judge —— Binary Trees Aizu - ALDS1_7_B.cpp created by VB_KoKing on 2019-05-08:09.
/* Procedural objectives:
Variables required by the program:
Procedural thinking:
Functions required by the program:
Determination algorithm:
Determining data structure:
*/
/* My dear Max said:
"I like you,
So the first bunch of sunshine I saw in the morning is you,
The first gentle breeze that passed through my ear is you,
The first star I see is also you.
The world I see is all your shadow."
FIGHTING FOR OUR FUTURE!!!
*/
#include <iostream>
#define MAX 10007
#define NIL -1
using namespace std;
struct Node {
int parent, left, right;
};
Node T[MAX];
int n, D[MAX], H[MAX];
void set_depth(int u, int d) {
if (u == NIL) return;
D[u] = d;
set_depth(T[u].left, d + 1);
set_depth(T[u].right, d + 1);
}
int set_height(int u) {
int h1 = 0, h2 = 0;
if (T[u].left != NIL)
h1 = set_height(T[u].left) + 1;
if (T[u].right != NIL)
h2 = set_height(T[u].right) + 1;
return H[u] = max(h1, h2);
}
int get_sibling(int u) {
if (T[u].parent == NIL) return NIL;
if (T[T[u].parent].left != u && T[T[u].parent].left != NIL)
return T[T[u].parent].left;
if (T[T[u].parent].right != u && T[T[u].parent].right != NIL)
return T[T[u].parent].right;
return NIL;
}
void print(int u) {
cout << "node " << u << ": ";
cout << "parent = " << T[u].parent << ", ";
cout << "sibling = " << get_sibling(u) << ", ";
int deg = 0;
if (T[u].left != NIL) deg++;
if (T[u].right != NIL) deg++;
cout << "degree = " << deg << ", ";
cout << "depth = " << D[u] << ", ";
cout << "height = " << H[u] << ", ";
if (T[u].parent == NIL)
cout << "root" << endl;
else if (T[u].left == NIL && T[u].right == NIL)
cout << "leaf" << endl;
else
cout << "internal node" << endl;
}
int main() {
int v, l, r, root = 0;
cin >> n;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
T[i].parent = NIL;
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
cin >> v >> l >> r;
T[v].left = l;
T[v].right = r;
if (l != NIL) T[l].parent = v;
if (r != NIL) T[r].parent = v;
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
if (T[i].parent == NIL)
root = i;
set_depth(root, 0);
set_height(root);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
print(i);
return 0;
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号