[java源码解析]对HashMap源码的分析(二)
上文我们讲了HashMap那骚骚的逻辑结构,这一篇我们来吹吹它的实现思想,也就是算法层面。有兴趣看下或者回顾上一篇HashMap逻辑层面的,可以看下HashMap源码解析(一)。
使用了哈希表得“拉链法”.
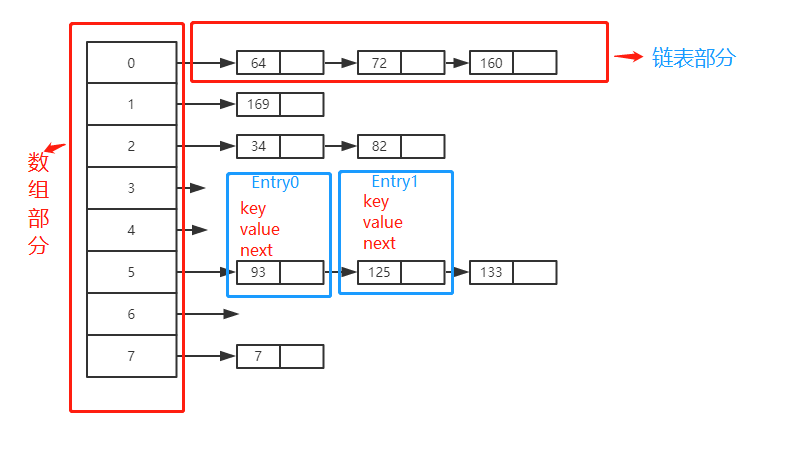
我打算按这个顺序来讲HashMap:几个关键属性 -> 构造方法-> 存取元素方法 ->解决hash冲突方法->HashMap扩容问题。
4个关键属性:
/** *HashMap的存储大小 */ transient int size; /** * HashMap的大小临界值,如果达到这个值就需要重新分配大小 */ int threshold; /** * 负载因子(默认值一般是0.75),哈希表在其容量自动增加之前可以达到多满的一种尺度。 *当哈希表中的条目数超出了 负载因子与当前容量的乘积时, *则要对该哈希表进行 rehash 操作(即重建内部数据结构),从而哈希表将具有大约两倍的桶数。 *负载因子过高虽然减少了空间开销,但同时也增加了查询成本 * static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f; * @serial */ final float loadFactor; /** * HashMap修改总数(修改数+删除数) */ transient int modCount;
构造方法 :
/**对四个构造函数的简单描述 **/ // 默认构造函数 public HashMap(); // 指定“容量大小”的构造函数 public HashMap(int initialCapacity); // 指定“容量大小”和“负载因子’‘的构造函数 public HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) ; // 包含”子Map的构造函数’ public HashMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m);
详细描述:
*默认构造 *使用默认负载因子DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR(0.75)以及 *默认容量大小 DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY */ public HashMap() { this(DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY, DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR); } /** *指定负载因子以及容量大小构造函数(前三个构造函数以这个构造函数为核心对‘容量大小’和‘负载因子’进行不同的赋值,来达到不同构造函数的效果) * @param initialCapacity the initial capacity 容量大小 * @param loadFactor the load factor 负载因子值 * @throws IllegalArgumentException if the initial capacity is negative * or the load factor is nonpositive */ public HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) { // 容量大小不能小于0 if (initialCapacity < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal initial capacity: " + initialCapacity); //HashMap最大容量不能超过MAXIMUM_CAPACITY if (initialCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) initialCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY; if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor)) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal load factor: " + loadFactor); this.loadFactor = loadFactor; threshold = initialCapacity; init(); } /** 包含子Map的构造函数 * 主要对通过对子Map的容量大小的处理给本HashMap的容量大小赋值 *以及clone子Map给本HashMap */ public HashMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) { //子Map的条目数/负载因子+1会大致等于子 Map的容量大小,通过比较当前子Map的容量大小和 //默认容易大小对比,找出最大的那个作为该HashMap的容量大小 this(Math.max((int) (m.size() / DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR) + 1, DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY), DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR); //不让容量大小超过MAXIMUM_CAPACITY ,让容量大小一直保持为2的幂次方 inflateTable(threshold); //将子Map的元素全部添加到本HashMap中。 putAllForCreate(m); }
HashMap的存取方法:
既然是线性数组,为什么能随机存取?这里HashMap用了一个小算法,大致是这样实现:
// 存储时:
int hash = key.hashCode(); // 这个hashCode方法这里不详述,只要理解每个key的hash是一个固定的int值
int index = hash % Entry[].length;
Entry[index] = value;
// 取值时:
int hash = key.hashCode();
int index = hash % Entry[].length;
return Entry[index];
一些工具方法的解析:
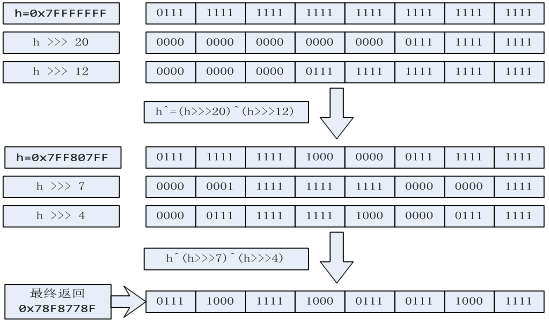
/** *计算hash值 */ final int hash(Object k) { //hashSeed表示一个与当前实例关联并且可以减少哈希碰撞概率应用于键的哈希码计算的随机种子。 int h = hashSeed; if (0 != h && k instanceof String) { return sun.misc.Hashing.stringHash32((String) k); } //对h和键的哈希码进行‘异或’并赋值运算 h ^= k.hashCode(); //h右移20位 异或 h右移12位 ,下一行同理。运算过程看下图2 h ^= (h >>> 20) ^ (h >>> 12); return h ^ (h >>> 7) ^ (h >>> 4); } /**返回索引值 * @param h 通过hash(Object k)方法计算得来的哈希码 * @param length 表示桶的数量(即数组的长度) * */ static int indexFor(int h, int length) { // assert Integer.bitCount(length) == 1 : "length must be a non-zero power of 2"; // 将哈希码和length进行按位与运算 return h & (length-1); }
图2:
取元素:
//通过key获取value public V get(Object key) { 如果key为null,则返回null键的值 if (key == null) return getForNullKey(); //获取键为key的实体类 Entry<K,V> entry = getEntry(key); return null == entry ? null : entry.getValue(); } /** * 根据键找到对应的实体类 * 实现思路:①:通过计算key的hash值,用indexFor(key,table.length)获取所在数组位置的下标。 * ②:通过寻找处于该下标位置链表”上查找“键值等于key”的元素。 */ final Entry<K,V> getEntry(Object key) { if (size == 0) { return null; } //计算key的hash值 int hash = (key == null) ? 0 : hash(key); for (Entry<K,V> e = table[indexFor(hash, table.length)]; e != null; e = e.next) { Object k; if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) return e; } //找不到则返回null return null; } /** * 获取null键的值 */ private V getForNullKey() { if (size == 0) { return null; } //null键一般在table下标为0的位置 for (Entry<K,V> e = table[0]; e != null; e = e.next) { if (e.key == null) return e.value; } return null; }
存元素:
/**往HashMap存储元素 * * @param key 键 * @param value 值 * @return * */ public V put(K key, V value) { //防止table的容量为0; if (table == EMPTY_TABLE) { inflateTable(threshold); } //如果key为null,则判断该hashMap的null键是否有值, //如果有,则将这个新value存入覆盖老的value,返回老的value if (key == null) return putForNullKey(value); //计算key的哈希值 int hash = hash(key); //通过key的哈希值以及数组的长度计算索引 int i = indexFor(hash, table.length); 找到数组此索引下的链表,一个一个得找,看有没有找到键值==该key的元素 for (Entry<K,V> e = table[i]; e != null; e = e.next) { Object k; //如果有,则用新value覆盖老的value oldValue,并返回oldValue; if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k))) { V oldValue = e.value; e.value = value; e.recordAccess(this); return oldValue; } } //如果没有,则modCount++,并添加新元素 modCount++; //添加新元素,具体实现思路,看下面该函数得定义 addEntry(hash, key, value, i); return null; } /** * 新增Entry */ void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) { //如果size比临界值大,而且该下标元素不为空,则对HashMap进行扩容,然后新增一个Entry实例 if ((size >= threshold) && (null != table[bucketIndex])) { resize(2 * table.length); hash = (null != key) ? hash(key) : 0; bucketIndex = indexFor(hash, table.length); } createEntry(hash, key, value, bucketIndex); } /** * *新增一个Entry实例,并将该实例得next指向原来得table[bucketIndex]; */ void createEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) { // 设置“e”为“新Entry的下一个节点” Entry<K,V> e = table[bucketIndex]; table[bucketIndex] = new Entry<>(hash, key, value, e); size++; }
解决hash冲突方法:下面只具体讲了拉链法,其它有兴趣可自行了解~
开放定址法(线性探测再散列,二次探测再散列,伪随机探测再散列)
再哈希法
链地址法 :就是在冲突的位置上简历一个链表,然后将冲突的元素插入到链表尾端。
建立一个公共溢出区
HashMap扩容:resize方法
/** 重新调整HashMap中桶的数量 * *通过判断新容量大小值, *如果 oldCapacity 超过Entty数量的最大值,则将Integer.MAX_VALUE赋给临界值(阀值), *直接返回不进行扩容(这样以后都不会扩容) *如果 oldCapacity 不超过Entty数量的最大值,则创建一个新的数组,将数据转移到新的数组里 *并重新修改阀值 * @param newCapacity the new capacity, 新容量大小值 */ void resize(int newCapacity) { //引用扩容前的Entry数组 Entry[] oldTable = table; int oldCapacity = oldTable.length; // 扩容前的数组大小如果已经达到最大(2^30)了 if (oldCapacity == MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) { //修改阈值为int的最大值(2^31-1),这样以后就不会扩容了 threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE; return; } Entry[] newTable = new Entry[newCapacity]; //将原有Entry数组的元素拷贝到新的Entry数组里 transfer(newTable, initHashSeedAsNeeded(newCapacity)); //HashMap的table属性引用新的Entry数组 table = newTable; //修改阈值 threshold = (int)Math.min(newCapacity * loadFactor, MAXIMUM_CAPACITY + 1); } /** * 将原有Entry数组的元素拷贝到新的Entry数组里 */ void transfer(Entry[] newTable, boolean rehash) { int newCapacity = newTable.length; for (Entry<K,V> e : table) { while(null != e) { Entry<K,V> next = e.next; if (rehash) { e.hash = null == e.key ? 0 : hash(e.key); } //重新计算每个元素在数组中的位置 int i = indexFor(e.hash, newCapacity); //标记[1] e.next = newTable[i]; //将元素放在数组上 newTable[i] = e; ////访问下一个Entry链上的元素 e = next; } } }
这是对HashMap的实现思路的基本分析。HashMap能讲的太多了。比如*线程,遍历迭代,红黑树*......每一部分都能独立开篇来讲。以后有机会出
以上是本人对HashMap的一点理解,有什么理解不当欢迎指出~



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号