多线程学习笔记
一、Java实现多线程的方式
主要有四种
1.继承Thread类
public class MyThread extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
System.out.println("Thread name:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyThread myThread1 = new MyThread();
myThread1.setName("Thread-1");
MyThread myThread2 = new MyThread();
myThread2.setName("Thread-2");
myThread1.start();
myThread2.start();
}
}
2.实现Runnable接口
public class MyRunnable implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
System.out.println("Thread name:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread thread1 = new Thread(new MyRunnable());
thread1.setName("thread-1");
Thread thread2 = new Thread(new MyRunnable());
thread2.setName("thread-2");
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
}
}
3.实现Callable接口
public class MyCallable implements Callable<Integer> {
@Override
public Integer call() {
int a = 5;
int b = 10;
System.out.println("Thread name:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
return a + b;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
FutureTask<Integer> futureTask1 = new FutureTask<>(new MyCallable());
FutureTask<Integer> futureTask2 = new FutureTask<>(new MyCallable());
Thread thread1 = new Thread(futureTask1);
Thread thread2 = new Thread(futureTask2);
thread1.setName("thread-1");
thread2.setName("thread-2");
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
System.out.println("返回值为:" + futureTask1.get());
System.out.println("返回值为:" + futureTask2.get());
}
}
4.使用Executor线程池
介绍三种
//这边三种方式,注释其中两个,打开其中一个运行即可
public class MyExecutor {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
/**
* 第一种newFixedThreadPool()
* 1.构造一个固定大小的线程池,空闲的线程会一直保留着
* 2.提交的任务数多于空闲线程数,就会把未得到服务的任务放到队列中等待。
*/
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);
// /**
// * 第二种newCachedThreadPool()
// * 1.构建的线程池会立即执行任务
// * 2.当前存在空闲线程,直接执行任务
// * 3.当前不存在空闲线程,则创建一个新线程执行任务
// * 4.该线程池内的空闲线程只会保留 60 秒
// */
// ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
//
// /**
// *第三种newSingleThreadExecutor()
// * 构建的线程池只存在一个线程,会顺序地执行所提交的任务。
// */
// ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
// 2.调用 Runnable 任务
executorService.execute(new TestRunnable());
}
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
// 2.调用 Callable 任务
Future<Integer> submit = executorService.submit(new TestCallable());
System.out.println("Callable返回值:" + submit.get());
}
//关闭连接
executorService.shutdown();
}
}
class TestRunnable implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("Thread name::" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
}
class TestCallable implements Callable<Integer> {
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception {
System.out.println("Thread name::" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
return 666;
}
}
二、多线程的使用
1.停止线程
推荐的使用方式
//核心思想就是用一个方法去改变flag的值,如果flag等于false就停止线程
public class MyRunnable implements Runnable {
private boolean flag = true;
@Override
public void run() {
while (flag) {
System.out.println("Thread name:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
}
public void stop() {
this.flag = !this.flag;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
MyRunnable myRunnable = new MyRunnable();
Thread thread1 = new Thread(myRunnable);
thread1.setName("thread-1");
thread1.start();
//由于电脑性能不同,有可能线程没启动就执行完循环了,多重启几次试试。
for (int i = 1; i < 1000; i++) {
System.out.println("main" + i);
if (i == 800) {
myRunnable.stop();
System.out.println("停止线程");
break;
}
}
}
}
2.线程休眠Sleep
每个对象都有一个锁,sleep不会释放锁
public static void main(String[] args) {
while (true) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println(new SimpleDateFormat("HH:mm:ss").format(new Date()));
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
3.Thread.yield()
线程礼让,让CPU重新调度,但不一定礼让成功
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyYield myYield = new MyYield();
new Thread(myYield, "a").start();
new Thread(myYield, "b").start();
}
}
class MyYield implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "开始");
Thread.yield();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "结束");
}
}
4.join
强行插队,少使用,容易堵塞线程
//运行代码,刚开始两个线程一起跑,当主线程的循环i == 300时“线程a”插队进来,主线程得等“线程a”执行完才能继续执行。
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread thread = new Thread(new MyJoin(), "线程a");
thread.start();
for (int i = 0; i < 600; i++) {
if (i == 300) {
//当i等于300的时候让“线程a”插队进来执行
thread.join();
}
System.out.println("main-----" + i);
}
}
}
class MyJoin implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "我浅浅的插个队--------" + i);
}
}
}
5.线程状态
new->runnable->timed_waiting<->执行->terminated
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread thread = new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("线程执行");
}
});
Thread.State state = thread.getState();
System.out.println("新建" + state);
thread.start();
state = thread.getState();
System.out.println("启动" + state);
while (state != Thread.State.TERMINATED) {
Thread.sleep(100);
state = thread.getState();
System.out.println(state);
}
}
}
6.线程优先级
先设置优先级,再启动。优先级是1-10之间,主线程默认优先级是5
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
//特别说明主线程得优先级是默认的
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "--------->" + Thread.currentThread().getPriority());
MyPriority myPriority = new MyPriority();
Thread thread1 = new Thread(myPriority);
Thread thread2 = new Thread(myPriority);
Thread thread3 = new Thread(myPriority);
Thread thread4 = new Thread(myPriority);
Thread thread5 = new Thread(myPriority);
Thread thread6 = new Thread(myPriority);
thread1.setPriority(Thread.MIN_PRIORITY);//最小优先级1
thread2.setPriority(2);
thread3.setPriority(4);
thread4.setPriority(7);
thread5.setPriority(6);
thread6.setPriority(Thread.MAX_PRIORITY);//最大优先级10
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
thread3.start();
thread4.start();
thread5.start();
thread6.start();
}
}
class MyPriority implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "--------->" + Thread.currentThread().getPriority());
}
}
7.守护线程
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
God god = new God();
You you = new You();
Thread thread = new Thread(god);
//设置为守护线程,默认为false
thread.setDaemon(true);
thread.start();
new Thread(you).start();
}
}
class God implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
System.out.println("上帝在守护着你,直到你死亡");
}
}
}
class You implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 1; i <= 3650; i++) {
System.out.println("我活着的第" + i + "天");
if (i == 3650) {
System.out.println("终于走到人生的镜头,你死了,上帝发现你死了,一会他也就退出对你的守护了-------------------------------");
}
}
}
}
三、线程同步
形成条件:队列+锁(解决线程不安全的问题,锁机制:synchronized)
下面举出三个线程不全的案例:
1.买票
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
BuyTicket buyTicket = new BuyTicket();
new Thread(buyTicket, "小红").start();
new Thread(buyTicket, "小白").start();
new Thread(buyTicket, "小绿").start();
}
}
class BuyTicket implements Runnable {
//十张票
private int ticketNums = 10;
private boolean flag = true;
@Override
public void run() {
while (flag) {
try {
buy();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
private void buy() throws InterruptedException {
if (this.ticketNums <= 0) {
this.flag = false;
return;
}
Thread.sleep(300);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "拿到" + this.ticketNums-- + "张票");
}
}
2.取钱
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Account account = new Account(100, "结婚基金");
Drawing you = new Drawing(account,50,"you");
Drawing girlFriend = new Drawing(account,100,"girlFriend");
you.start();
girlFriend.start();
}
}
//账户
class Account {
int money;//余额
String name;//卡名
public Account(int money, String name) {
this.money = money;
this.name = name;
}
}
//银行
class Drawing extends Thread {
Account account;//账户
int drawingMoney;//取了多少钱
int nowMoney;//现在还有多少钱
public Drawing(Account account, int drawingMoney, String name) {
super(name);
this.account = account;
this.drawingMoney = drawingMoney;
}
@Override
public void run() {
//判断有没有钱
if (account.money - drawingMoney < 0) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "钱不够,取不了");
return;
}
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
account.money -= drawingMoney;
nowMoney += drawingMoney;
System.out.println(account.name + "的余额为:" + account.money + "元");
System.out.println(this.getName() + "手里的钱" + this.nowMoney);
}
}
3.list添加
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
new Thread(() -> {
list.add(Thread.currentThread().getName());
}).start();
}
Thread.sleep(3000);
System.out.println(list.size());
}
}
4.synchronized锁 同步方法,同步代码块
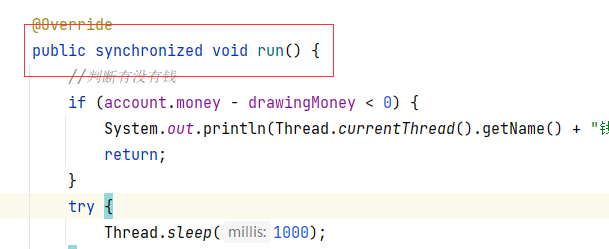
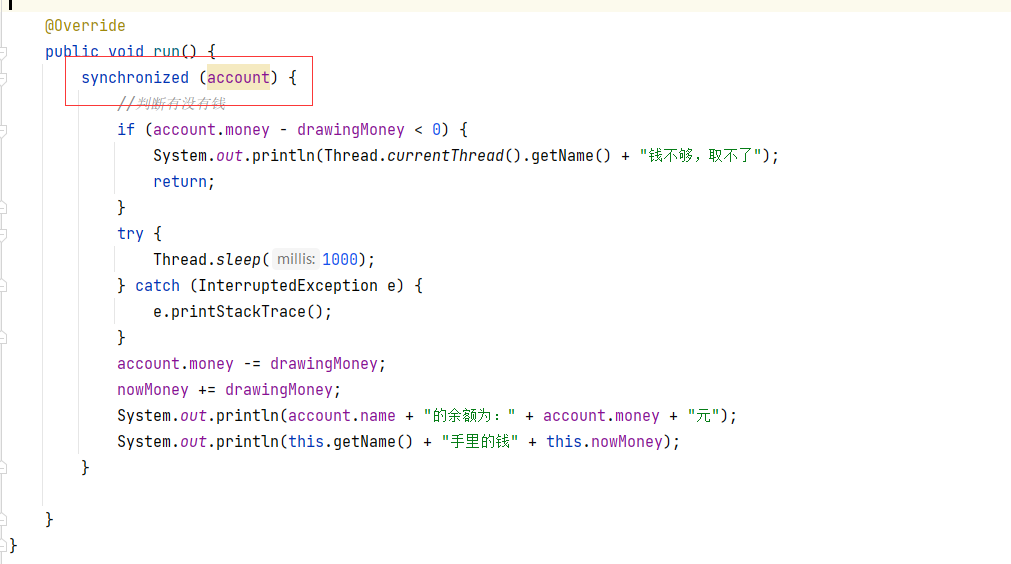
5.lock锁
JDK5.0开始,显示定义同步锁
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyLock myLock = new MyLock();
new Thread(myLock).start();
;
new Thread(myLock).start();
;
new Thread(myLock).start();
;
}
}
class MyLock implements Runnable {
private int ticketNums = 10;
//定义lock锁
private final ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
try {
//加锁
lock.lock();
if (ticketNums > 0) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(ticketNums--);
} else {
break;
}
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
}
6.synchronized 与 Lock 对比

四、线程协作

1.管程法
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SynContainer synContainer = new SynContainer();
new Producers(synContainer).start();
new Consumer(synContainer).start();
}
}
//生产者
class Producers extends Thread {
SynContainer synContainer;
public Producers(SynContainer synContainer) {
this.synContainer = synContainer;
}
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
synContainer.push(new Chicken(synContainer.count));
}
}
}
//消费者
class Consumer extends Thread {
SynContainer synContainer;
public Consumer(SynContainer synContainer) {
this.synContainer = synContainer;
}
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
synContainer.pop();
}
}
}
//产品
class Chicken {
int id;//产品编号
public Chicken(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public Chicken() {
}
}
//缓存区
class SynContainer {
//容器大小
Chicken[] chickens = new Chicken[1000];
//容器技术器
int count = 0;
//生产者放入产品
public synchronized void push(Chicken chicken) {
//如果容器满了通知消费者消费
if (count == chickens.length) {
//通知消费者,生产者等待
try {
this.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//如果容器没有满,放入产品
chickens[count] = chicken;
count++;
System.out.println("生产了1只鸡" + "当前有" + count + "只鸡");
this.notifyAll();
}
//消费者去除产品
public synchronized void pop() {
//判断能否消费
if (count == 0) {
//没有产品了,等待生产者生产
try {
this.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
count--;
System.out.println("消费了1只鸡" + "当前有" + count + "只鸡");
//消费了一个产品通知生产者生产
this.notifyAll();
}
}
2.信号灯法
//信号灯法,通过标志位解决。
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TV tv = new TV();
new Player(tv).start();
new Watcher(tv).start();
}
}
//演员
class Player extends Thread {
TV tv;
public Player(TV tv) {
this.tv = tv;
}
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
if (i % 2 == 0) {
this.tv.play("快乐大本营");
} else {
this.tv.play("抖音激励美好生活");
}
}
}
}
//观众
class Watcher extends Thread {
TV tv;
public Watcher(TV tv) {
this.tv = tv;
}
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
this.tv.watch();
}
}
}
//产品
class TV {
//演员表演,观众等待 T
//观众观看。演员等待 F
String voice;//表演的节目
boolean flag = true;
//表演
public synchronized void play(String voice) {
if (!flag) {
try {
this.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println("演员表演了:" + voice);
//通知观众观看
this.notifyAll();
this.voice = voice;
this.flag = !this.flag;
}
//观看
public synchronized void watch() {
if (flag) {
try {
this.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println("观众观看了:" + voice);
this.notifyAll();
this.flag = !this.flag;
}
}

