算法设计与分析PTA考试
7-1 递归二路归并排序
题目
本题目要求读入N个整数,采用递归的二路归并排序法进行排序,输出前3轮排序后的结果。
输入格式
输入不超过100的正整数N和N个整数(空格分隔)。
输出格式
输出三行,第一行为第一轮排序结果,第二行为第二轮排序结果,第三行为第三轮排序结果。数据间用
一个空格分隔。
为简便起见,最后一个元素后也有一个空格。
输入样例
5
54321
输出样例
4 5 3 2 1
3 4 5 2 1
3 4 5 1 2
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define mst(x, y) memset(x, y, sizeof x)
#define endl '\n'
#define INF LONG_LONG_MAX
#define int long long
#define Lson u << 1, l, mid
#define Rson u << 1 | 1, mid + 1, r
#define FAST ios::sync_with_stdio(false), cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0)
const int N = 2000010, MOD = 1e9 + 7;
const double EPS = 1e-6;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
int T;
int n;
int idx = 1;
int a[N], tmp[N];
void merge_sort(int q[], int l, int r)
{
if (l >= r)
return;
int mid = l + r >> 1;
merge_sort(q, l, mid), merge_sort(q, mid + 1, r);
int k = 0, i = l, j = mid + 1;
while (i <= mid && j <= r)
if (q[i] <= q[j])
tmp[k++] = q[i++];
else
tmp[k++] = q[j++];
while (i <= mid)
tmp[k++] = q[i++];
while (j <= r)
tmp[k++] = q[j++];
for (i = l, j = 0; i <= r; i++, j++)
q[i] = tmp[j];
if (idx <= 3)
{
idx++;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
cout << a[i] << " ";
cout << endl;
}
}
void solve()
{
cin >> n;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
cin >> a[i];
merge_sort(a, 0, n - 1);
}
signed main()
{
FAST;
T = 1;
// cin >> T;
while (T--)
solve();
return 0;
}
7-2 非递归二路归并排序
为啥不直接sort,谁出的题谁写去吧,一写一个不吱声
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define mst(x, y) memset(x, y, sizeof x)
#define endl '\n'
#define INF LONG_LONG_MAX
#define int long long
#define Lson u << 1, l, mid
#define Rson u << 1 | 1, mid + 1, r
#define FAST ios::sync_with_stdio(false), cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0)
const int N = 2000010, MOD = 1e9 + 7;
const double EPS = 1e-6;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
int n;
int T = 1;
int a[N], t[N];
void merge_sort()
{
int cnt = 0;
for (int len = 1; len <= n; len <<= 1)
{
int tt = 0;
for (int i = 1, j; i <= n;)
{
j = i + len;
if (j > n)
break;
int zr = i + len - 1, yr = min(n, j + len - 1);
while (i <= zr && j <= yr)
{
if (a[i] <= a[j])
t[++tt] = a[i++];
else
t[++tt] = a[j++];
}
while (i <= zr)
t[++tt] = a[i++];
while (j <= yr)
t[++tt] = a[j++];
i = yr + 1;
}
for (int k = 1; k <= tt; ++k)
a[k] = t[k];
cnt++;
if (cnt <= 3)
{
for (int k = 1; k <= n; ++k)
cout << a[k] << " ";
cout << endl;
}
}
}
void solve()
{
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
cin >> a[i];
merge_sort();
}
signed main()
{
FAST;
// cin >> T;
while (T--)
solve();
return 0;
}
7-3 最长公共子序列
题目
给定两个序列 X=<x1,x2,...,xm> 和 Y=<y1,y2,...,yn>,要求找出 X 和 Y 的一个最长公共子序列。
输入格式
共有两行。每行为一个由大写字母构成的长度不超过 1000 的字符串,表示序列 X 和 Y。
输出格式
第一行为一个非负整数。表示所求得的最长公共子序列的长度。若不存在公共子序列,则输出文件仅有一行输出一个整数 0。
输入样例
ADCBDAB
BDCABC
输出样例
4
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define mst(x, y) memset(x, y, sizeof x)
#define endl '\n'
#define INF LONG_LONG_MAX
#define int long long
#define Lson u << 1, l, mid
#define Rson u << 1 | 1, mid + 1, r
#define FAST ios::sync_with_stdio(false), cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0)
const int N = 2010, MOD = 1e9 + 7;
const double EPS = 1e-6;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
int T;
int n, m;
string a, b;
int f[N][N];
void solve()
{
cin >> a >> b;
a = " " + a, b = " " + b;
n = a.size() - 1, m = b.size() - 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++)
{
f[i][j] = max(f[i - 1][j], f[i][j - 1]);
if (a[i] == b[j])
f[i][j] = max(f[i][j], f[i - 1][j - 1] + 1);
}
cout << f[n][m] << endl;
}
signed main()
{
FAST;
T = 1;
// cin >> T;
while (T--)
solve();
return 0;
}
7-4 0-1背包
题目
给定n(n<=100)种物品和一个背包。物品的重量是Wi(wi<=100),价值为Vi(vi<=100),背包的容量为C(C<=1000)。
应如何选择装入背包中的物品,使得装入背包中物品的总价值最大?在选择装入背包的物品时,对每种物品只有两个选择:装
入或不装入。不能将物品装入多次,也不能只装入部分物品。
输入格式
共有n+1行输入:
第一行为n值和c值,表示n件物品和背包容量c;
接下来的n行,每行有两个数据,分别表示第i (1≤isn)件物品的重量和价值。
输出格式
输出装入背包中物品的最大总价值。
输入样例
5 10
26
23
65
54
46
输出样例
15
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define mst(x, y) memset(x, y, sizeof x)
#define endl '\n'
#define INF LONG_LONG_MAX
#define int long long
#define Lson u << 1, l, mid
#define Rson u << 1 | 1, mid + 1, r
#define FAST ios::sync_with_stdio(false), cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0)
const int N = 2010, MOD = 1e9 + 7;
const double EPS = 1e-6;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
int T;
int n, m;
int f[N];
int w[N], v[N];
void solve()
{
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
cin >> v[i] >> w[i];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
for (int j = m; j >= v[i]; j--)
{
f[j] = max(f[j], f[j - v[i]] + w[i]);
}
}
cout << f[m] << endl;
}
signed main()
{
FAST;
T = 1;
// cin >> T;
while (T--)
solve();
return 0;
}
7-5 单源最短路径
题目
请编写程序求给定正权有向图的单源最短路径长度。图中包含n个顶点,编号为0至n-1,以顶点0作为源点。
输入格式:
输入第一行为两个正整数n和e,分别表示图的顶点数和边数,其中n不超过20000,e不超过1000。接下来e行表示每条边
的信息,每行为3个非负整数a、b、c,其中a和b表示该边的端点编号,c表示权值。各边并非按端点编号顺序排列。
输出格式:
输出为一行整数,为按顶点编号顺序排列的源点0到各顶点的最短路径长度(不含源点到源点),每个整数后一个空格。
如源点到某顶点无最短路径,则不输出该条路径长度。
输入样例:
44
011
031
131
201
输出样例:
11
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define mst(x, y) memset(x, y, sizeof x)
#define endl '\n'
#define INF LONG_LONG_MAX
#define int long long
#define Lson u << 1, l, mid
#define Rson u << 1 | 1, mid + 1, r
#define FAST ios::sync_with_stdio(false), cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0)
const int N = 100010, MOD = 1e9 + 7;
const double EPS = 1e-6;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
int T;
int n, m;
int h[N], e[N], ne[N], idx;
int w[N];
int dist[N];
bool st[N];
void add(int x, int y, int c)
{
w[idx] = c;
e[idx] = y;
ne[idx] = h[x];
h[x] = idx++;
}
int dijkstra()
{
memset(dist, 0x3f, sizeof(dist));
dist[0] = 0;
priority_queue<PII, vector<PII>, greater<PII>> heap;
heap.push({0, 0});
while (heap.size())
{
PII k = heap.top();
heap.pop();
int ver = k.second, distance = k.first;
if (st[ver])
continue;
st[ver] = true;
for (int i = h[ver]; i != -1; i = ne[i])
{
int j = e[i];
if (dist[j] > distance + w[i])
{
dist[j] = distance + w[i];
heap.push({dist[j], j});
}
}
}
if (dist[n] == 0x3f3f3f3f)
return -1;
else
return dist[n];
}
void solve()
{
memset(h, -1, sizeof(h));
cin >> n >> m;
while (m--)
{
int x, y, c;
cin >> x >> y >> c;
add(x, y, c);
}
dijkstra();
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
if (dist[i] < 0x3f3f3f3f)
cout << dist[i] << " ";
}
}
signed main()
{
FAST;
T = 1;
// cin >> T;
while (T--)
solve();
return 0;
}
7-6 最小生成树
题目
给定结点数为 n, 边数为 m 的带权无向连通图 G, 所有结点编号为 1,2,…,n。
求 G 的最小生成树的边权和。
输入格式
第一行两个正整数 n,m。
之后的 m 行,每行三个正整数 ui, vi, w;(1 < ui, vi < n, 0<wi≤109),描述一条连接结点 ui
和 vi, 边权为 w; 的边。
输出格式
一个整数表示 G 的最小生成树的边权和。
输入样例
7 12
129
152
163
235
267
346
373
456
472
563
576
671
输出样例
16
数据范围与提示
1 < n < 2 × 1e5, 0 < m < 5e5
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define mst(x, y) memset(x, y, sizeof x)
#define endl '\n'
#define INF LONG_LONG_MAX
#define int long long
#define Lson u << 1, l, mid
#define Rson u << 1 | 1, mid + 1, r
#define FAST ios::sync_with_stdio(false), cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0)
const int N = 2e5 + 10, M = 5e5 + 10, MOD = 1e9 + 7;
const double EPS = 1e-6;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
int T;
int n, m;
int p[N];
struct Edge
{
int a, b, w;
bool operator<(const Edge &e) const
{
return w < e.w;
}
} es[M];
int find(int x)
{
if (p[x] != x)
p[x] = find(p[x]);
return p[x];
}
int kruskal()
{
int cnt = 0, res = 0;
sort(es, es + m);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
p[i] = i;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
int a = es[i].a, b = es[i].b, w = es[i].w;
a = find(a), b = find(b);
if (a != b)
{
p[a] = b;
res += w;
cnt++;
}
}
return res;
}
void solve()
{
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
int a, b, w;
cin >> a >> b >> w;
es[i] = {a, b, w};
}
int t = kruskal();
cout << t << endl;
}
signed main()
{
FAST;
T = 1;
// cin >> T;
while (T--)
solve();
return 0;
}
7-7 n 皇后问题
题目
将 n 个皇后放在 nxn 的国际象棋棋盘上,使得皇后不能相互攻击到。即任意两个皇后都不
能处于同一行、同一列或同一斜线上。
输入格式
共一行,包含整数 n(1≤ n ≤12)。
输出格式
给出所有可能摆放情况的种数,结尾无空格换行。
输入样例
4
输出样例
2
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define mst(x, y) memset(x, y, sizeof x)
#define endl '\n'
#define INF LONG_LONG_MAX
#define int long long
#define Lson u << 1, l, mid
#define Rson u << 1 | 1, mid + 1, r
#define FAST ios::sync_with_stdio(false), cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0)
const int N = 2010, MOD = 1e9 + 7;
const double EPS = 1e-6;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
int T;
int n, res;
bool col[N], dg[N], udg[N];
void dfs(int u)
{
if (u == n)
{
res++;
return;
}
int x = u;
for (int y = 0; y < n; y++)
{
if (!col[y] && !dg[y - x + n] && !udg[y + x])
{
col[y] = dg[y - x + n] = udg[y + x] = true;
dfs(x + 1);
col[y] = dg[y - x + n] = udg[y + x] = false;
}
}
}
void solve()
{
cin >> n;
dfs(0);
cout << res << endl;
}
signed main()
{
FAST;
T = 1;
// cin >> T;
while (T--)
solve();
return 0;
}
7-8 旅行售货员
题目
某售货员要到若干城市去推销商品,已知各城市之间的路程(或旅费)。他要选定一条从驻地出发,经过每个城市
一遍,最后回到驻地的路线,使总的路程(或总旅费)最小。
输入格式
第一行为城市数 n
下面 n 行 n 列给出一个完全有向图,如 i 行 j 列表示第 i 个城市到第 j 个城市的距离。
输出格式
一个数字,表示最短路程长度。
输入样例
3
021
102
210
输出样例
3
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define mst(x, y) memset(x, y, sizeof x)
#define endl '\n'
#define INF LONG_LONG_MAX
#define int long long
#define Lson u << 1, l, mid
#define Rson u << 1 | 1, mid + 1, r
#define FAST ios::sync_with_stdio(false), cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0)
const int N = 20, MOD = 1e9 + 7;
const double EPS = 1e-6;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
int T;
int n;
int g[N][N];
int f[1 << 10][N];
void solve()
{
cin >> n;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j)
cin >> g[i][j];
mst(f, 0x3f);
f[1][0] = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < 1 << n; i += 2)
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j)
if (i >> j & 1)
for (int k = 0; k < n; ++k)
if (j != k && (i >> k & 1))
f[i][j] = min(f[i][j], f[i - (1 << j)][k] + g[k][j]);
int res = INF;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
res = min(res, f[(1 << n) - 1][i] + g[i][0]);
cout << res << endl;
}
signed main()
{
FAST;
T = 1;
// cin >> T;
while (T--)
solve();
return 0;
}
7-9 装箱问题
题目
假设有N项物品,大小分别为s1、s2、…、si、…、sn,其中si为满足1≤si≤100的整数。要把这些物品装入到容量为100的一批箱子(序号1-N)中。装箱方法是:对每项物品, 顺序扫描箱子,把该物品放入足以能够容下它的第一个箱子中。请写一个程序模拟这种装箱过程,并输出每个物品所在的箱子序号,以及放置全部物品所需的箱子数目。
输入格式
输入第一行给出物品个数N(≤1000);第二行给出N个正整数si(1≤si≤100,表示第i项物品的大小)。
输出格式
按照输入顺序输出每个物品的大小及其所在的箱子序号,每个物品占1行,最后一行输出所需的箱子数目。
输入样例
8
60 70 80 90 30 40 10 20
输出样例
60 1
70 2
80 3
90 4
30 1
40 5
10 1
20 2
5
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define mst(x, y) memset(x, y, sizeof x)
#define endl '\n'
#define INF LONG_LONG_MAX
#define int long long
#define Lson u << 1, l, mid
#define Rson u << 1 | 1, mid + 1, r
#define FAST ios::sync_with_stdio(false), cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0)
const int N = 2000010, MOD = 1e9 + 7;
const double EPS = 1e-6;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
int T;
int n;
int res = 1;
int a[N], v[N];
int id[N];
void solve()
{
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
cin >> a[i];
v[i] = 100;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++)
{
if (a[i] <= v[j])
{
v[j] -= a[i];
id[i] = j;
break;
}
else if (j == res)
{
res++;
v[res] -= a[i];
id[i] = res;
break;
}
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
cout << a[i] << " " << id[i] << endl;
cout << res << endl;
}
signed main()
{
FAST;
T = 1;
// cin >> T;
while (T--)
solve();
return 0;
}
7-10 电路布线
题目
在解决电路布线问题时,一种很常用的方法就是在布线区域叠上一个网格,该网格把布线区域划分成m*n个方格,布线时,转弯处必须采用直角,如已经有某条线路经过一个方格时,则在该方格上不允许叠加布线。如下图所示,如从一个方格a(2,1)的中心点到另一个方格b(8,8)的中心点布线时, 每个方格布线时需要1个单位的电路材料,所需要最少的电路材料是16。
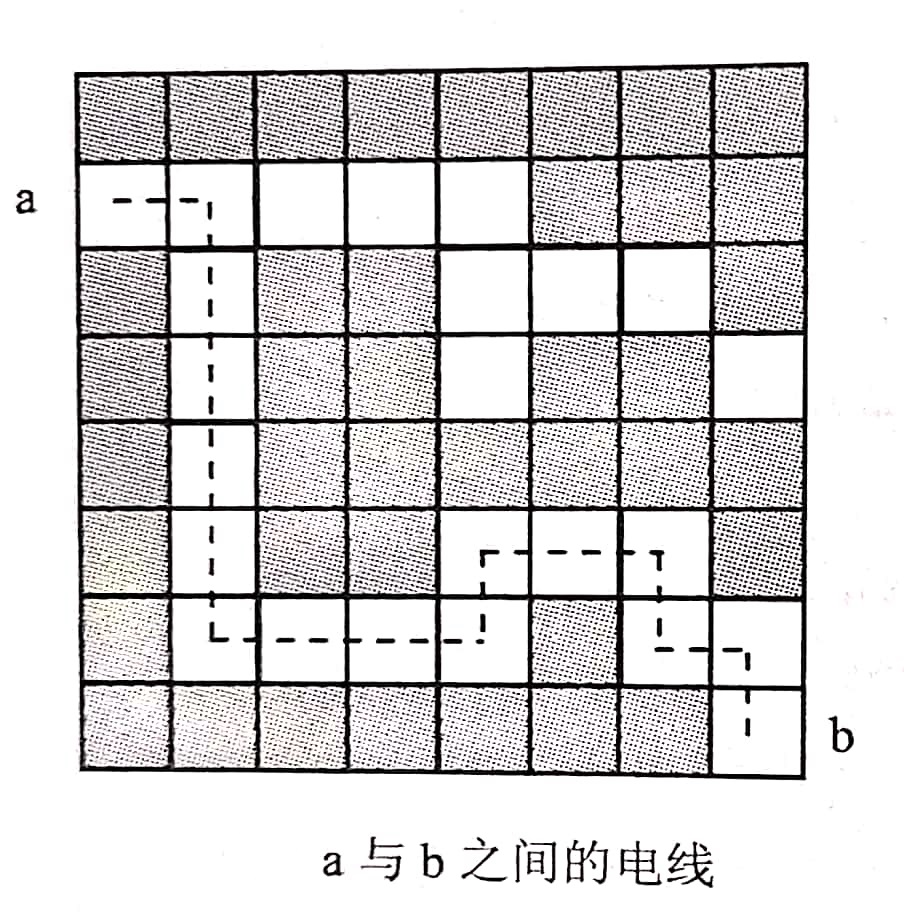
输入格式
第一行输入网格的m和n
第二行开始输入网格中已经布线的情况,如果已经有布线时,用1表示,尚未布线时,用0表示。
接下来两行分别输入需要布线的起始位置a和结束位置b。
输出格式
输出从起始位置a到结束位置b布线时所需要的最少电路材料。
输入样例
8 8
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1
1 0 1 1 0 0 0 1
1 0 1 1 0 1 1 0
1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1
1 0 1 1 0 0 0 1
1 0 0 0 0 1 0 0
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0
2 1
8 8
输出样例
16
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define mst(x, y) memset(x, y, sizeof x)
#define endl '\n'
#define INF LONG_LONG_MAX
#define int long long
#define Lson u << 1, l, mid
#define Rson u << 1 | 1, mid + 1, r
#define FAST ios::sync_with_stdio(false), cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0)
const int N = 2010, MOD = 1e9 + 7;
const double EPS = 1e-6;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
int T;
int dx[4] = {-1, 0, 1, 0}, dy[4] = {0, 1, 0, -1};
int n, m;
int stx, sty, edx, edy;
int g[N][N], d[N][N];
int res;
void bfs(int stx, int sty)
{
queue<PII> q;
q.push({stx, sty});
d[stx][sty] = 1;
while (q.size())
{
auto t = q.front();
q.pop();
int x = t.first, y = t.second;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
int xx = x + dx[i], yy = y + dy[i];
if (xx >= 1 && xx <= n && yy >= 1 && yy <= m && g[xx][yy] && !d[xx][yy])
{
d[xx][yy] = d[x][y] + 1;
q.push({xx, yy});
}
}
}
}
void solve()
{
mst(d, 0);
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++)
cin >> g[i][j], g[i][j] = 1 - g[i][j];
cin >> stx >> sty >> edx >> edy;
bfs(stx, sty);
cout << d[edx][edy] << endl;
}
signed main()
{
FAST;
T = 1;
// cin >> T;
while (T--)
solve();
return 0;
}
MD文件自取
免责申明:免责声明
尊敬的读者:
感谢您访问本博客。在此,我郑重声明,本博客与任何形式的考试作弊行为无关,也不提倡或支持任何违反考试规定、道德准则或法律法规的行为。
本博客的目的是为读者提供有关各种主题的信息和观点,以促进知识的交流和分享。然而,本博客的内容仅供参考,不构成任何具体建议或指导。读者在采纳本博客中的任何观点或建议时,应谨慎行事,并在必要时寻求专业意见。
作者对于读者可能在学业或其他方面面临的挑战概不负责。本博客的内容不应被解读为鼓励或支持违反任何考试规则或规定的行为。任何因读者采取与本博客相关的行动而导致的后果,作者概不负责。
请注意,在任何考试或学术环境中,诚实和守规则是至关重要的。任何试图通过作弊手段获取不正当好处的行为都是不道德的,并可能受到法律追究。
最后,本免责声明可随时更新,而无需提前通知。请您定期查阅以获取最新信息。
感谢您对本博客的关注与支持。
[347do]



