实验1 对指令操作码进行霍夫曼编码
一、实验目的
了解和掌握指令编码的基本要求和基本原理
二、实验内容
使用编程工具编写一个程序,对一组指令进行霍夫曼编码,并输出最后的编码结果以及对指令码的长度进行评价,与扩展操作码和等长编码进行比较。
例如: 有一组指令的操作码共分七类,它们出现概率如下表所示。
| 指令 | P1 | P2 | P3 | P4 | P5 | P6 | P7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 出现概率 | 0.45 | 0.30 | 0.15 | 0.05 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.01 |
对此组指令进行 huffman 编码如下图所示:
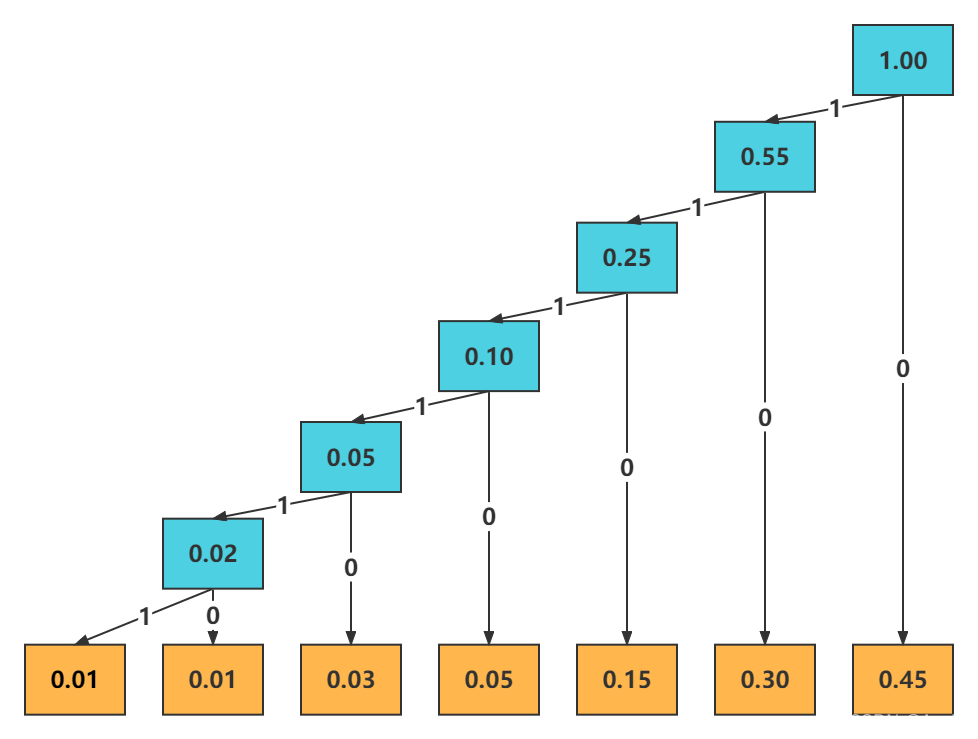
最后得到的 huffman 编码如下表所示:
| 指令 | P1 | P2 | P3 | P4 | P5 | P6 | P7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 出现概率 | 0.45 | 0.30 | 0.15 | 0.05 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| huffman编码 | 0 | 10 | 110 | 1110 | 11110 | 111110 | 111111 |
| 编码长度 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 6 |
huffman 编码长度为:
H = 0.45 x 1 + 0.30 x 2 + 0.15 x 3 + 0.05 x 4 + 0.03 x 5 + 0.01 x 6 + 0.01 x 6 = 1.97
要对指令的操作码进行 huffman 编码,只要根据指令的各类操作码的出现概率构造 huffman 树再进行 huffman 编码。此过程的难点在于构造 huffman 树,进行 huffman 编码只要对所生成的 huffman 树进行中序遍历即可完成编码工作。
三、实验步骤
观察上图,不难看出构造 huffman 树所要做的工作:
- 先对各指令操作码的出现概率进行排序,构造一个有序链表。
- 再取出两个最小的概率节点相加,生成一个生的节点加入到链表中,同时从两表中删除此两个节点。
- 在对链表进行排序,链表是否只有一个节点,是则 huffman 树构造完毕,否则继续做步骤 2 的操作。
- 为此设计一个工作链表、huffman 树节点、huffman 编码表节点。
四、实验结果
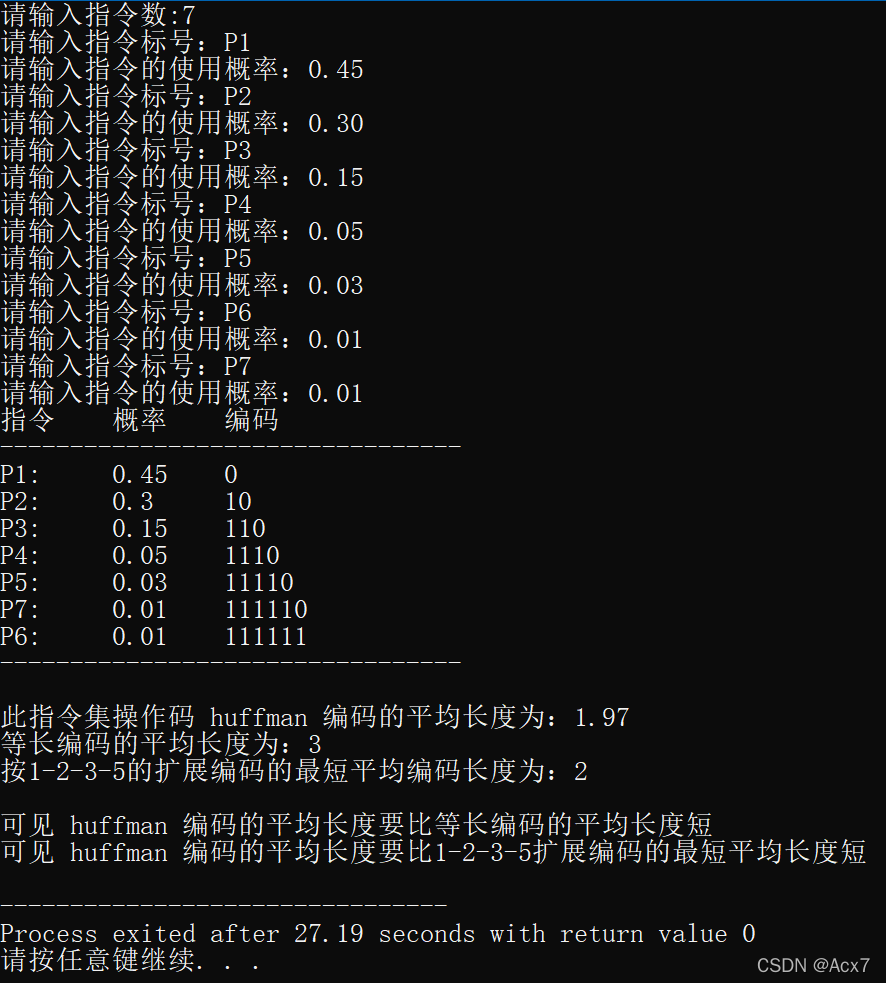
四、实验代码
#include<iostream>
#include<cmath>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
const int N = 8; // huffman编码最大长度
class huff_p {
public:
huff_p* r_child; // 大概率的节点
huff_p* l_child; // 小概率的节点
char op_mask[3]; // 指令标号
float p; // 指令使用概率
};
class f_min_p{
public:
f_min_p* next;
char op_mask[3]; // 指令标号
float p; // 指令使用概率
huff_p* huf_p;
};
// huff_man code
class huff_code{
public:
huff_code* next;
float p;
char op_mask[3];
char code[N]; // huffman 编码
};
f_min_p* input_instruct_set(); // 输入指令集子模块;
huff_p* creat_huffman_tree(f_min_p* head); // 构造huffman树;
f_min_p* fin_min(f_min_p* h);
f_min_p* del_min(f_min_p* h,f_min_p* p);
void insert_n(f_min_p* h,f_min_p* p);
huff_p* creat_huffp(f_min_p* p);
void creat_huffman_code(huff_p* h1,huff_code* h);// 生成 huffman 编码;
void r_find(huff_p* p1,char code[],int i,huff_code* h);
void output_huffman(huff_code* head);// 输出huffman编码;
void cal_sort_length(huff_code* head);// 计算指令用huffman编码的平均编码字长
void print(huff_p* h1);
int main() {
f_min_p *h, *h1;
huff_p *root;
huff_code* head, *pl;
h = input_instruct_set();
h1 = h;
root = creat_huffman_tree(h1);
head = new huff_code;
head->next = NULL;
creat_huffman_code(root, head);
output_huffman(head);
cal_sort_length(head);
pl = head->next;
while (pl) {
delete head;
head = pl;
pl = pl->next;
}
}
f_min_p* input_instruct_set() {
f_min_p* head;
f_min_p* h;
h = new f_min_p;
h->next = NULL;
h->huf_p = NULL;
head = h;
int n;
cout << "请输入指令数:";
cin >> n;
cout << "请输入指令标号:";
cin >> h->op_mask;
cout << "请输入指令的使用概率:";
cin >> h->p;
f_min_p* point;
f_min_p* p1 = head;
for (int i = 0; i < n-1; i++) {
point = new f_min_p;
cout << "请输入指令标号:";
cin >> point->op_mask;
point->op_mask[2] = '\0';
cout << "请输入指令的使用概率:";
cin >> point->p;
point->huf_p = NULL;
point->next = p1->next;
p1->next = point;
p1 = point;
}
return head;
}
huff_p* creat_huffman_tree(f_min_p* h) {
f_min_p *h1, *min1, *min2, *comb;
huff_p* head, *rd, *ld, *parent;
h1 = h;
min1 = fin_min(h1);
ld = creat_huffp(min1);
h1 = del_min(h1, min1);
if (h1->next) {
min2 = fin_min(h1);
} else {
min2 = h1;
}
rd = creat_huffp(min2);
comb = new f_min_p;
comb->next = NULL;
comb->p = rd->p + ld->p;
comb->op_mask[0] = '\0';
comb->op_mask[1] = '\0';
parent = creat_huffp(comb);
insert_n(h1, comb);
if (h1->next != NULL) {
h1 = del_min(h1, min2);
}
parent->l_child = ld;
parent->r_child = rd;
comb->huf_p = parent;
head = parent;
while (h1->next != NULL) {
min1 = fin_min(h1);
if (min1->huf_p == NULL) {
ld = creat_huffp(min1);
} else {
ld = min1->huf_p;
}
h1 = del_min(h1, min1);
if (h1->next) {
min2=fin_min(h1);
} else {
min2=h1;
}
if (min2->huf_p == NULL) {
rd = creat_huffp(min2);
} else {
rd = min2->huf_p;
}
comb = new f_min_p;
comb->next = NULL;
comb->p = rd->p + ld->p;
comb->op_mask[0] = '\0';
comb->op_mask[1] = '\0';
parent = creat_huffp(comb);
if (h1 != NULL) {
insert_n(h1, comb);
}
if (h1->next != NULL) {
h1 = del_min(h1, min2);
}
if (h1->next == NULL && ld->p < rd->p) {
huff_p* tmp = ld;
ld = rd;
rd = tmp;
}
parent->l_child = ld;
parent->r_child = rd;
comb->huf_p = parent;
head = parent;
if (h1->next == NULL) {
break;
}
}
delete comb;
return head;
}
f_min_p* fin_min(f_min_p* h) {
f_min_p *h1, *p1;
h1 = h;
p1 = h1;
float min = h1->p;
h1 = h1->next;
while (h1) {
if (min > (h1->p)) {
min = h1->p;
p1 = h1;
}
h1 = h1->next;
}
return p1;
}
f_min_p* del_min(f_min_p *h,f_min_p *p) {
f_min_p *p1, *p2;
p1 = h;
p2 = h;
if (h == p) {
h = h->next;
delete p;
} else {
while (p1->next != NULL) {
p1 = p1->next;
if (p1 == p) {
p2->next = p1->next;
delete p;
break;
}
p2 = p1;
}
}
return h;
}
void insert_n(f_min_p *h, f_min_p *p1) {
p1->next = h->next;
h->next = p1;
}
huff_p* creat_huffp(f_min_p* d) {
huff_p* p1;
p1 = new huff_p;
p1->l_child = NULL;
p1->r_child = NULL;
p1->p = d->p;
p1->op_mask[0] = d->op_mask[0];
p1->op_mask[1] = d->op_mask[1];
return p1;
}
void r_find(huff_p* p1, char code[], int i, huff_code* h) {
if (p1->l_child) {
code[i] = '1';
r_find(p1->l_child, code, i+1, h);
}
if (p1->op_mask[0] != '\0') {
huff_code* p2 = new huff_code;
p2->op_mask[0] = p1->op_mask[0];
p2->op_mask[1] = p1->op_mask[1];
p1->op_mask[2] = '\0';
p2->p = p1->p;
int j = 0;
for (; j < i; j++) {
p2->code[j] = code[j];
}
p2->code[j] = '\0';
p2->next = h->next;
h->next = p2;
}
if (p1->r_child) {
code[i] = '0';
r_find(p1->r_child, code, i+1, h);
}
delete p1;
}
void creat_huffman_code(huff_p* h1, huff_code* h) {
int i = 0;
char code[N] = {'\0'};
r_find(h1, code, i, h);
}
void output_huffman(huff_code* head) {
huff_code* h = head->next;
cout << "指令\t" << "概率\t" << "编码" << endl;
cout<<"---------------------------------"<<endl;
while (h) {
h->op_mask[2] = '\0';
cout << h->op_mask << ":\t" << h->p << "\t" << h->code << endl;
h = h->next;
}
cout << "---------------------------------" << endl;
cout << endl;
}
void cal_sort_length(huff_code* head) {
huff_code *h = head->next;
double j = 0;
float one_length = 0;
float per_length = 0;
float ext_length = 0;//按1-2-3-5扩展编码的最小长度为。
while (h) {
float length = 0;
int i = 0;
while (h->code[i] != '\0') {
length++;
i++;
}
one_length = h->p*length;
per_length = per_length + one_length;
h = h->next;
j++;
}
int i1 = int(j);
huff_code *p2 = head->next;
float* p_a = new float[i1];
//sort指令概率
int i0 = 0;
while (p2) {
p_a[i0++] = p2->p;
p2 = p2->next;
}
float max, temp;
int l;
for (int s = 0; s < i1; s++) {
max = p_a[s];
l = s;
for (int k = s+1; k < i1; k++) {
if (max<p_a[k]) {
max = p_a[k];
l = k;
}
}
temp = p_a[s];
p_a[s] = max;
p_a[l] = temp;
}
//计算1-2-3-5扩展编码的最短平均长度
float* code_len = new float[i1];
code_len[0] = 1;
code_len[1] = 2;
code_len[2] = 3;
code_len[3] = 5;
for (int i = 4; i < j; i++) {
code_len[i]=5;
}
l = 0;
while (l<i1) {
ext_length = ext_length + code_len[l]*p_a[l];
l++;
}
//计算等长编码平均长度;
int q_length = ceil(log10(j)/log10(2));
cout << "此指令集操作码 huffman 编码的平均长度为:" << per_length<<endl;
cout << "等长编码的平均长度为:" << q_length << endl;
cout << "按1-2-3-5的扩展编码的最短平均编码长度为:" << ext_length;
cout << endl;
cout << endl;
if (q_length > per_length) {
cout << "可见 huffman 编码的平均长度要比等长编码的平均长度短" << endl;
} else {
cout << "huffman 编码有问题请仔细查看算法,以及输入的指令集的概率之和是否大于1。" << endl;
}
if (ext_length>per_length) {
cout << "可见 huffman 编码的平均长度要比1-2-3-5扩展编码的最短平均长度短" << endl;
} else {
cout << "huffman 编码有问题请仔细查看算法,以及输入的指令集的概率之和是否大于1。" << endl;
}
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号