Gated Recurrent Unit (GRU)
Gated Recurrent Unit (GRU)
Outline
Background
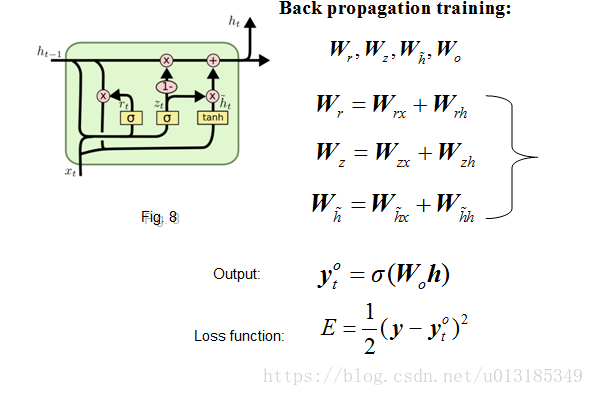
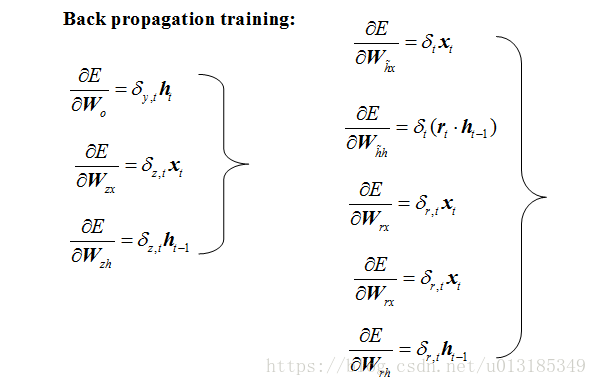
GRU Network
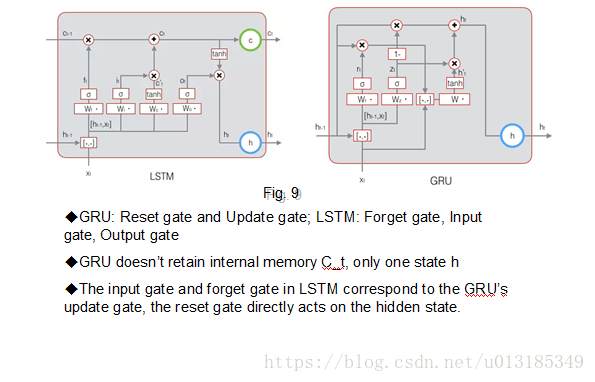
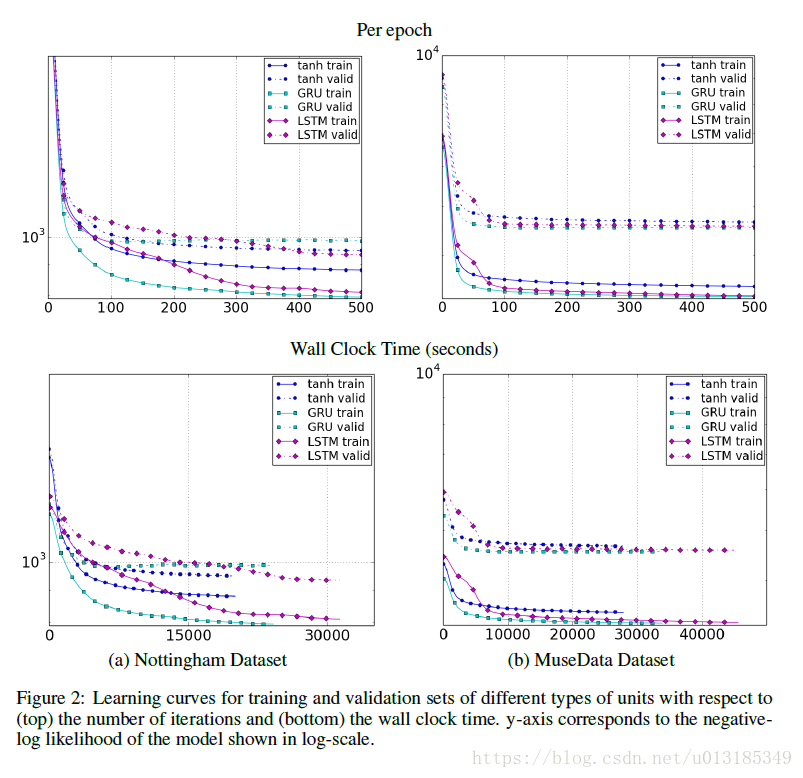
GRU vs. LSTM
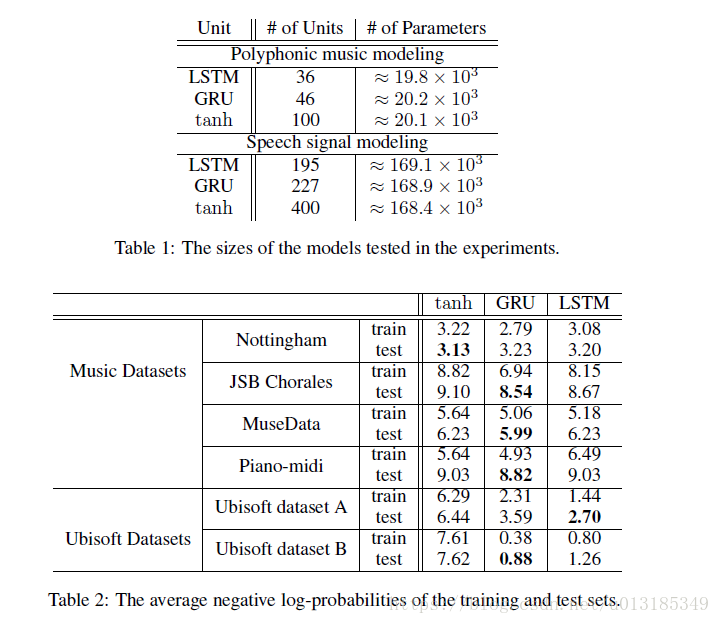
Experiment
References
Background
A gated recurrent unit (GRU) was proposed by Cho et al. [2014] to make each recurrent unit to adaptively capture dependencies of different time scales.
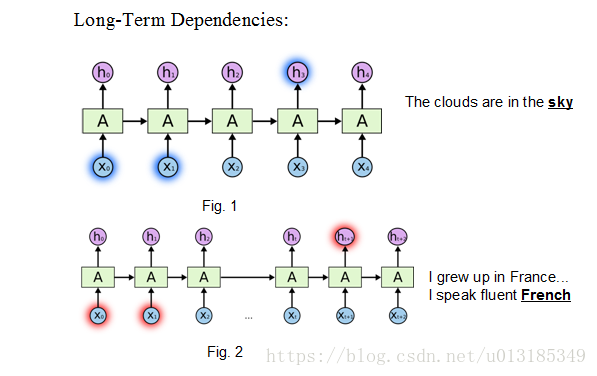
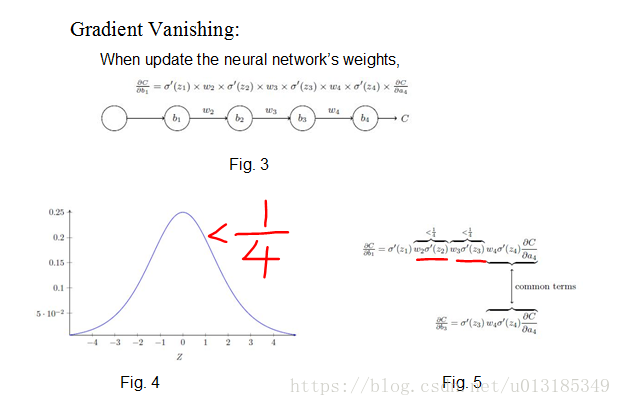
Solving problems existed in RNN: Gradient Vanishing.
Example:
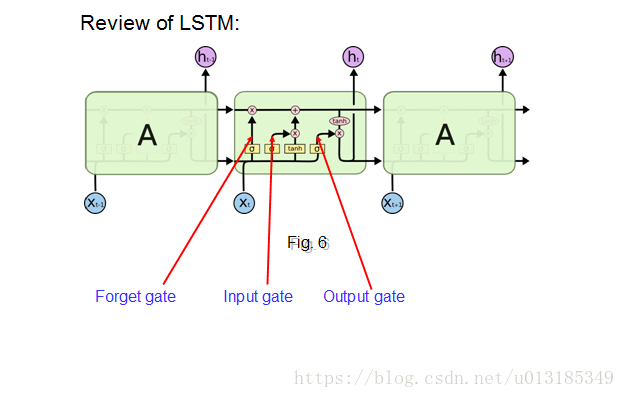
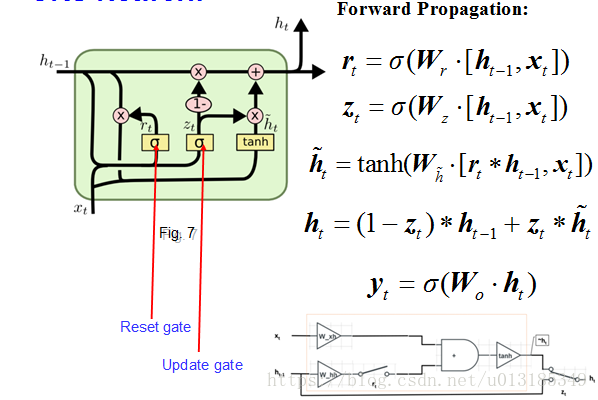
GRU Network
GRU vs. LSTM
Code Example:
import tensorflow as tf
x = tf.constant([[1]], dtype = tf.float32)
…
state0_lstm = lstm_cell.zero_state(1,dtype=tf.float32)
output,state = lstm_cell(x,state0_lstm)
state0_gru = gru_cell.zero_state(1,dtype=tf.float32)
output2,state2 = gru_cell(x,state0_gru)
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(init)
print(sess.run(output))
print(sess.run(state))
print(sess.run(output2))
print(sess.run(state2))
Experiment
References
1. Empirical Evaluation of Gated Recurrent Neural Networks on Sequence Modeling
2. Learned-norm pooling for deep feedforward and recurrent neural networks
3. Long short-term memory
<script>
(function(){
function setArticleH(btnReadmore,posi){
var winH = $(window).height();
var articleBox = $("div.article_content");
var artH = articleBox.height();
if(artH > winH*posi){
articleBox.css({
'height':winH*posi+'px',
'overflow':'hidden'
})
btnReadmore.click(function(){
articleBox.removeAttr("style");
$(this).parent().remove();
})
}else{
btnReadmore.parent().remove();
}
}
var btnReadmore = $("#btn-readmore");
if(btnReadmore.length>0){
if(currentUserName){
setArticleH(btnReadmore,3);
}else{
setArticleH(btnReadmore,1.2);
}
}
})()
</script>
</article>




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号