python中的scatter()方法
1、scatter函数原型
2、其中散点的形状参数marker如下:
3、其中颜色参数c如下:

4、基本的使用方法如下:
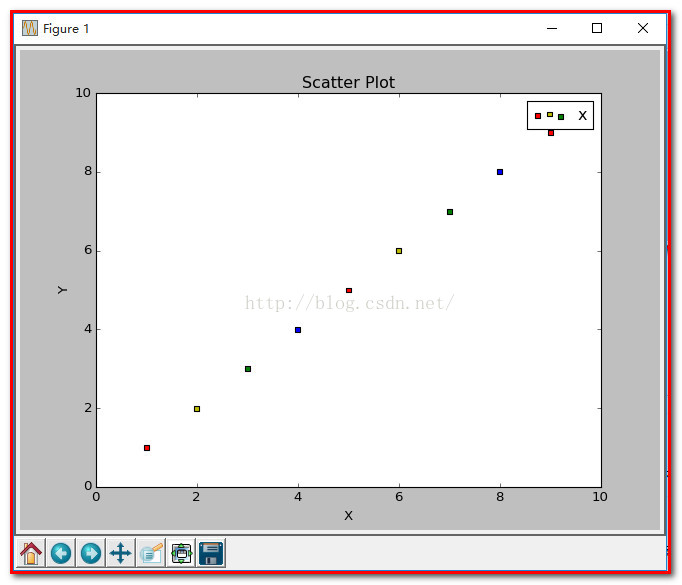
结果如下:
5、当scatter后面参数中数组的使用方法,如s,当s是同x大小的数组,表示x中的每个点对应s中一个大小,其他如c,等用法一样,如下:
(1)、不同大小
#导入必要的模块 import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt #产生测试数据 x = np.arange(1,10) y = x fig = plt.figure() ax1 = fig.add_subplot(111) #设置标题 ax1.set_title('Scatter Plot') #设置X轴标签 plt.xlabel('X') #设置Y轴标签 plt.ylabel('Y') #画散点图 sValue = x*10 ax1.scatter(x,y,s=sValue,c='r',marker='x') #设置图标 plt.legend('x1') #显示所画的图 plt.show()
(2)、不同颜色
结果:
(3)、线宽linewidths
注: 这就是scatter基本的用法。
PS:下面举个示例
本文记录了python中的数据可视化——散点图scatter,令x作为数据(50个点,每个30维),我们仅可视化前两维。labels为其类别(假设有三类)。
这里的x就用random来了,具体数据具体分析。
label设定为[1:20]->1, [21:35]->2, [36:50]->3,(python中数组连接方法:先强制转为list,用+,再转回array)
用matplotlib的scatter绘制散点图,legend和matlab中稍有不同,详见代码。
x = rand(50,30) from numpy import * import matplotlib import matplotlib.pyplot as plt #basic f1 = plt.figure(1) plt.subplot(211) plt.scatter(x[:,1],x[:,0]) # with label plt.subplot(212) label = list(ones(20))+list(2*ones(15))+list(3*ones(15)) label = array(label) plt.scatter(x[:,1],x[:,0],15.0*label,15.0*label) # with legend f2 = plt.figure(2) idx_1 = find(label==1) p1 = plt.scatter(x[idx_1,1], x[idx_1,0], marker = 'x', color = 'm', label='1', s = 30) idx_2 = find(label==2) p2 = plt.scatter(x[idx_2,1], x[idx_2,0], marker = '+', color = 'c', label='2', s = 50) idx_3 = find(label==3) p3 = plt.scatter(x[idx_3,1], x[idx_3,0], marker = 'o', color = 'r', label='3', s = 15) plt.legend(loc = 'upper right')
result:
figure(1):

figure(2):









 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号