详细的TensorBoard的使用
花了很长时间才搞好的tensorboard的使用 详细说明
一、输入代码
首先在Spyder输入代码
import tensorflow as tf import numpy as np #输入数据 x_data = np.linspace(-1,1,300)[:, np.newaxis] noise = np.random.normal(0,0.05, x_data.shape) y_data = np.square(x_data)-0.5+noise #输入层 with tf.name_scope('input_layer'): #输入层。将这两个变量放到input_layer作用域下,tensorboard会把他们放在一个图形里面 xs = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 1], name = 'x_input') # xs起名x_input,会在图形上显示 ys = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 1], name = 'y_input') # ys起名y_input,会在图形上显示 #隐层 with tf.name_scope('hidden_layer'): #隐层。将隐层权重、偏置、净输入放在一起 with tf.name_scope('weight'): #权重 W1 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([1,10])) tf.summary.histogram('hidden_layer/weight', W1) with tf.name_scope('bias'): #偏置 b1 = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([1,10])+0.1) tf.summary.histogram('hidden_layer/bias', b1) with tf.name_scope('Wx_plus_b'): #净输入 Wx_plus_b1 = tf.matmul(xs,W1) + b1 tf.summary.histogram('hidden_layer/Wx_plus_b',Wx_plus_b1) output1 = tf.nn.relu(Wx_plus_b1) #输出层 with tf.name_scope('output_layer'): #输出层。将输出层权重、偏置、净输入放在一起 with tf.name_scope('weight'): #权重 W2 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([10,1])) tf.summary.histogram('output_layer/weight', W2) with tf.name_scope('bias'): #偏置 b2 = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([1,1])+0.1) tf.summary.histogram('output_layer/bias', b2) with tf.name_scope('Wx_plus_b'): #净输入 Wx_plus_b2 = tf.matmul(output1,W2) + b2 tf.summary.histogram('output_layer/Wx_plus_b',Wx_plus_b2) output2 = Wx_plus_b2 #损失 with tf.name_scope('loss'): #损失 loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.reduce_sum(tf.square(ys-output2),reduction_indices=[1])) tf.summary.scalar('loss',loss) with tf.name_scope('train'): #训练过程 train_step = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.1).minimize(loss) #初始化 init = tf.global_variables_initializer() sess = tf.Session() sess.run(init) merged = tf.summary.merge_all() #将图形、训练过程等数据合并在一起 writer = tf.summary.FileWriter('logs',sess.graph) #将训练日志写入到logs文件夹下 #训练 for i in range(1000): sess.run(train_step,feed_dict={xs:x_data,ys:y_data}) if(i%50==0): #每50次写一次日志 result = sess.run(merged,feed_dict={xs:x_data,ys:y_data}) #计算需要写入的日志数据 writer.add_summary(result,i) #将日志数据写入文件
执行当前代码,会在当前目录/logs”目录下生成一个events.out.tfevents.{time}.{machine-name}的文件
二、tensorboard
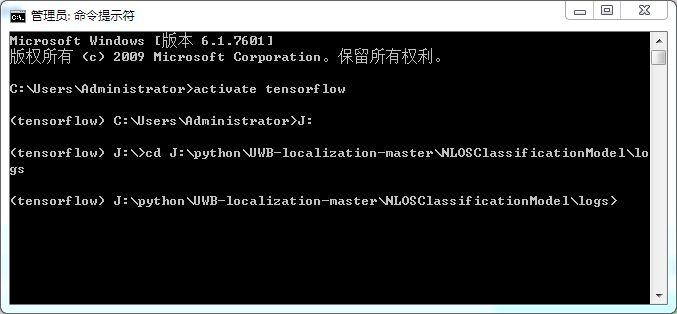
打开终端:在cmd中打开和在AnacondaPrompt中打开是一样,主要是路径等等的设置相同就行
这里选择直接在cmd中打开
注意:
- 激活TensorFlow环境
- 进入到logs所在的目录
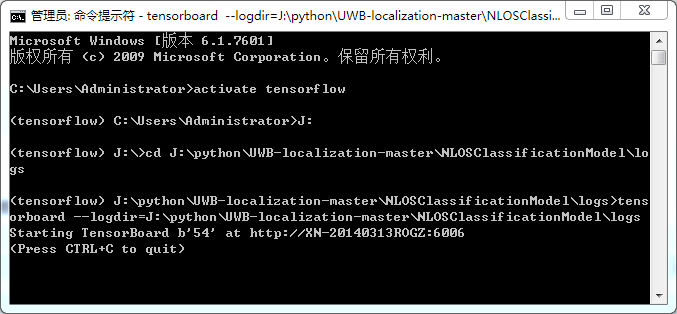
之后输入:
tensorboard --logdir=logs
注意:其中logs表示文件目录,不用加""
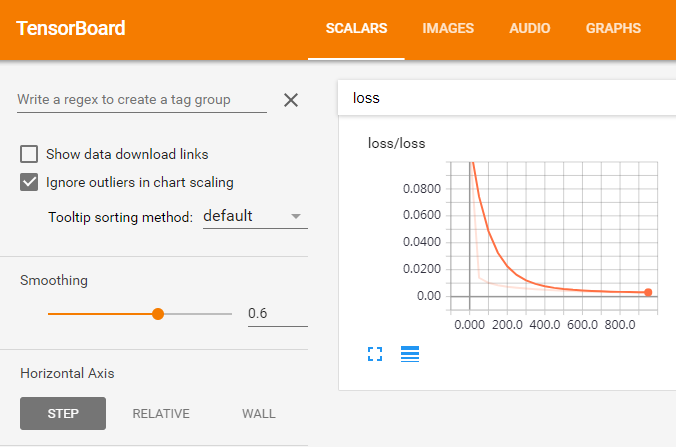
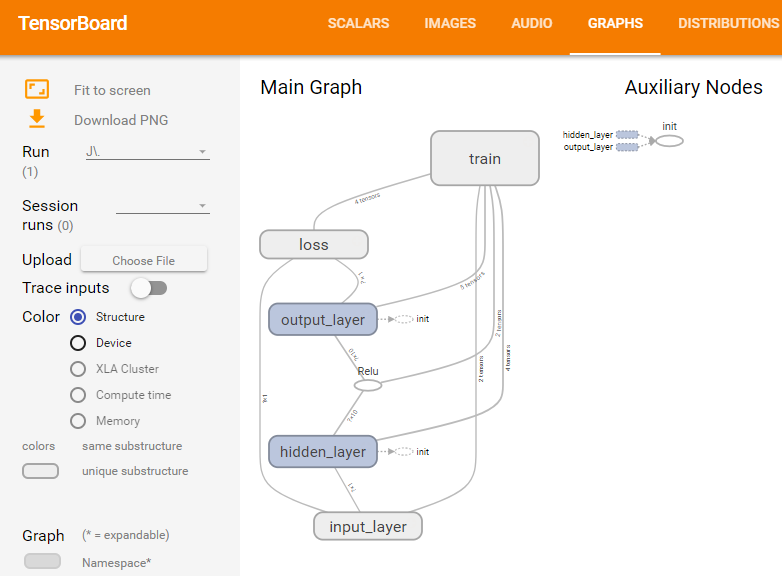
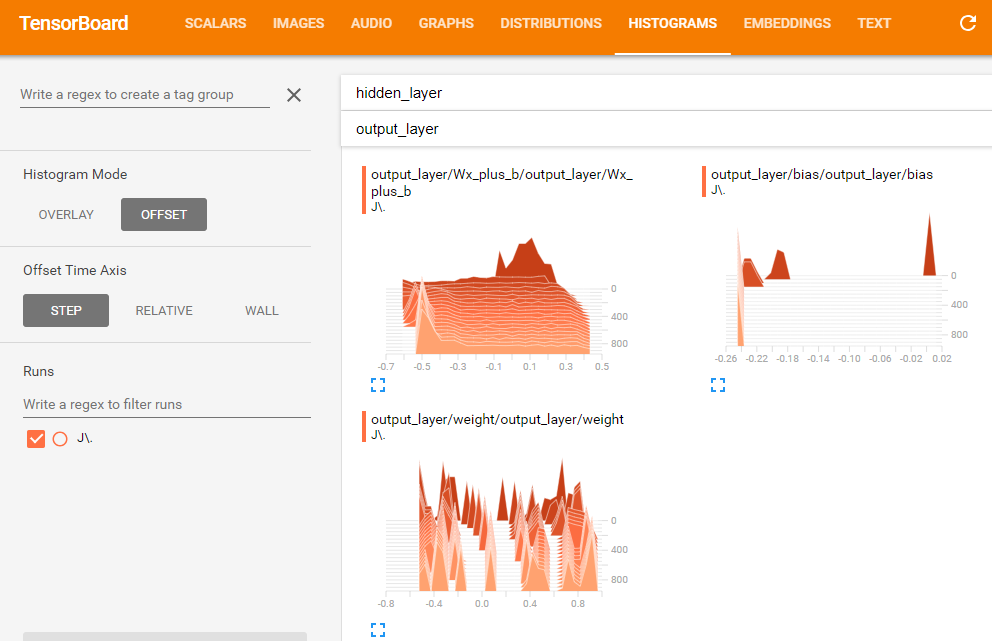
执行上述bat文件,打开浏览器,输入地址:http://localhost:6006,或者http://XN-20140313ROGZ:6006,就可以查看训练过程中的各种图形。
其他好的文章


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号