032❤基本运算符
一、算数运算符
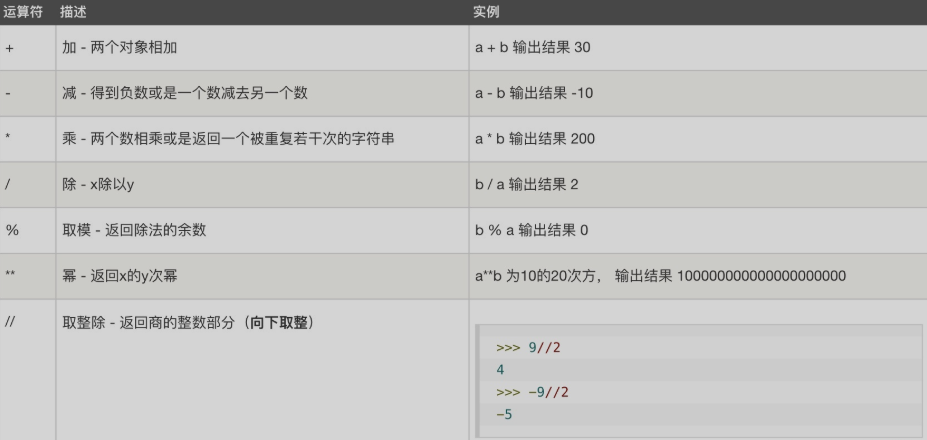
算数运算符就是我们小时候学习的加减乘除
#代码:
print(2+2)
print(3-3)
print(4/4)
print(5*5)
#执行结果:
4
0
1
25
#代码:
print(10/3) # / 有零有整除,得到一个浮点型
print(10//3) # //地板除,只取整数的部分
print(10%3) #求余
print(2**10) #幂运算
#执行结果:
3.3333333333333335
3
1
1024
二、比较运算符
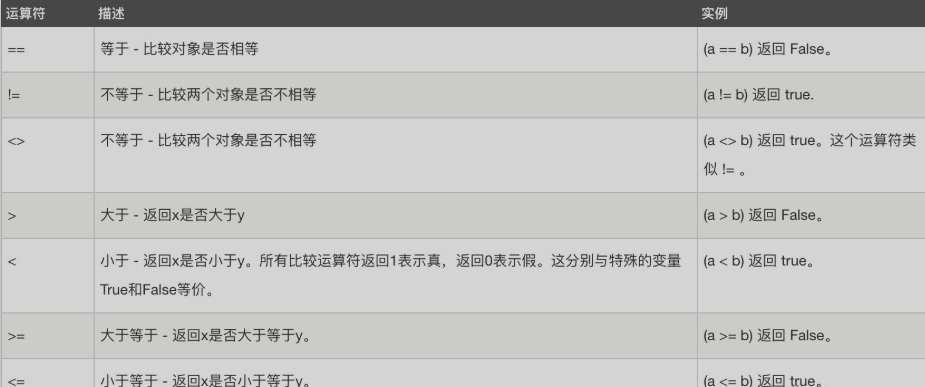
#代码:
pwd = '520'
print(
pwd !='520'
)
print(
pwd =='520'
)
#执行结果:
False
True
#代码:
l1 = [1,'n',3]
l2 = [4]
print(l1<l2)
print(l2<l1)
#执行结果:
True
False
#代码:
try:
l3 = [1, 3]
print(l1 < l3) # 报错,列表比较大小仅限于同一位置的对应的值是相同的类型
except Exception as e:
print(e)
#执行结果:
name 'l1' is not define
三、赋值运算符
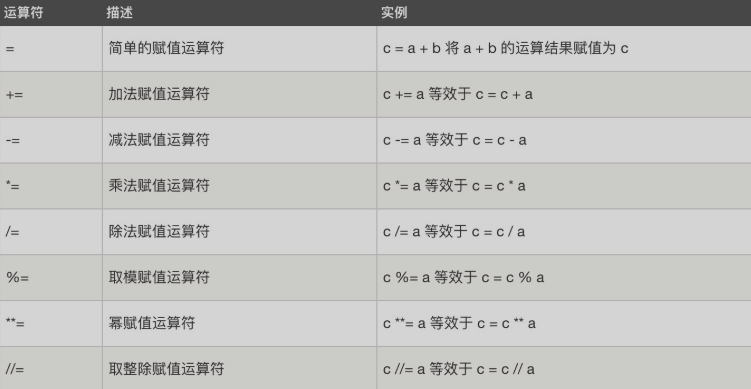
#实例:
age = 19
age = age + 1
print(age)
# 执行结果:
20
#代码:
age = 19
age += 1
print(age)
# 执行结果:
20
#代码:
age = 19
age *= 10
print(age)
# 执行结果:
190
#交叉赋值
#代码:
x = 10
y = 20
x,y = y,x
print(x,y)
# 执行结果:
20 10
# 解压赋值
#代码:
l = [1,2,3,4,5]
a,b,c,d,e = l
print(a,b,c,d,e)
# 执行结果:
1 2 3 4 5
#代码:
p = [1,2]
x,y = p
print(x,y)
# 执行结果:
1 2
四、逻辑运算符
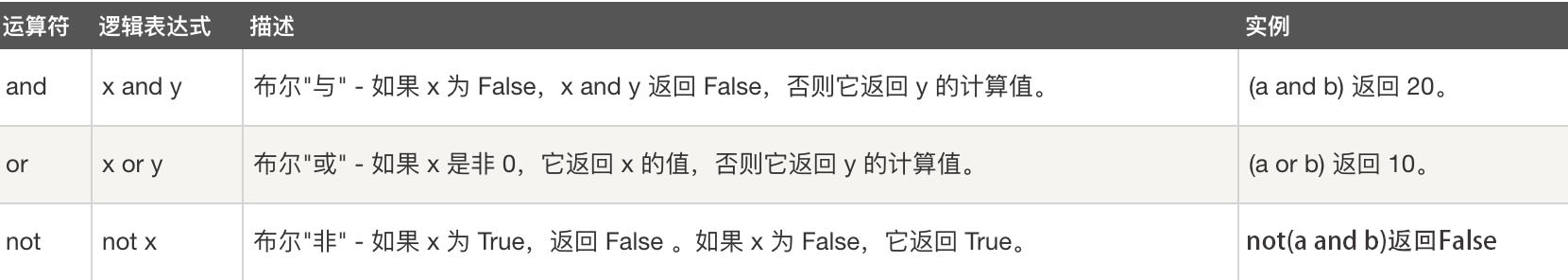
4.1 条件
什么是条件?
- 条件可以是比较运算符
age = 18
print(age>16)
#执行结果:
True
- 条件可以是布尔值
beautiful = True
print(beautiful)
#执行结果:
True
- 隐式布尔值
其中0,None,空(空字符串,空列表,空字典等等)代表的布尔值为False,其余的都是True
4.2 逻辑运算符
用于连接条件,从左到右的方式找到逻辑运算符(not,and,or),找到运算符的左边,左边成立,再去找到逻辑运算符的右边
#not:逻辑非
# 把紧跟其后的那个条件取反,并且与他是不可分割的整体
print(16>18)
print(not 16>18)
# 执行结果
False
True
#and:逻辑与
# 用于连接左右两个条件(条件一 and 条件二 and 条件三)
# 所有的条件同时为真,最终的结果才为真,否则为False
print(True and 10 >3)
print(True and 10 > 3 and 1>2)
print(True and 10 > 3 and 1>2 and 4 ==4) #偷懒原则,算到1>2时就结束了
# 执行结果:
True
False
#or:逻辑或
#or用来连接多有两个条件,只要有一个为真,最终的结果就为True,所有的条件都为假,随后的结果才为False
print(1<2 or 1 == 1 or 1>2) #偷懒原则,1<2为真,后面的不用算了
print(1>2 or 1 == 2 or 3>2) #不可以偷懒原则,要算到最后一个
print(2>3 and 1>2 or 3>1)
#执行结果:
True
4.3 逻辑运算符的优先级
如果单一的使用and,or,not那么从左到右运算就可以了,如果混合使用,那么要考虑运算符的优先级
优先级:not>and>or
# 优先级
print(3>4 and not 4>3 or 1 == 3 and 'x' =='x' or 3>3)
# 3>4 and (not 4>3) or 1 == 3 and 'x' =='x' or 3>3
# (3>4 and (not 4>3)) or 1 == 3 and 'x' =='x' or 3>3
# (3>4 and (not 4>3)) or (1 == 3 and 'x' =='x') or 3>3
# (3>4 and (not 4>3)) or ((1 == 3 and 'x' =='x') or 3>3)
print(((3>4 and (not 4>3)) or ((1 == 3 and 'x' =='x') or 3>3)))
#执行结果:
False
False
尽量用括号把not,or括起来,只剩下用and连接的语句
五、成员运算符
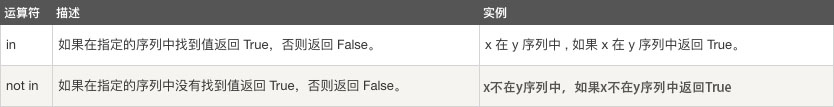
# in:在内部
print('lwx' in 'lwx handsome') #判断小字符串是否是在大字符串中
print('l' in 'lwx') #判断字符是否是在字符串中
#执行结果:
True
True
# not in
print('a' not in 'lwx') #推荐使用
print(not 'a' in 'lwx') #逻辑同上,但不
#执行结果:
True
True
六、身份运算符

is和==的区别:
- is:用于判断两个变量引用的对象是否为同一个(是否在同一块内存中)
- ==:用于判断引用变量的值是否相等
#代码:
x = 257
y = x
z = 520
print(f'x is y:{x is y}')
print(f'x == y:{x == y}')
print(f'x is z:{x is z}')
print(f'x == z:{x == z}')
#结果:
x is y:True
x == y:True
x is z:False
x == z:False
七、位运算符
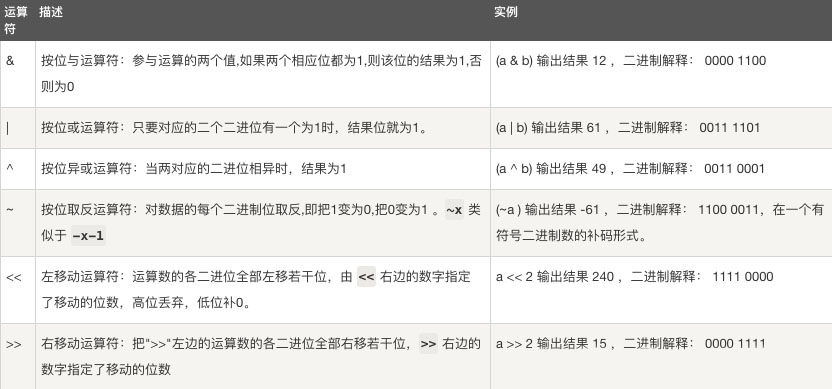
按位运算符是把数字看作二进制来进行计算的。Python中的按位运算法则如下:
下表中变量 a 为 60,b 为 13,二进制格式如下:
a = 0011 1100
b = 0000 1101
-----------------
a&b = 0000 1100
a|b = 0011 1101
a^b = 0011 0001
~a = 1100 0011
八、Python运算符优先级
Python运算符的优先级,相当于数学中的先乘除后加减,但是这样很愚蠢,优先级高的直接用括号括起来就好了


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号