标准模板库(STL)学习指南之vector向量
拷贝构造函数和重载的赋值操作符)
三.必须包含的头文件#include <vector>
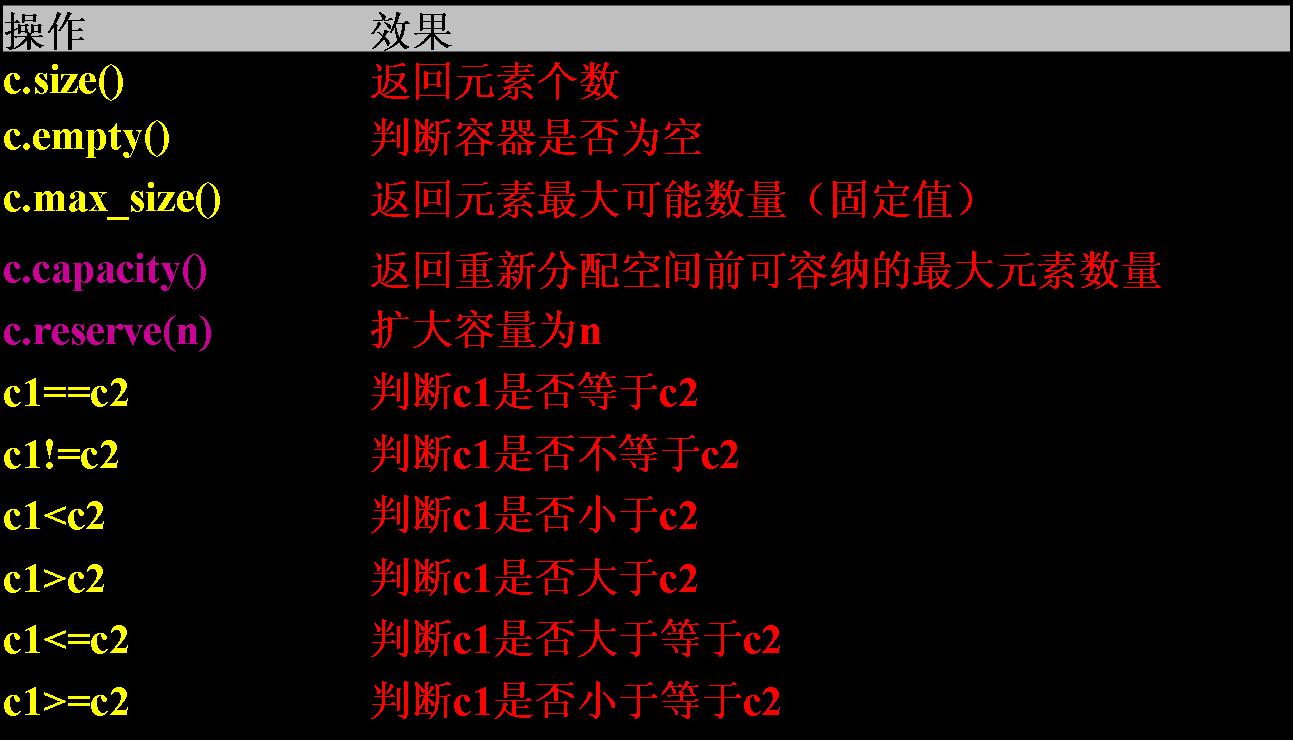
capacity返回vector能容纳的元素最大数量。如果插入元素时,元素个数超过capacity,
需要重新配置内部存储器。
->构造、拷贝和析构

->非变动操作
eg.
vector<int> v1(10); cout << "The capacity of v1 is " << v1.capacity() << endl; cout << "The size of v1 is " << v1.size() << endl; vector<int> v2; v2.reserve(20); cout << "The capacity of v2 is " << v2.capacity() << endl; cout << "The size of v2 is " << v2.size() << endl;
output :
The capacity of v1 is 10 The size of v1 is 10 The capacity of v2 is 20 The size of v2 is 0
->赋值操作

所有的赋值操作都有可能调用元素类型的默认构造函数,拷贝构造函数,赋值操作符和析构函数
如:
eg.
vector<int> v; v.assign( 10, 42 ); for( vector<int>::size_type i = 0; i < v.size(); i++ ) { cout << v[i] << " "; } cout << endl;
OutPut :
42 42 42 42 42 42 42 42 42 42
vector<int> v1; for( int i = 0; i < 10; i++ ) { v1.push_back( i ); } vector<int> v2; v2.assign( v1.begin(), v1.end() ); for( vector<int>::size_type i = 0; i < v2.size(); i++ ) { cout << v2[i] << " "; }
cout << endl;
output :
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
元素存取

下面的操作是错误的:
std::vector<T> v;//empty
eg.
string str; while( cin >> str ) words.push_back(str); sort( words.begin(), words.end() ); cout << "In alphabetical order, the first word is '" << words.front() << "'." << endl;
假设输入是: now is the time for all good men to come to the aid of their country
output:
In alphabetical order, the first word is 'aid'.
vector<int> v; for( int i = 0; i < 5; i++ ) { v.push_back(i); } cout << "The first element is " << v.front() << " and the last element is " << v.back() << endl;
output:
The first element is 0 and the last element is 4
迭代器相关函数

使用迭代器时应注意:
迭代器持续有效,除非发生以下两种情况:
eg.
vector<string> words; string str; while( cin >> str ) words.push_back(str); for( vector<string>::const_iterator iter = words.begin(); iter != words.end(); ++iter ) { cout << *iter << endl; }
假设输入是 : hey mickey you're so fine
output:
hey
mickey
you're
so
fine
插入(insert)元素

eg.
vector<char> alphaVector; for( int i=0; i < 10; i++ ) { alphaVector.push_back( i + 'A' ); } // Insert four C's into the vector vector<char>::iterator theIterator = alphaVector.begin(); alphaVector.insert( theIterator, 4, 'C' ); // Display the vector for( theIterator = alphaVector.begin(); theIterator != alphaVector.end(); ++theIterator ) { cout << *theIterator; }
output:
CCCCABCDEFGHIJ
vector<int> v1; v1.push_back( 0 ); v1.push_back( 1 ); v1.push_back( 2 ); v1.push_back( 3 ); vector<int> v2; v2.push_back( 5 ); v2.push_back( 6 ); v2.push_back( 7 ); v2.push_back( 8 ); cout << "Before, v2 is: "; for( vector<int>::size_type i = 0; i < v2.size(); i++ ) { cout << v2[i] << " "; } cout << endl; v2.insert( v2.end(), v1.begin(), v1.end() ); cout << "After, v2 is: "; for( vector<int>::size_type i = 0; i < v2.size(); i++ ) { cout << v2[i] << " "; }
cout << endl;
output :
Before, v2 is: 5 6 7 8
After, v2 is: 5 6 7 8 0 1 2 3

eg.
vector<char> alphas; for( int i=0; i < 10; i++ ) { static const char letters[] = "ABCDEFGHIJ"; alphas.push_back( letters[i] ); } vector<char>::size_type size = alphas.size(); vector<char>::iterator startIterator; vector<char>::iterator tempIterator; for( vector<char>::size_type i=0; i < size; i++ ) { startIterator = alphas.begin(); alphas.erase( startIterator ); // Display the vector for( tempIterator = alphas.begin(); tempIterator != alphas.end(); ++tempIterator ) { cout << *tempIterator; } cout << endl; }
output:
BCDEFGHIJ
CDEFGHIJ
DEFGHIJ
EFGHIJ
FGHIJ
GHIJ
HIJ
IJ
J
vector<char> alphas; for( int i=0; i < 10; i++ ) { static const char letters[] = "ABCDEFGHIJ"; alphas.push_back( letters[i] ); } // display the complete vector for( vector<char>::size_type i = 0; i < alphas.size(); i++ ) { cout << alphas[i]; } cout << endl; // use erase to remove all but the first two and last three elements // of the vector alphas.erase( alphas.begin()+2, alphas.end()-3 ); // display the modified vector for( vector<char>::size_type i = 0; i < alphas.size(); i++ ) { cout << alphas[i]; }
cout << endl;
output:
ABCDEFGHIJ
ABHIJ
#include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <iterator> using namespace std; int main() { vector<char> alphas; for( int i=0; i < 10; i++ ) { static const char letters[] = "ABCDEFGHIJ"; alphas.push_back( letters[i] ); } vector<char>::iterator iter = alphas.begin(); while( iter != alphas.end() ) { if (*iter == 'B' || *iter == 'D') iter = alphas.erase( iter ); else ++iter; } copy(alphas.begin(), alphas.end(), ostream_iterator<char>(cout, "")); cout << endl; }
output :
ACEFGHIJ
转载自:http://www.cppblog.com/MiYu/archive/2010/08/31/125459.html
作者:ACShiryu
出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/ACShiryu/
若非注明,本博客文章均为原创,版权归作者和博客园共有,欢迎转载,但必须保留此段声明,且在文章页面明显位置给出原文链接,否则保留追究法律责任的权利。
该文章也同步发布在我的新浪微博中-ACShiryu's weibo,欢迎收听。


