GCD Table
GCD Table
The GCD table G of size n × n for an array of positive integers a of length n is defined by formula
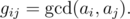
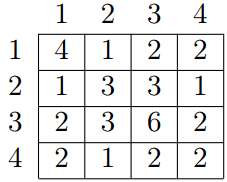
Let us remind you that the greatest common divisor (GCD) of two positive integers x and y is the greatest integer that is divisor of both xand y, it is denoted as 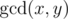 . For example, for array a = {4, 3, 6, 2} of length 4 the GCD table will look as follows:
. For example, for array a = {4, 3, 6, 2} of length 4 the GCD table will look as follows:
Given all the numbers of the GCD table G, restore array a.
The first line contains number n (1 ≤ n ≤ 500) — the length of array a. The second line contains n2 space-separated numbers — the elements of the GCD table of G for array a.
All the numbers in the table are positive integers, not exceeding 109. Note that the elements are given in an arbitrary order. It is guaranteed that the set of the input data corresponds to some array a.
In the single line print n positive integers — the elements of array a. If there are multiple possible solutions, you are allowed to print any of them.
4
2 1 2 3 4 3 2 6 1 1 2 2 1 2 3 2
4 3 6 2
1
42
42
2
1 1 1 1
1 1
模拟寻找过程,暴力就好:
首先num[]数组记录各个值出现次数。
必定寻找最大值,num[]--,b[]数组记录最大值,然后寻找次大值x,并且GCD求出y = __gcd(b[],x),num[y] -= 2;
然后将其记录在b[]数组中。
#include<cstdio> #include<iostream> #include<cstring> #include<algorithm> #include<map> using namespace std; int gcd(int x, int y){ return y==0 ? x : gcd(y, x%y); } bool cmp(int x,int y){ return x > y; } map<int, int>num; int a[250005]; int b[505]; int main(){ int n; scanf("%d",&n); for(int i = 0; i < n*n; i++){ scanf("%d",&a[i]); num[a[i]]++; } int cnt = 0; sort(a,a+n*n,cmp); for(int i = 0; i < n*n; i++){ if(!num[a[i]])continue; num[a[i]]--; for(int j = 0; j < cnt; j++){ int x = gcd(a[i],b[j]); num[x] -= 2; } b[cnt++] = a[i]; } for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){ if(i)printf(" "); printf("%d",b[i]); } return 0; }




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号