树状数组1,ACM暑期培训
〔manim | 算法 | 数据结构〕 完全理解并深入应用树状数组 | 支持多种动态维护区间操作_哔哩哔哩_bilibili
五分钟丝滑动画讲解 | 树状数组_哔哩哔哩_bilibili
(23条消息) 树状数组(详细分析+应用),看不懂打死我!_树形数组_鲜果维他命的博客-CSDN博客 注意:
1、树状数组一般的数组一般从下标1开始赋值0作为一个边界 ,lowbit(0)=0会陷入死循环。
2、树状数组基本用法是:区间修改,区间查询 ,其他用法均在此基础上拓展
3、树状数组我个人的理解就是差分的升级版,能更快的解决差分问题
P3374 【模板】树状数组 1
P3374 【模板】树状数组 1 - 洛谷 | 计算机科学教育新生态 (luogu.com.cn)
题目描述
如题,已知一个数列,你需要进行下面两种操作:
-
将某一个数加上 x
-
求出某区间每一个数的和
输入格式
第一行包含两个正整数 n,m,分别表示该数列数字的个数和操作的总个数。
第二行包含 n 个用空格分隔的整数,其中第 i 个数字表示数列第 i 项的初始值。
接下来 m 行每行包含 3 个整数,表示一个操作,具体如下:
-
1 x k含义:将第 x 个数加上 k -
2 x y含义:输出区间 [x,y] 内每个数的和
输出格式
输出包含若干行整数,即为所有操作 2 的结果。
输入输出样例
输入 #1复制
5 5 1 5 4 2 3 1 1 3 2 2 5 1 3 -1 1 4 2 2 1 4
输出 #1复制
14 16
说明/提示
【数据范围】
对于 30%30% 的数据, 1≤n≤8, 1≤m≤10;
对于 70%70% 的数据, 1≤n,m≤104;
对于 100%100% 的数据, 1≤n,m≤5×105。
数据保证对于任意时刻, a 的任意子区间(包括长度为 11 和 n 的子区间)和均在 [−231,231)[−231,231) 范围内。
解析:树状数组
这道题单独用差分做不了,因为要求区间和,而差分只能用修改区间值(这里是修改长度为一的区间值);单独用累加也做不了,因为累加没法改变某点的值;那差分和累加一起用呢,这个确实可以,但看这道题的数据范围会导致超时。
这道题的正解是树状数组或线段树(树状数组能做的线段树一定能做)
树状数组:区间修改,单点查询
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<string>
#include<cstring>
#include<cmath>
#include<ctime>
#include<algorithm>
#include<utility>
#include<stack>
#include<queue>
#include<vector>
#include<set>
#include<map>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int N = 5e5 + 5;
int n, m;
int arr[N];
int c[N];
void add(int x, int d) {
for (; x <= n; x += x & -x)
c[x] += d;
}
int sum(int x) {
int ans = 0;
for (; x; x -= x & -x)
ans += c[x];
return ans;
}
int main() {
scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
scanf("%d", &arr[i]);
add(i, arr[i]);
}
for (int i = 1, a, b, c; i <= m; i++) {
scanf("%d%d%d", &a, &b, &c);
if (a == 1) {
add(b, c);
}
else {
cout << sum(c)-sum(b-1) << endl;
}
}
return 0;
}P3368 【模板】树状数组 2
P3368 【模板】树状数组 2 - 洛谷 | 计算机科学教育新生态 (luogu.com.cn)
复制Markdown 展开
题目描述
如题,已知一个数列,你需要进行下面两种操作:
-
将某区间每一个数加上 x;
-
求出某一个数的值。
输入格式
第一行包含两个整数 N、M,分别表示该数列数字的个数和操作的总个数。
第二行包含 N 个用空格分隔的整数,其中第 i 个数字表示数列第 i 项的初始值。
接下来 M 行每行包含 2 或 4个整数,表示一个操作,具体如下:
操作 1: 格式:1 x y k 含义:将区间 [x,y] 内每个数加上 k;
操作 2: 格式:2 x 含义:输出第 x 个数的值。
输出格式
输出包含若干行整数,即为所有操作 22 的结果。
输入输出样例
输入 #1复制
5 5 1 5 4 2 3 1 2 4 2 2 3 1 1 5 -1 1 3 5 7 2 4
输出 #1复制
6 10
说明/提示
数据规模与约定
对于 30% 的数据:N≤8,M≤10;
对于 70% 的数据:N≤10000,M≤10000;
对于 100%的数据:1≤N,M≤500000,1≤x,y≤n,保证任意时刻序列中任意元素的绝对值都不大于 2^30。
解析:树状数组,差分
这道题目由于是区间修改,单点查询,而树状数组的基本用法是处理区间修改,单点查询,因此我们无法直接使用树状数组,所以我们要先求出原数组的差分数组,然后对差分数组的单点进行修改,即原数组的区间进行修改,而差分数组的前缀和即时原数组的对应点的值,又因为树状数组能直接求出区间和,因此就将问题转换成了树状数组能处理的问题
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<string>
#include<cstring>
#include<cmath>
#include<ctime>
#include<algorithm>
#include<utility>
#include<stack>
#include<queue>
#include<vector>
#include<set>
#include<map>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int N = 5e5 + 5;
int n, m;
int arr[N],su[N];
int c[N];
void add(int x, int d) {
for (; x <= n; x += x & -x)
c[x] += d;
}
int sum(int x) {
int ans = 0;
for (; x; x -= x & -x)
ans += c[x];
return ans;
}
int main() {
scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
scanf("%d", &arr[i]);
su[i] = arr[i] - arr[i - 1];
add(i, su[i]);
}
for (int i = 1, a, b, c,d; i <= m; i++) {
scanf("%d", &a);
if (a == 1) {
scanf("%d%d%d", &b, &c,&d);
add(b, d);
add(c + 1, -d);
}
else {
scanf("%d", &b);
cout << sum(b) << endl;
}
}
return 0;
}P5057 [CQOI2006] 简单题
题目描述
有一个 n 个元素的数组,每个元素初始均为 0。有 m 条指令,要么让其中一段连续序列数字反转——0 变 1,1 变 0(操作 1),要么询问某个元素的值(操作 2)。 例如当 n = 20 时,10 条指令如下:
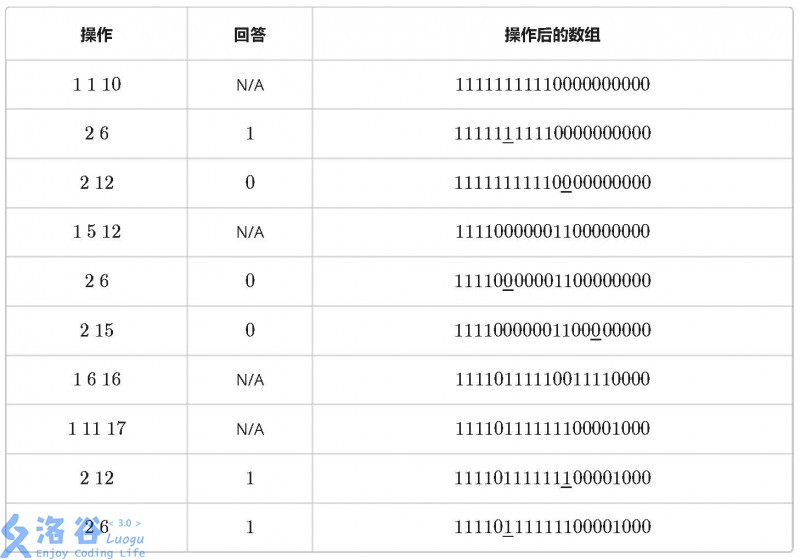
输入格式
第一行包含两个整数 n, m,表示数组的长度和指令的条数; 以下 m 行,每行的第一个数 t 表示操作的种类:
若 t = 1,则接下来有两个数 L, R,表示区间 [L, R] 的每个数均反转; 若 t = 2,则接下来只有一个数 i,表示询问的下标。
输出格式
每个操作 2 输出一行(非 0 即 1),表示每次操作 2 的回答。
输入输出样例
输入 #1复制
20 10 1 1 10 2 6 2 12 1 5 12 2 6 2 15 1 6 16 1 11 17 2 12 2 6
输出 #1复制
1 0 0 0 1 1
说明/提示
对于 50% 的数据,1 ≤ n ≤ 103103, 1 ≤ m ≤ 104104; 对于 100% 的数据,1 ≤ n ≤ 105105, 1 ≤ m ≤ 5 × 105105,保证 L ≤ R。
解析:树状数组,异或差分
这道题和上面那题很像,只是将加减差分改为异或差分
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<string>
#include<cstring>
#include<cmath>
#include<ctime>
#include<algorithm>
#include<utility>
#include<stack>
#include<queue>
#include<vector>
#include<set>
#include<map>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int N = 1e+5;
int n, m;
int c[N];
void add(int x, int b) {
for (; x <= n; x += x & -x) {
if (c[x] == 1)
c[x] = 0;
else
c[x] = 1;
}
}
int sum(int x) {
int ans = 0;
for (; x; x -= x & -x) {
ans ^= c[x];
}
return ans;
}
int main() {
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 1, t, l, r; i <= m; i++) {
scanf("%d", &t);
if (t == 1) {
scanf("%d%d", &l, &r);
add(l, 0);
add(r + 1, 0);
}
else {
scanf("%d", &l);
printf("%d\n", sum(l));
}
}
return 0;
}P1908 逆序对
题目描述
猫猫 TOM 和小老鼠 JERRY 最近又较量上了,但是毕竟都是成年人,他们已经不喜欢再玩那种你追我赶的游戏,现在他们喜欢玩统计。
最近,TOM 老猫查阅到一个人类称之为“逆序对”的东西,这东西是这样定义的:对于给定的一段正整数序列,逆序对就是序列中ai>aj 且 i<j 的有序对。知道这概念后,他们就比赛谁先算出给定的一段正整数序列中逆序对的数目。注意序列中可能有重复数字。
Update:数据已加强。
输入格式
第一行,一个数 n,表示序列中有 n个数。
第二行 n 个数,表示给定的序列。序列中每个数字不超过 109。
输出格式
输出序列中逆序对的数目。
输入输出样例
输入 #1复制
6 5 4 2 6 3 1
输出 #1复制
11
说明/提示
对于 25%25% 的数据,0n≤2500
对于 50%50% 的数据,n≤4×104。
对于所有数据,n≤5×105
请使用较快的输入输出
应该不会O(n2) 过 50 万吧 by chen_zhe
题解:树状数组,离散化数据处理
这是一道非常好的题目
P1908 逆序对 - 洛谷 | 计算机科学教育新生态 (luogu.com.cn)
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<string>
#include<cstring>
#include<cmath>
#include<ctime>
#include<algorithm>
#include<utility>
#include<stack>
#include<queue>
#include<vector>
#include<set>
#include<map>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int N = 5e5 + 5;
int n;
typedef struct st {
int num, index;
}st;
st arr[N], temp[N];
int c[N];
void add(int x, int d) {
for (; x<=n; x += x & -x) {
c[x] += d;
}
}
int sum(int x) {
int ans = 0;
for (; x; x -= x & -x) {
ans += c[x];
}
return ans;
}
int cmp(const st& a, const st& b) {
if (a.num == b.num)
return a.index < b.index;
return a.num < b.num;
}
int main() {
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
cin >> temp[i].num;
temp[i].index = i;
}
arr[1].num = 1;
arr[1].index = temp[1].index;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
if (temp[i].num == temp[i - 1].num) {
arr[i].num = arr[i - 1].num;
}
else {
arr[i].num = i;
}
arr[i].index = temp[i].index;
}
LL ans = 0;
for (int i = n; i > 0; i--) {
ans += sum(arr[i].index - 1);
add(arr[i].index, 1);
}
cout << ans << endl;
return 0;
}

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号