数据结构:第7章:查找(复习)
目录
顺序查找:
ASL=
折半查找:
这里 j 表示 二叉查找树的第 j 层
二叉排序树:
二叉排序树(Binary Search Tree,BST)是一种特殊的二叉树,定义:
- 对于二叉排序树的每个节点,其左子树的所有节点的值都小于该节点的值。
- 对于二叉排序树的每个节点,其右子树的所有节点的值都大于该节点的值。
- 对于二叉排序树的每个节点,其左右子树也分别是二叉排序树。
可以发现二叉排序树的定义时递归定义。
这些性质保证了对于二叉排序树中的任意节点,其左子树的节点值小于它,右子树的节点值大于它,从而形成了一种有序的结构。
二叉排序树的有序性质使得在其中进行查找、插入和删除等操作时具有较高的效率。对于给定的值,可以通过比较节点的值,按照二叉排序树的性质在树中快速定位所需的节点。
二叉排序树的难点在于删除树中的某个值。删除某个键值为 key 的节点时,有三中情况要考虑:
1.该节点 r 的左孩子为空:r=r->lch;
2.该节点 r 的右孩子为空:l=l->rch;
3.该节点的左右孩子均不位空:选择左孩子中 key 值最大的节点替换 r;
4. (程序题)
二叉排序树插入、删除
键盘输入若干整型数据,以0做结束,利用二叉排序树的插入算法创建二叉排序树,并中序遍历该二叉树。之后输入一个整数x,在二叉排序树中查找,若找到则输出“该数存在”,否则输出“该数不存在”;再输入一个要删除的一定存在的整数y,完成在该二叉树中删除y的操作,并输出删除y后的二叉树中序遍历的结果。
输出数据之间用一个空格分隔。
输入:
1 5 4 2 3 6 8 7 9 11 14 13 12 16 19 0
输出:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 11 12 13 14 16 19
输入:
19
输出:
该数存在
输入:
14
输出:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 11 12 13 16 19
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<cstring>
#include<cmath>
#include<ctime>
#include<algorithm>
#include<utility>
#include<stack>
#include<queue>
#include<vector>
#include<set>
#include<math.h>
#include<map>
#include<sstream>
#include<deque>
#include<unordered_map>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
typedef struct Info {
int key;
}Info;
typedef struct Node {
Info data;
struct Node* lch;
struct Node* rch;
}Node,*Tree;
void print(Tree& r) {
if (r == NULL)return;
print(r->lch);
cout << r->data.key << " ";
print(r->rch);
}
void Insert(Tree& r, int key) {
if (r == NULL) {
Node* p = new Node;
p->data.key = key;
p->rch = p->lch = NULL;
r = p;
}
else if(r->data.key<key) {
Insert(r->rch, key);
}
else {
Insert(r->lch, key);
}
}
void build(Tree& r) {
int in;
cin >> in;
while (in) {
Insert(r, in);
cin >> in;
}
}
int search(Tree& r, int key) {
if (r == NULL)return 0;
if (r->data.key == key) {
return 1;
}
if (r->data.key < key) {
if (search(r->rch, key))return 1;
}
else {
if (search(r->lch, key))return 1;
}
return 0;
}
int del(Tree& r, int key) {
if (r == NULL)return 0;
if (r->data.key == key) {
if (r->lch == NULL) {
r =r->rch;
}
else if (r->rch == NULL) {
r =r->lch;
}
else {
//cout << r->data.key << endl;
Node* p = r->lch;
Node* fa = r;
while (p->rch != NULL) {
fa = p;
p = p->rch;
}
Node* t = r;
if (fa != r)
fa->rch = p->lch;
if (r->lch != p)
p->lch = r->lch;
p->rch = r->rch;
//cout << p->data.key << endl;
r = p;
delete t;
}
return 1;
}
if (r->data.key < key) {
if (del(r->rch, key))return 1;
}
else {
if (del(r->lch, key))return 1;
}
return 0;
}
int main() {
Node* root = NULL;
build(root);
print(root);
int in;
cin >> in;
if (search(root, in)) {
cout << "该数存在" << endl;
}
else {
cout << "该数不存在" << endl;
}
cin >> in;
del(root, in);
print(root);
return 0;
}用例1:
输入
1 5 4 2 3 6 8 7 9 11 14 13 12 16 19 0 19 14
输出
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 11 12 13 14 16 19 该数存在 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 11 12 13 16 19
用例2:
输入
10 9 8 7 11 12 13 14 0 14 8
输出
7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 该数存在 7 9 10 11 12 13 14
用例3:
输入
23 45 67 21 12 15 9 10 55 0 19 9
输出
9 10 12 15 21 23 45 55 67 该数不存在 10 12 15 21 23 45 55 67
平衡二叉树:
平衡二叉树的定义
平衡二叉排序树查找算法的性能取决于二叉树的结构,而二叉树的形状则取决于其数据集。
如果数据呈有序排列,则二叉排序树是线性的,查找的时间复杂度为O(n);反之,如果二叉排序
树的结构合理,则查找速度较快,查找的时间复杂度为O(logn)。事实上,树的高度越小,查找
速度越快。因此,希望二叉树的高度尽可能小。本节将讨论一种特殊类型的二叉排序树,称为平
衡二叉树(Balanced Binary Tree 或 Height-Balanced Tree),因由前苏联数学家 Adelson-Velskii 和
Landis 提出,所以又称AVL树。
平衡二叉树或者是空树,或者是具有如下特征的二叉排序树:
(1)左子树和右子树的深度之差的绝对值不超过1;
(2)左子树和右子树也是平衡二叉树。
若将二叉树上结点的平衡因子(Balance Factor,BF)定义为该结点左子树和右子树的深度之
差,则平衡二叉树上所有结点的平衡因子只可能是-1、0和1。只要二叉树上有一个结点的平衡
因子的绝对值大于1,则该二叉树就是不平衡的。图7.11(a)所示为两棵平衡二叉树,而图 7.11
(b)所示为两棵不平衡的二叉树,结点中的值为该结点的平衡因子。
平衡二叉树的调整(重难点)
LL型调整操作:由于在A左子树根结点的左子树上插入结点,A的平衡因子由1增至2,致使以A为根的子树失去平衡,则需进行一次向右的顺时针旋转操作

RR 型调整操作:当在 A 的右子树的右子树上插入结点时,A 的平衡因子由 -1 变为 -2,导致以 A 为根结点的子树失去平衡。此时,需要进行一次向左的逆时针旋转操作,将 A 的右子树作为其左子树的右子树,并将 A 作为其左子树的根结点。

LR型调整操作:由于在A的左子树根结点的右子树上插入结点, A的平衡因子由1增至2,致使以A为根结点的子树失去平衡,则需进行两次旋转操作。第一次对B及其右子树进行递时针旋转,C转上去成为B的根,这时变成了LL型,所以第二次进行LL型的顺时针旋转即可恢复平衡。如果C原来有左子树,则调整C的左子树为B的右子树,
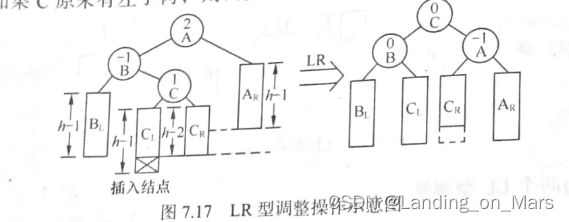
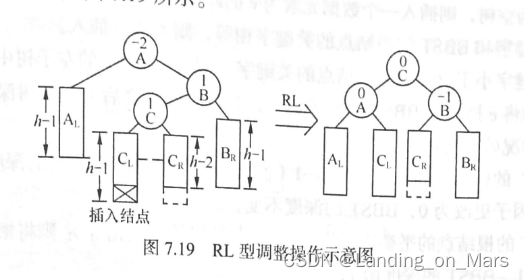
RL型调整操作:由于在A的右子树根结点的左子树上插入结点,A的平衡因子由-1变为-2,致使以A 为根结点的子树失去平衡,则旋转方法和LR型相对称,也需进行两次旋转,先顺时针右旋,再逆时针左旋。
左,右旋转调整代码:mp用来记录某个节点的高度
void Turnleft(TreeNode*& r) {
TreeNode* A = r;
TreeNode* B = r->right;
A->right = B->left;
B->left = A;
r = B;
mp[r->left] -= 2;
mp[r] = mp[r->right] + 1;
}
void Turnright(TreeNode*& r) {
TreeNode* A = r;
TreeNode* B = r->left;
A->left = B->right;
B->right = A;
r = B;
mp[r->right] -= 2;
mp[r] = mp[r->left] + 1;
}
判断不平衡类型类型的代码:
void fun1(vector<int>& g, TreeNode* r) {
if ( r == NULL||(r->left==NULL&&r->right==NULL))return;
if (mp[r->left] == mp[r->right])return;
g.push_back(mp[r->left] - mp[r->right]);
fun1(g, r->left);
fun1(g, r->right);
}
string check(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int>g;
fun1(g, root);
if (g[0] == 2&&g[1]==1)return "LL";
else if (g[0] == 2&&g[1]==-1)return "LR";
else {
if (g[0] == -2&&g[1]==1)return "RL";
return "RR";
}
return "NO";
}建立平衡二叉树的代码
class Solution {
public:
unordered_map<TreeNode*, int>mp;
void fun1(vector<int>& g, TreeNode* r) {
if (r == NULL || (r->left == NULL && r->right == NULL))return;
if (mp[r->left] == mp[r->right])return;
g.push_back(mp[r->left] - mp[r->right]);
fun1(g, r->left);
fun1(g, r->right);
}
string check(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int>g;
fun1(g, root);
if (g[0] == 2 && g[1] == 1)return "LL";
else if (g[0] == 2 && g[1] == -1)return "LR";
else {
if (g[0] == -2 && g[1] == 1)return "RL";
return "RR";
}
return "NO";
}
void Turnleft(TreeNode*& r) {
TreeNode* A = r;
TreeNode* B = r->right;
A->right = B->left;
B->left = A;
r = B;
mp[r->left] -= 2;
mp[r] = mp[r->right] + 1;
}
void Turnright(TreeNode*& r) {
TreeNode* A = r;
TreeNode* B = r->left;
A->left = B->right;
B->right = A;
r = B;
mp[r->right] -= 2;
mp[r] = mp[r->left] + 1;
}
void change(TreeNode*& r, string ret) {
if (ret == "LL") {
Turnright(r);
}
else if (ret == "RR") {
Turnleft(r);
}
else if (ret == "RL") {
Turnright(r->right);
Turnleft(r);
}
else {
Turnleft(r->left);
Turnright(r);
}
}
void Insert(TreeNode*& r, int key) {
if (r == NULL) {
TreeNode* p = new TreeNode;
p->val = key;
p->left = p->right = NULL;
r = p;
mp[r] = 1;
return ;
}
if (key > r->val) {
Insert(r->right, key);
}
else {
Insert(r->left, key);
}
mp[r] = max(mp[r->left], mp[r->right]) + 1;
int h = mp[r->left] - mp[r->right];
if (h == 2 || h == -2) {
//cout <<" ___________________"<< r->val << endl;
string ret = check(r);
//cout << ret << endl;
change(r, ret);
/* for (unordered_map<TreeNode*, int>::iterator it = mp.begin(); it != mp.end(); it++) {
if (it->first != NULL) {
cout << "KKKK " << it->first->val << " " << it->second << endl;
}
}
cout << "先 ";
inorderTraversal1(r);
cout << endl;
cout << "中 ";
inorderTraversal(r);
cout << endl;*/
}
}
TreeNode* balanceBST(TreeNode*& root,vector<int>preorder) {
for (int i = 0; i <preorder.size(); i++) {
Insert(root, preorder[i]);
}
return root;
}
};完整代码:
代码中有测试样例
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<cstring>
#include<cmath>
#include<ctime>
#include<algorithm>
#include<utility>
#include<stack>
#include<queue>
#include<vector>
#include<set>
#include<math.h>
#include<map>
#include<sstream>
#include<deque>
#include<unordered_map>
using namespace std;
// Definition for a binary tree node.
struct TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode* left;
TreeNode* right;
TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
TreeNode(int x, TreeNode* left, TreeNode* right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
};
// Function to insert a value into BST
TreeNode* insertIntoBST(TreeNode* root, int val) {
if (!root) {
return new TreeNode(val);
}
if (val < root->val) {
root->left = insertIntoBST(root->left, val);
}
else {
root->right = insertIntoBST(root->right, val);
}
return root;
}
// Function to construct BST from preorder traversal
TreeNode* bstFromPreorder(vector<int>& preorder) {
TreeNode* root = nullptr;
for (int val : preorder) {
if (val == 0)continue;
root = insertIntoBST(root, val);
}
return root;
}
// Function to perform inorder traversal (for verification)
void inorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
if (root) {
inorderTraversal(root->left);
cout << root->val << " ";
inorderTraversal(root->right);
}
}
void inorderTraversal1(TreeNode* root) {
if (root) {
cout << root->val << " ";
inorderTraversal1(root->left);
inorderTraversal1(root->right);
}
}
// Function to perform level order traversal
void levelOrderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
if (!root) {
return;
}
queue<TreeNode*> q;
q.push(root);
while (!q.empty()) {
TreeNode* current = q.front();
q.pop();
cout << current->val << " ";
if (current->left) {
q.push(current->left);
}
if (current->right) {
q.push(current->right);
}
}
}
class Solution {
public:
unordered_map<TreeNode*, int>mp;
void fun1(vector<int>& g, TreeNode* r) {
if (r == NULL || (r->left == NULL && r->right == NULL))return;
if (mp[r->left] == mp[r->right])return;
g.push_back(mp[r->left] - mp[r->right]);
fun1(g, r->left);
fun1(g, r->right);
}
string check(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int>g;
fun1(g, root);
if (g[0] == 2 && g[1] == 1)return "LL";
else if (g[0] == 2 && g[1] == -1)return "LR";
else {
if (g[0] == -2 && g[1] == 1)return "RL";
return "RR";
}
return "NO";
}
void Turnleft(TreeNode*& r) {
TreeNode* A = r;
TreeNode* B = r->right;
A->right = B->left;
B->left = A;
r = B;
mp[r->left] -= 2;
mp[r] = mp[r->right] + 1;
}
void Turnright(TreeNode*& r) {
TreeNode* A = r;
TreeNode* B = r->left;
A->left = B->right;
B->right = A;
r = B;
mp[r->right] -= 2;
mp[r] = mp[r->left] + 1;
}
void change(TreeNode*& r, string ret) {
if (ret == "LL") {
Turnright(r);
}
else if (ret == "RR") {
Turnleft(r);
}
else if (ret == "RL") {
Turnright(r->right);
Turnleft(r);
}
else {
Turnleft(r->left);
Turnright(r);
}
}
void Insert(TreeNode*& r, int key) {
if (r == NULL) {
TreeNode* p = new TreeNode;
p->val = key;
p->left = p->right = NULL;
r = p;
mp[r] = 1;
return ;
}
if (key > r->val) {
Insert(r->right, key);
}
else {
Insert(r->left, key);
}
mp[r] = max(mp[r->left], mp[r->right]) + 1;
int h = mp[r->left] - mp[r->right];
if (h == 2 || h == -2) {
//cout <<" ___________________"<< r->val << endl;
string ret = check(r);
//cout << ret << endl;
change(r, ret);
/* for (unordered_map<TreeNode*, int>::iterator it = mp.begin(); it != mp.end(); it++) {
if (it->first != NULL) {
cout << "KKKK " << it->first->val << " " << it->second << endl;
}
}
cout << "先 ";
inorderTraversal1(r);
cout << endl;
cout << "中 ";
inorderTraversal(r);
cout << endl;*/
}
}
TreeNode* balanceBST(TreeNode*& root,vector<int>preorder) {
for (int i = 0; i <preorder.size(); i++) {
Insert(root, preorder[i]);
}
return root;
}
};
int main() {
vector<int> preorder = { 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,31,25,47,16,28,30 };
/*
1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10
19,10,4,17,5
31,25,47,40,69,43
1,2,3,4
31,25,47,40,69,36
31,25,47,16,28,26
31,25,47,16,28,30
1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,31,25,47,16,28,30
*/
TreeNode* root = NULL;
Solution solve;
solve.balanceBST(root,preorder);
levelOrderTraversal(root);
cout << endl;
cout << "先 ";
inorderTraversal1(root);
cout << endl;
cout << "中 ";
inorderTraversal(root);
cout << endl;
return 0;
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号