树的同构
03-树1 树的同构(25 分)
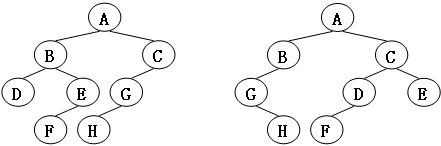
给定两棵树T1和T2。如果T1可以通过若干次左右孩子互换就变成T2,则我们称两棵树是“同构”的。例如图1给出的两棵树就是同构的,因为我们把其中一棵树的结点A、B、G的左右孩子互换后,就得到另外一棵树。而图2就不是同构的。
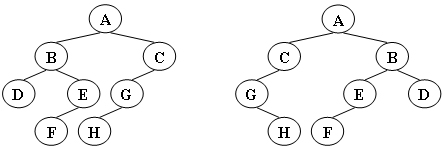
图1
图2
输入格式:
输入给出2棵二叉树树的信息。对于每棵树,首先在一行中给出一个非负整数N (≤10),即该树的结点数(此时假设结点从0到N−1编号);随后N行,第i行对应编号第i个结点,给出该结点中存储的1个英文大写字母、其左孩子结点的编号、右孩子结点的编号。如果孩子结点为空,则在相应位置上给出“-”。给出的数据间用一个空格分隔。注意:题目保证每个结点中存储的字母是不同的。
输出格式:
如果两棵树是同构的,输出“Yes”,否则输出“No”。
输入样例1(对应图1):
8
A 1 2
B 3 4
C 5 -
D - -
E 6 -
G 7 -
F - -
H - -
8
G - 4
B 7 6
F - -
A 5 1
H - -
C 0 -
D - -
E 2 -
输出样例1:
Yes
输入样例2(对应图2):
8
B 5 7
F - -
A 0 3
C 6 -
H - -
D - -
G 4 -
E 1 -
8
D 6 -
B 5 -
E - -
H - -
C 0 2
G - 3
F - -
A 1 4
输出样例2:
No

1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<vector> 3 #define Maxsize 10 4 #define tree int 5 #define Null -1 6 using namespace std; 7 struct treenode{ 8 char data; 9 int left; 10 int right; 11 }T1[Maxsize],T2[Maxsize]; 12 tree buildtree(struct treenode T[]) 13 { 14 char cl,cr; 15 int N,i; cin>>N; 16 vector<int> check(10,0); 17 if(N){ 18 for(i=0;i<N;i++){ 19 cin>>T[i].data>>cl>>cr; 20 if(cl!='-'){ 21 T[i].left=cl-'0'; 22 check[T[i].left]=1; 23 }else T[i].left=Null; 24 if(cr!='-'){ 25 T[i].right=cr-'0'; 26 check[T[i].right]=1; 27 }else T[i].right=Null; 28 } 29 } 30 else return Null; 31 for(i=0;i<N;i++) 32 if(check[i]==0) return i; 33 } 34 int isomorphic(tree r1,tree r2) 35 { 36 if(r1==Null&&r2==Null) return 1; 37 if(((r1!=Null)&&(r2==Null))||((r1==Null)&&(r2!=Null))) return 0; 38 if(T1[r1].data!=T2[r2].data) return 0; 39 if((T1[r1].left==Null)&&(T2[r2].left==Null)) return isomorphic(T1[r1].right,T2[r2].right); 40 if(((T1[r1].left!=Null)&&(T2[r2].left!=Null))&&(T1[T1[r1].left].data==T2[T2[r2].left].data)) 41 return (isomorphic(T1[r1].left,T2[r2].left)&&isomorphic(T1[r1].right,T2[r2].right)); 42 else 43 return (isomorphic(T1[r1].right,T2[r2].left)&&isomorphic(T1[r1].left,T2[r2].right)); 44 } 45 int main(){ 46 tree r1,r2; 47 r1=buildtree(T1); 48 r2=buildtree(T2); 49 if(isomorphic(r1,r2)) cout<<"Yes"<<endl; else cout<<"No"<<endl; 50 return 0; 51 }