排序二叉树的特征是:
某个节点的左子树的所有节点值都不大于本节点值。
某个节点的右子树的所有节点值都不小于本节点值。
为了能形象地观察二叉树的建立过程,小明写了一段程序来显示出二叉树的结构来。
#include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> #define N 1000 #define HEIGHT 100 #define WIDTH 1000 struct BiTree { int v; struct BiTree* l; struct BiTree* r; }; int max(int a, int b) { return a>b? a : b; } struct BiTree* init(struct BiTree* p, int v) { p->l = NULL; p->r = NULL; p->v = v; return p; } void add(struct BiTree* me, struct BiTree* the) { if(the->v < me->v){ if(me->l==NULL) me->l = the; else add(me->l, the); } else{ if(me->r==NULL) me->r = the; else add(me->r, the); } } //获得子树的显示高度 int getHeight(struct BiTree* me) { int h = 2; int hl = me->l==NULL? 0 : getHeight(me->l); int hr = me->r==NULL? 0 : getHeight(me->r); return h + max(hl,hr); } //获得子树的显示宽度 int getWidth(struct BiTree* me) { char buf[100]; sprintf(buf,"%d",me->v); int w = strlen(buf); if(me->l) w += getWidth(me->l); if(me->r) w += getWidth(me->r); return w; } int getRootPos(struct BiTree* me, int x){ return me->l==NULL? x : x + getWidth(me->l); } //把缓冲区当二维画布用 void printInBuf(struct BiTree* me, char buf[][WIDTH], int x, int y) { int p1,p2,p3,i; char sv[100]; sprintf(sv, "%d", me->v); p1 = me->l==NULL? x : getRootPos(me->l, x); p2 = getRootPos(me, x); p3 = me->r==NULL? p2 : getRootPos(me->r, p2+strlen(sv)); buf[y][p2] = '|'; for(i=p1; i<=p3; i++) buf[y+1][i]='-'; for(i=0; i<strlen(sv); i++) buf[y+1][p2+i]=sv[i]; if(p1<p2) buf[y+1][p1] = '/'; if(p3>p2) buf[y+1][p3] = '\\'; if(me->l) printInBuf(me->l,buf,x,y+2); if(me->r) ; //填空位置 } void showBuf(char x[][WIDTH]) { int i,j; for(i=0; i<HEIGHT; i++){ for(j=WIDTH-1; j>=0; j--){ if(x[i][j]==' ') x[i][j] = '\0'; else break; } if(x[i][0]) printf("%s\n",x[i]); else break; } } void show(struct BiTree* me) { char buf[HEIGHT][WIDTH]; int i,j; for(i=0; i<HEIGHT; i++) for(j=0; j<WIDTH; j++) buf[i][j] = ' '; printInBuf(me, buf, 0, 0); showBuf(buf); } int main() { struct BiTree buf[N]; //存储节点数据 int n = 0; //节点个数 init(&buf[0], 500); n++; //初始化第一个节点 add(&buf[0], init(&buf[n++],200)); //新的节点加入树中 add(&buf[0], init(&buf[n++],509)); add(&buf[0], init(&buf[n++],100)); add(&buf[0], init(&buf[n++],250)); add(&buf[0], init(&buf[n++],507)); add(&buf[0], init(&buf[n++],600)); add(&buf[0], init(&buf[n++],650)); add(&buf[0], init(&buf[n++],450)); add(&buf[0], init(&buf[n++],440)); add(&buf[0], init(&buf[n++],220)); show(&buf[0]); return 0; }
class BiTree { private int v; private BiTree l; private BiTree r; public BiTree(int v){ this.v = v; } public void add(BiTree the){ if(the.v < v){ if(l==null) l = the; else l.add(the); } else{ if(r==null) r = the; else r.add(the); } } public int getHeight(){ int h = 2; int hl = l==null? 0 : l.getHeight(); int hr = r==null? 0 : r.getHeight(); return h + Math.max(hl,hr); } public int getWidth(){ int w = (""+v).length(); if(l!=null) w += l.getWidth(); if(r!=null) w += r.getWidth(); return w; } public void show(){ char[][] buf = new char[getHeight()][getWidth()]; printInBuf(buf, 0, 0); showBuf(buf); } private void showBuf(char[][] x){ for(int i=0; i<x.length; i++){ for(int j=0; j<x[i].length; j++) System.out.print(x[i][j]==0? ' ':x[i][j]); System.out.println(); } } private void printInBuf(char[][] buf, int x, int y){ String sv = "" + v; int p1 = l==null? x : l.getRootPos(x); int p2 = getRootPos(x); int p3 = r==null? p2 : r.getRootPos(p2+sv.length()); buf[y][p2] = '|'; for(int i=p1; i<=p3; i++) buf[y+1][i]='-'; for(int i=0; i<sv.length(); i++) buf[y+1][i+p2]=sv.charAt(i) (37分); //填空位置 if(p1<p2) buf[y+1][p1] = '/'; if(p3>p2) buf[y+1][p3] = '\\'; if(l!=null) l.printInBuf(buf,x,y+2); if(r!=null) r.printInBuf(buf,p2+sv.length(),y+2); } private int getRootPos(int x){ return l==null? x : x + l.getWidth(); } } public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { BiTree tree = new BiTree(500); tree.add(new BiTree(200)); tree.add(new BiTree(509)); tree.add(new BiTree(100)); tree.add(new BiTree(250)); tree.add(new BiTree(507)); tree.add(new BiTree(600)); tree.add(new BiTree(650)); tree.add(new BiTree(450)); tree.add(new BiTree(510)); tree.add(new BiTree(440)); tree.add(new BiTree(220)); tree.show(); } }
对于上边的测试数据,应该显示出: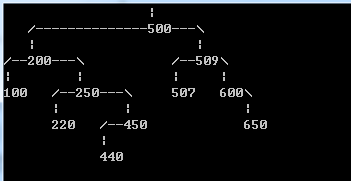
(如有对齐问题,请参考【图1.png】)
请分析程序逻辑,填写划线部分缺失的代码。
注意,只填写缺少的部分,不要填写已有的代码或符号,也不要加任何说明文字。
p2是root的位置,加上此处数字的长度就是要填的内容,可以看到左子树传入的就是x,也就是说要传入的参数应该是子树的左端点位置。sprintf是在这里是把数字传入字符串,计算数字的长度。
如果觉得有帮助,点个推荐啦~

