大学ACM第二周心得
小小分个类
一:图论
1. tarjan
这里推荐这篇博客:[https://blog.csdn.net/mengxiang000000/article/details/51672725]
例:受欢迎的牛[https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P2341]
由题可得,受欢迎的奶牛只有可能是图中唯一的出度为零的强连通分量中的所有奶牛,所以若出现两个以上出度为0的强连通分量则不存在明星奶牛,因为那几个出度为零的分量的爱慕无法传递出去。那唯一的分量能受到其他分量的爱慕同时在分量内相互传递,所以该分量中的所有奶牛都是明星。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define INF 1000001
using namespace std;
int p=0,top=0,inde=0,maxn=0,block=0,n,m,sum=0;
int head[INF],aa[INF],dfn[INF],vis[INF],low[INF],book[INF],ans[INF],dis[INF];
int used[INF],deg[INF],stac[INF],x[INF],y[INF];
struct node
{
int to,next,val;
}a[INF];
void add(int u,int v)
{
a[++p].next=head[u];
head[u]=p;
a[p].to=v;
}
void tarjan(int u)
{
dfn[u]=++inde;
low[u]=inde;
book[u]=1;stac[++top]=u;
for (int i=head[u];i;i=a[i].next)
{
int ne=a[i].to;
if (!dfn[ne])
{
tarjan(ne);
low[u]=min(low[u],low[ne]);
}
else if(book[ne])
low[u]=min(low[u],dfn[ne]);
}
if (low[u]==dfn[u])
{
++block;
while (stac[top+1]!=u)
{
vis[stac[top]]=block;
book[stac[top]]=0;
ans[block]++;
top--;
}
}
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
for (int i=1;i<=m;i++)
{
scanf("%d%d",&x[i],&y[i]);
add(x[i],y[i]);
}
for (int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
if (!dfn[i])
tarjan(i);
}
/*for (int i=1;i<=m;i++)
{
if (vis[x[i]]!=vis[y[i]])
{
deg[vis[x[i]]]++;
}
}*/
for (int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
for (int j=head[i];j;j=a[j].next)
{
int u=a[j].to;
if (vis[i]!=vis[u])
deg[vis[i]]++;
}
}
for (int i=1;i<=block;i++)
{
if (deg[i]==0)
sum++,maxn=ans[i];
}
if (sum==1)
{
printf("%d",maxn);
return 0;
}
else printf("0");
return 0;
}
2. 割点割桥
割点定义:在无向连通图中,如果将其中一个点以及所有连接该点的边去掉,图就不再连通,那么这个点就叫做割点
可参考:[https://www.cnblogs.com/collectionne/p/6847240.html]
从学tarjan的时候一直就疑惑这句代码 low[k]=min(low[k],dfn[u])为什么不换成low[u]=min(low[u],low[v])
而且这个能被hack的反例也很难找,在缩点里两种打法都能过。但是在割点里只要数据强一点就不行。
举个栗子,看下这张图: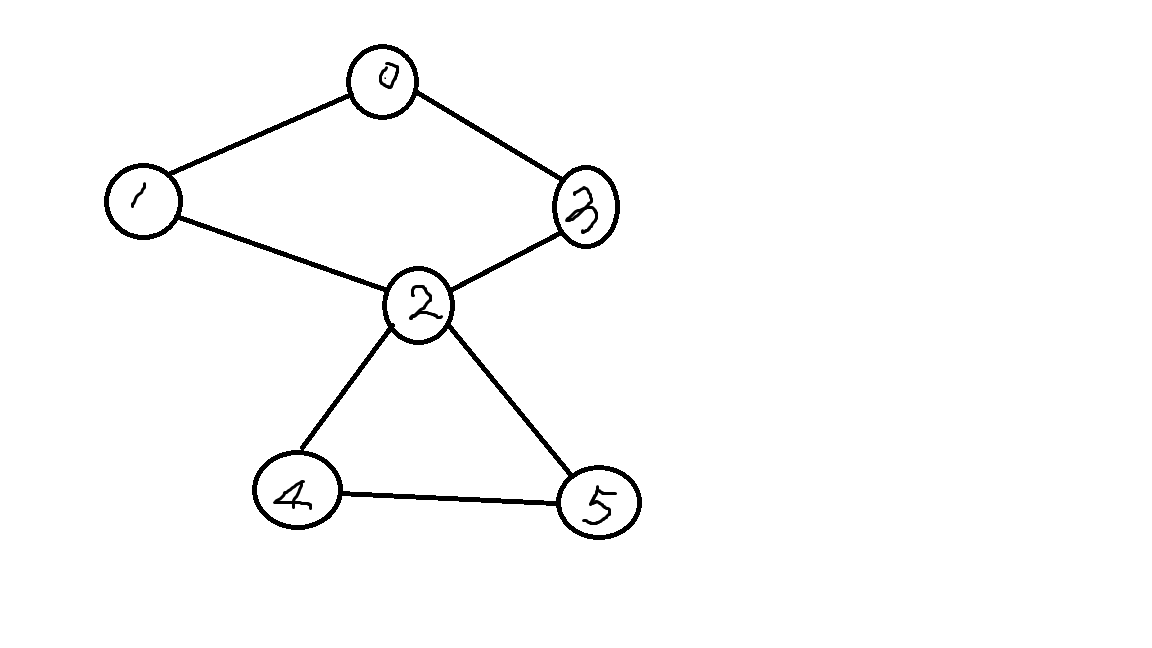
假设按以下顺序dfs,括号里表示的是回溯的过程
0-1-2-3-0(-3-2)-4-5-2(-5-4-2)-5(-2-1-0)-3(-0)
low和dfn比较:low[0]=low[1]=low[2]=low[3]=0
low[4]=low[5]=2
low和low比较:全部都是0…
问题出在low[5]上,如果是low[5]和dfn[2]比较low[5]=2,如果是和low[2]比较,low[5]=0
当low[5]=2的时候,2判断是割点,当low[5]=0的时候,2判断就不是割点了。
而实际上2是割点。
这里是模板题链接[https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P3388]
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int dfn[200010],low[200010],p,ans,n,m,used[200010],head[200010],inde;
struct node
{
int to,next,num;
}e[200010];
void add(int u,int v)
{
e[++p].next=head[u];
head[u]=p;
e[p].to=v;
}
void dfs(int u,int fa)
{
dfn[u]=low[u]=++inde;
int son=0;
for (int i=head[u];i;i=e[i].next)
{
int v=e[i].to;
if (!dfn[v])
{
son++;
dfs(v,u);
low[u]=min(low[u],low[v]);
if (low[v]>=dfn[u]&&!used[u])
ans++,used[u]=1;
}
else if(v!=fa)
low[u]=min(low[u],low[v]);
}
if (fa<0&&son==1) ans--,used[u]=0;
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
for (int i=1;i<=m;i++)
{
int x,y;
scanf("%d%d",&x,&y);
add(x,y),add(y,x);
}
for (int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
if (!dfn[i])
dfs(i,-1);
}
printf("%d\n",ans);
for (int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
if (used[i])
printf("%d ",i);
}
return 0;
}
3. 最短路
有三种求最短路的方法:
1. Floyd算法
Floyd算法比较简单,就是暴力枚举了所有可能,将所有可能路径找遍,就知道了两点之间的最短路
void floyd()
{
for(int k=1;k<=n;k++)
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
for(int j=1;j<=n;j++)
dis[i][j]=min(dis[i][j],dis[i][k]+dis[k][j]);
}
需要注意的是第一层循环是枚举中间点
原因可以看这篇:[https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_42488861/article/details/97909849]
2. SPFA
- 初始时,只有把起点放入队列中。
- 遍历与起点相连的边,如果可以松弛就更新距离dis[],然后判断如果这个点没有在队列中就入队标记。
- 出队队首,取消标记,循环2-3步,直至队为空。
- 所有能更新的点都更新完毕,dis[]数组中的距离就是,起点到其他点的最短距离。
3. Dijkstra
一般就是指堆优化了的dijkstra
struct node
{
long long len;
int x;
};
bool operator < (node a, node b)
{
return a.len > b.len;
}
void dijkstar()
{
d[1] = 0;
priority_queue <node> q;
node t;
t.len = 0;
t.x = 1;
q.push(t);
while (!q.empty())
{
while (!q.empty() && vis[q.top().x])
q.pop();
if (q.empty())
break;
node u = q.top();
q.pop();
long long len = u.len;
int x = u.x;
vis[x] = 1;
for (int i = head[x]; i;i = nextt[i])
{
int v = to[i];
if (len + w[i] < d[v])
{
d[v] = len + w[i];
node temp;
temp.len = d[v];
temp.x = v;
q.push(temp);
}
}
}
}
为什么SPFA可以处理负边:因为在SPFA中每一个点松弛过后说明这个点距离更近了,所以有可能通过这个点会再次优化其他点,所以将这个点入队再判断一次,而Dijkstra中是贪心的策略,每个点选择之后就不再更新,如果碰到了负边的存在就会破坏这个贪心的策略就无法处理了。
如何判断成环:
在储存边时,记录下每个点的入度,每个点入队的时候记录一次,如果入队的次数大于这个点的入度,说明从某一条路进入了两次,即该点处成环。
三种求最短路的优缺点:
- Floyd算法是多源最短路算法,复杂度最高(n^3),通常用在点比较少的起点不固定的问题中。能解决负边(负权)但不能解决负环。
- Dijkstra算法是单源最短路算法,时间复杂度优化后可以达到(ElogE),不能解决负边问题,稀疏图(点的范围很大但是边不多,边的条数|E|远小于|V|²)需要耗费比较多的空间。
- SPFA算法适合稀疏图,可以解决带有负权边,负环的问题,但是在稠密图中效率比Dijkstra要低。 SPFA算法的时间复杂度为 O(KM) K为常数,在稀疏图里约等于2,稠密图里就是很大的数字了。
二:数据结构
线段树各种模板:[https://www.cnblogs.com/71-111/p/13908171.html]
Splay模板题:[https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P3369]
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll long long
#define inf 1e10
#define N 100010
#define lson rt<<1
#define rson rt<<1|1
#define FR freopen("tset.in","r",stdin)
#define FW freopen("test.out","w",stdout)
using namespace std;
ll read()
{
ll x=0;int f=1;char ch=getchar();
while (ch<'0'||ch>'9') {if (ch=='-') f=-1;ch=getchar();}
while (ch>='0'&&ch<='9') {x=x*10+ch-'0';ch=getchar();}
return x*f;
}
int ch[N][2],sz[N],cnt[N],key[N],f[N],rt,tot,n;
int pd(int x)
{
return ch[f[x]][1]==x;
}
void update(int x)
{
if (x)
{
sz[x]=cnt[x];
if (ch[x][0]) sz[x]+=sz[ch[x][0]];
if (ch[x][1]) sz[x]+=sz[ch[x][1]];
}
}
void clear(int x)
{
ch[x][0]=ch[x][1]=f[x]=cnt[x]=sz[x]=key[x]=0;
}
void rotate(int x)
{
int fa=f[x],ffa=f[fa],dir=pd(x);
ch[fa][dir]=ch[x][dir^1];f[ch[x][dir^1]]=fa;
ch[x][dir^1]=fa;f[fa]=x;
f[x]=ffa;
if (ffa) ch[ffa][ch[ffa][1]==fa]=x;
update(x);update(fa);
}
void Spl(int x)
{
int fa=f[x];
while (fa)
{
if (f[fa]) rotate(pd(x)==pd(fa)?fa:x);
rotate (x);rt=x;fa=f[x];
}
}
void insert(int x)
{
if (rt==0)
{
f[++tot]=0;
ch[tot][0]=ch[tot][1]=0;
key[tot]=x;rt=tot;
sz[tot]=cnt[tot]=1;
return ;
}
int nw=rt,fa=0;
while(1)
{
if (x==key[nw])//这个值之前存在
{
cnt[nw]++;
update(nw);
update(fa);
Spl(nw);break;
}
fa=nw;nw=ch[nw][x>key[nw]];
if (nw==0)//这个值之前不存在
{
f[++tot]=fa;
ch[fa][x>key[fa]]=tot;
ch[tot][1]=ch[tot][0]=0;
key[tot]=x;
sz[tot]=cnt[tot]=1;
update(fa);Spl(tot);
break;
}
}
}
int ask1(int x)
{
int nw=rt,res=0;
while(1)
{
if (x<key[nw]) nw=ch[nw][0];
else
{
if (ch[nw][0]) res+=sz[ch[nw][0]];
if (x==key[nw])
{
Spl(nw);
return res+1;
}
else res+=cnt[nw],nw=ch[nw][1];
}
}
}
int ask2(int x)
{
int nw=rt;
while (1)
{
if (ch[nw][0]&&x<=sz[ch[nw][0]])
nw=ch[nw][0];
else
{
if (ch[nw][0]) x-=sz[ch[nw][0]];
if (x<=cnt[nw]) return key[nw];
else {x-=cnt[nw];nw=ch[nw][1];}
}
}
}
int getpre()
{
int nw=ch[rt][0];
while (ch[nw][1]) nw=ch[nw][1];
return nw;
}
int getnex()
{
int nw=ch[rt][1];
while (ch[nw][0]) nw=ch[nw][0];
return nw;
}
void del(int x)
{
ask1(x);
if (cnt[rt]>1)
{
cnt[rt]--;
update(rt);
return ;
}
if (!ch[rt][0]&&!ch[rt][1])
{
clear(rt);
rt=0;
return ;
}
if (!ch[rt][0])
{
int old=rt;rt=ch[rt][1];
f[rt]=0;
clear(old);
return ;
}
if (!ch[rt][1])
{
int old=rt;rt=ch[rt][0];
f[rt]=0;
clear(old);
return ;
}
int pre=getpre(),old=rt;
Spl(pre);
ch[rt][1]=ch[old][1];
f[ch[old][1]]=rt;
clear(old);
update(rt);
}
int main()
{
n=read();
while (n--)
{
int ty=read(),x=read();
if (ty==1) insert(x);
if (ty==2) del(x);
if (ty==3) printf("%d\n",ask1(x));
if (ty==4) printf("%d\n",ask2(x));
if (ty==5)
{
insert(x);
printf("%d\n",key[getpre()]);
del(x);
}
if (ty==6)
{
insert(x);
printf("%d\n",key[getnex()]);
del(x);
}
}
}
splay区间翻转:
模板题链接:[https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P3391]
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define inf 1000000000
#define ll long long
#define N 100010
#define lson rt<<1
#define rson rt<<1|1
using namespace std;
inline ll read()
{
ll x=0,f=1;char ch=getchar();
while (ch<'0'||ch>'9') {if (ch=='-') f=-1;ch=getchar();}
while (ch>='0'&&ch<='9') x=x*10+ch-'0',ch=getchar();
return x*f;
}
int ch[N][2],sz[N],cnt[N],key[N],f[N],root,tot,n,a[N],tag[N],m;
void update(int x) {sz[x]=sz[ch[x][0]]+sz[ch[x][1]]+1;}
int pd(int x) {return ch[f[x]][1]==x;}
void pushdown(int x)
{
if (x&&tag[x])
{
tag[ch[x][0]]^=1;tag[ch[x][1]]^=1;
swap(ch[x][0],ch[x][1]);
tag[x]=0;
}
}
int build(int l,int r,int fa)
{
if (l>r) return 0;
int mid=(l+r)>>1;
int now=++tot;
key[now]=a[mid];f[now]=fa;tag[now]=0;
int ls=build(l,mid-1,now),rs=build(mid+1,r,now);
ch[now][0]=ls,ch[now][1]=rs;
update(now);
return now;
}
void rotate(int x)
{
pushdown(f[x]);pushdown(x);
int old=f[x],olf=f[old],dir=pd(x);
ch[old][dir]=ch[x][dir^1];f[ch[x][dir^1]]=old;
ch[x][dir^1]=old;f[old]=x;
f[x]=olf;if (olf) ch[olf][ch[olf][1]==old]=x;
update(old);update(x);
}
void Spl(int x,int goal)
{
int fa=f[x];
while (fa!=goal)
{
if (f[fa]!=goal) rotate(pd(x)==pd(fa)?fa:x);
rotate(x);if (!goal) root=x;fa=f[x];
}
}
int ask(int x)
{
int now=root;
while (1)
{
pushdown(now);
if (x<=sz[ch[now][0]]) now=ch[now][0];
else
{
x-=sz[ch[now][0]]+1;
if (!x) return now;
now=ch[now][1];
}
}
}
void print(int x)
{
pushdown(x);
if (ch[x][0]) print(ch[x][0]);
if (key[x]!=-1e9&&key[x]!=1e9)
printf("%d ",key[x]);
if (ch[x][1]) print(ch[x][1]);
}
int main()
{
n=read(),m=read();
a[1]=-1e9,a[n+2]=1e9;
for (int i=1;i<=n;i++) a[i+1]=i;
root=build(1,n+2,0);
for (int i=1;i<=m;i++)
{
int l=read(),r=read();
int aa=ask(l),bb=ask(r+2);
Spl(aa,0),Spl(bb,aa);
tag[ch[ch[root][1]][0]]^=1;
}
print(root);
}
数论:
逆元,求逆元,判断两直线相交都放在了[https://www.cnblogs.com/71-111/p/9745026.html]


