实验6:开源控制器实践——RYU
实验目的
1、能够独立部署RYU控制器;
2、能够理解RYU控制器实现软件定义的集线器原理;
3、能够理解RYU控制器实现软件定义的交换机原理。
实验环境
1、下载虚拟机软件Oracle VisualBox或VMware;
2、在虚拟机中安装Ubuntu 20.04 Desktop amd64,并完整安装Mininet;
基本要求
-
完成Ryu控制器的安装。

-
搭建下图所示SDN拓扑,协议使用Open Flow 1.0,并连接Ryu控制器。

-
通过Ryu的图形界面查看网络拓扑。
-
阅读Ryu文档的The First Application一节,运行并使用 tcpdump 验证L2Switch,分析和POX的Hub模块有何不同
阅读文档The First Application,自行编写L2Switch.py代码.
代码命令如下
from ryu.base import app_manager
from ryu.controller import ofp_event
from ryu.controller.handler import MAIN_DISPATCHER
from ryu.controller.handler import set_ev_cls
from ryu.ofproto import ofproto_v1_0
class L2Switch(app_manager.RyuApp):
OFP_VERSIONS = [ofproto_v1_0.OFP_VERSION]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
super(L2Switch, self).__init__(*args, **kwargs)
@set_ev_cls(ofp_event.EventOFPPacketIn, MAIN_DISPATCHER)
def packet_in_handler(self, ev):
msg = ev.msg
dp = msg.datapath
ofp = dp.ofproto
ofp_parser = dp.ofproto_parser
actions = [ofp_parser.OFPActionOutput(ofp.OFPP_FLOOD)]
data = None
if msg.buffer_id == ofp.OFP_NO_BUFFER:
data = msg.data
out = ofp_parser.OFPPacketOut(
datapath=dp, buffer_id=msg.buffer_id, in_port=msg.in_port,
actions=actions, data = data)
dp.send_msg(out)
并用命令ryu-manager L2Switch.py运行。
运行并使用tcpdump来验证L2Switch(验证方法同POX)
h1 ping h2

h1 ping h3
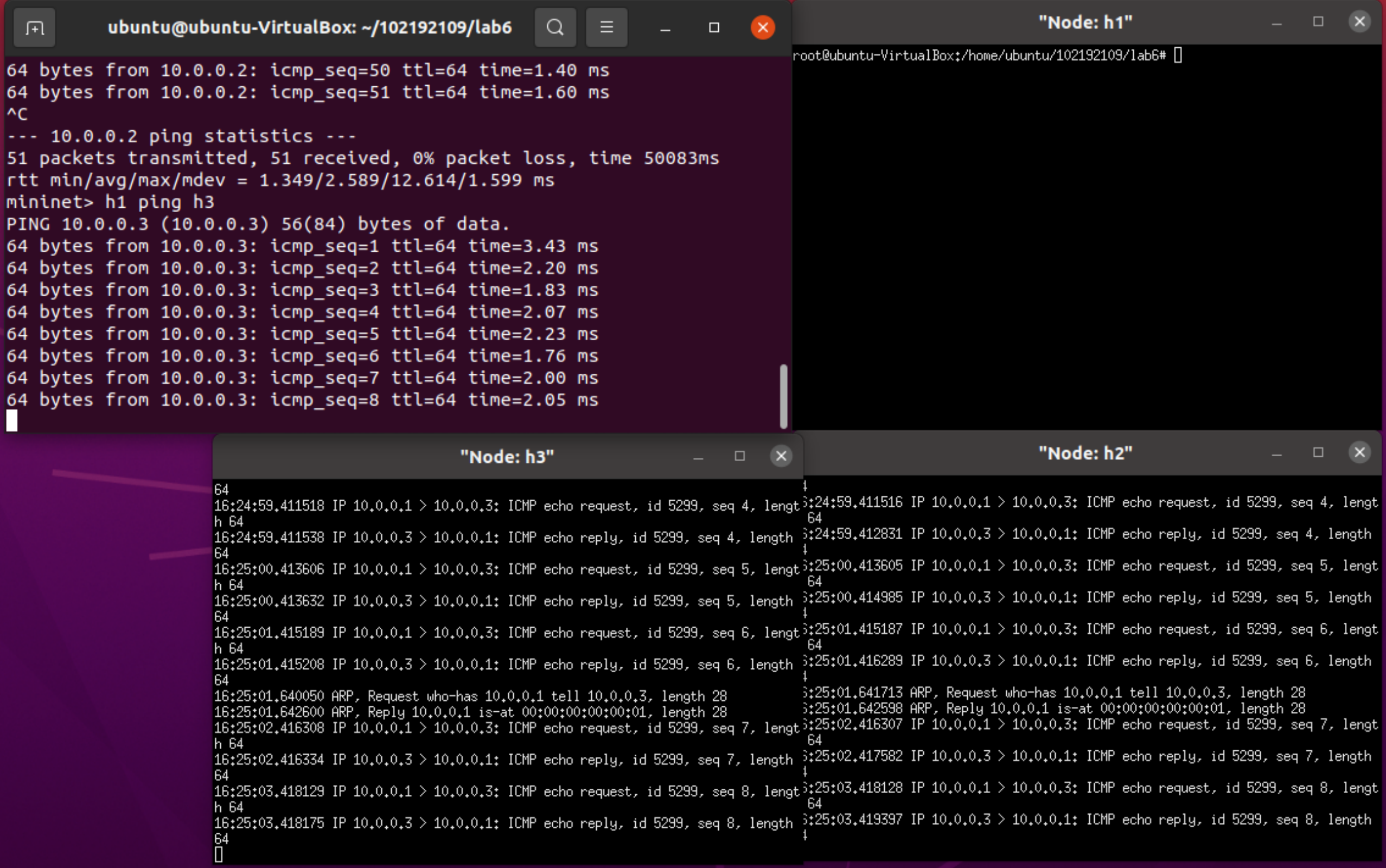
根据上方两张截图中的结果,与POX的Hub模块相比的区别是:
Hub和L2Switch实现的都是洪泛发送ICMP报文,比如当h1 ping h2时,h1发送给h2的ICMP报文,h3也会收到,但L2Switch下发的流表无法查看,而Hub可以查看。
进阶要求
- 阅读Ryu关于simple_switch.py和simple_switch_1x.py的实现,以simple_switch_13.py为例,
完成其代码的注释工作
# Copyright (C) 2011 Nippon Telegraph and Telephone Corporation.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or
# implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
# 引入包
from ryu.base import app_manager
from ryu.controller import ofp_event
from ryu.controller.handler import CONFIG_DISPATCHER, MAIN_DISPATCHER
from ryu.controller.handler import set_ev_cls
from ryu.ofproto import ofproto_v1_3
from ryu.lib.packet import packet
from ryu.lib.packet import ethernet
from ryu.lib.packet import ether_types
class SimpleSwitch13(app_manager.RyuApp):
# 定义openflow版本
OFP_VERSIONS = [ofproto_v1_3.OFP_VERSION]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
super(SimpleSwitch13, self).__init__(*args, **kwargs)
# 定义保存mac地址到端口的一个映射
self.mac_to_port = {}
# 处理EventOFPSwitchFeatures事件
@set_ev_cls(ofp_event.EventOFPSwitchFeatures, CONFIG_DISPATCHER)
def switch_features_handler(self, ev):
datapath = ev.msg.datapath
ofproto = datapath.ofproto
parser = datapath.ofproto_parser
# install table-miss flow entry
#
# We specify NO BUFFER to max_len of the output action due to
# OVS bug. At this moment, if we specify a lesser number, e.g.,
# 128, OVS will send Packet-In with invalid buffer_id and
# truncated packet data. In that case, we cannot output packets
# correctly. The bug has been fixed in OVS v2.1.0.
match = parser.OFPMatch()#match:流表项匹配,OFPMatch():不匹配任何信息
actions = [parser.OFPActionOutput(ofproto.OFPP_CONTROLLER,
ofproto.OFPCML_NO_BUFFER)]
self.add_flow(datapath, 0, match, actions)#添加流表项
# 添加流表函数
def add_flow(self, datapath, priority, match, actions, buffer_id=None):
# 获取交换机信息
ofproto = datapath.ofproto
parser = datapath.ofproto_parser
# 对action进行包装
inst = [parser.OFPInstructionActions(ofproto.OFPIT_APPLY_ACTIONS,
actions)]
# 判断是否有buffer_id,生成mod对象
if buffer_id:
mod = parser.OFPFlowMod(datapath=datapath, buffer_id=buffer_id,
priority=priority, match=match,
instructions=inst)
else:
mod = parser.OFPFlowMod(datapath=datapath, priority=priority,
match=match, instructions=inst)
# 发送mod
datapath.send_msg(mod)
# 触发packet in事件时,调用_packet_in_handler函数
@set_ev_cls(ofp_event.EventOFPPacketIn, MAIN_DISPATCHER)
def _packet_in_handler(self, ev):
# If you hit this you might want to increase
# the "miss_send_length" of your switch
if ev.msg.msg_len < ev.msg.total_len:
self.logger.debug("packet truncated: only %s of %s bytes",
ev.msg.msg_len, ev.msg.total_len)
# 获取包信息,交换机信息,协议等等
msg = ev.msg
datapath = msg.datapath
ofproto = datapath.ofproto
parser = datapath.ofproto_parser
in_port = msg.match['in_port']
pkt = packet.Packet(msg.data)
eth = pkt.get_protocols(ethernet.ethernet)[0]
# 忽略LLDP类型
if eth.ethertype == ether_types.ETH_TYPE_LLDP:
# ignore lldp packet
return
# 获取源端口,目的端口
dst = eth.dst
src = eth.src
dpid = format(datapath.id, "d").zfill(16)
self.mac_to_port.setdefault(dpid, {})
self.logger.info("packet in %s %s %s %s", dpid, src, dst, in_port)
# 学习包的源地址,和交换机上的入端口绑定
# learn a mac address to avoid FLOOD next time.
self.mac_to_port[dpid][src] = in_port
# 查看是否已经学习过该目的mac地址
if dst in self.mac_to_port[dpid]:
out_port = self.mac_to_port[dpid][dst]
# 否则进行洪泛
else:
out_port = ofproto.OFPP_FLOOD
actions = [parser.OFPActionOutput(out_port)]
# 下发流表处理后续包,不再触发 packet in 事件
# install a flow to avoid packet_in next time
if out_port != ofproto.OFPP_FLOOD:
match = parser.OFPMatch(in_port=in_port, eth_dst=dst, eth_src=src)
# verify if we have a valid buffer_id, if yes avoid to send both
# flow_mod & packet_out
if msg.buffer_id != ofproto.OFP_NO_BUFFER:
self.add_flow(datapath, 1, match, actions, msg.buffer_id)
return
else:
self.add_flow(datapath, 1, match, actions)
data = None
if msg.buffer_id == ofproto.OFP_NO_BUFFER:
data = msg.data
# 发送Packet_out数据包
out = parser.OFPPacketOut(datapath=datapath, buffer_id=msg.buffer_id,
in_port=in_port, actions=actions, data=data)
# 发送流表
datapath.send_msg(out)
并回答下列问题:
a) 代码当中的mac_to_port的作用是什么?
保存mac地址到交换机端口的映射,为交换机自学习功能提供数据结构进行mac端口的存储
b) simple_switch和simple_switch_13在dpid的输出上有何不同?
dpid = datapath.id # simple_switch的dpid赋值
dpid = format(datapath.id, "d").zfill(16) # simple_switch_13的dpid赋值
在python console进行测试,可以看到在simple_switch直接获取的id,在simple_switch_13中,会在前端加上0将其填充至16位
c) 相比simple_switch,simple_switch_13增加的switch_feature_handler实现了什么功能?
实现了交换机以特性应答消息响应特性请求
d) simple_switch_13是如何实现流规则下发的?
在接收到packetin事件后,首先获取包学习,交换机信息,以太网信息,协议信息等。如果以太网类型是LLDP类型,则不予处理。如果不是,则获取源端口目的端口,以及交换机id,先学习源地址对应的交换机的入端口,再查看是否已经学习目的mac地址,如果没有则进行洪泛转发。如果学习过该mac地址,则查看是否有buffer_id,如果有的话,则在添加流动作时加上buffer_id,向交换机发送流表
e) switch_features_handler和_packet_in_handler两个事件在发送流规则的优先级上有何不同?
switch_features_handler下发流表的优先级更高
个人总结
本次实验难度正常,进阶要求偏难。
本次实验的基础要求和实验五比较相似,二者连接控制器以及验证的过程差别不大,在进行基础要求时没碰到啥问题。
进阶要求中,问题有很多,需要自己对于相关代码的理解要十分全面,在起步时感到不太容易,需要多上网查询相关的知识,以及多理解程序自身配有的英文注释,阅读源码的部分比较复杂,需要对RYU的原理有更深入的了解,对源码分析和对openflow协议的理解也有一定的要求。经过这次进阶要求的以后遇到相关类型的代码时应该会比较熟悉。


